The Origins of Land Plant Cell Walls are Revealed in the

Methods S1: Supplementary experimental procedures for: High performance anion-exchange chromatography (HPAEC); Immunocytochemistry – light and immunofluorescence microscopy;
Immunogold labelling and transmission electron microscopy (TEM); and EST sequence generation and unigene assembly.
Figure S1. The cellulose content of the 10 CGA species used in this study and Arabidopsis thaliana mature stems as determined using the Updegraff assay method. Cellulose content is expressed as
μg glucose equivalents (cellulose, Avicel)/mg AIR (cell wall material) and values are means from three experiments. Error bars represent standard error mean (SEM) of three separate experiments.
Figure S2. Immunofluroescence localization of cell wall epitopes in selected CGA. (a) HG in the apical zone of C. corallina (mAb JIM5), (b) AGP in the corona of the oogonium of C. coralline (mAb
JIM13), (c) HG in C. Nitellarum (mAb JIM7), (d) HG in a young filament of C. nitellarum (mAb JIM5),
(e) HG in C. turpini (mAb JIM5), (f) xylan/arabinoxylan in C. turpini (mAb LM11), (g) XyG in C. turpini
(mAb) LM15, (h) HG in P. trabecula (mAb JIM5), (i) (1→3),(1→4)-
D -glucan in P. trabecula (mAb BS-
403) (j) AGP in a rhizoid of Spirogyra sp. (mAb JIM8), (k) Co-labelling of HG in P. margaritaceum with a low DE (mAb JIM5) and HG with a higher DE (mAb JIM7). The JIM7 epitope is localaised in the isthmus zone (arrowhead) and JIM5 epitope across the wall (double arrowhead), (l) AGP in the isthmus zone of P. margaritaceum (mAb JIM13), (m) AGP in N. digitus (mAb JIM13), (n) (1→3) D glucan in K. flaccidum (mAb BS-400-2), (o) xylan/arabinoxylan in K. flaccidum (mAb LM11), (p)
(1→3) D -glucan in C. atmophyticus (mAb BS-400-2), (q) AGP in C. atmophyticus (mAb JIM13). See
Supplementary Table S5 for antibody details. mAb, monoclonal antibody; HG, homogalacturonan;
XyG, xyloglucan; AGP, arabinogalactan protein; DE, degree pf methyl esterification. Scale bars: a,
1
330 µm; b, 125 µm; c, 20 µm; d, 12 µm; e, 9 µm; f, 11 µm; G, 10 µm; h, 10 µm; i, 11 µm; j, 15 µm; k,
6 µm; l, 18 µm; m, 12 µm; N, 5 µm; o, 6µm; p, 10 µm; q, 15 µm.
Figure S3. Immunogold labeling of the cell walls of select CGA highlighting wall-specific labeling. (a)
P. trabecula mAb BS-400-3, (1→3)(1→4)-
D -glucan, (b) C. atmophyticus, JIM13, AGP epitope, (c) C.
turpini, JIM5, HG; (D) C. turpini, BS-400-3, (1,3;1,4)-
D -glucan; (E) C. corallina, JIM5, HG; F) M.
furcata, BS-400-3, (1,3;1,4) D -glucan. Scale bars: a-d and f, =100 nm; e, 200 nm.
Figure S4. HPAEC chromatograms showing the relative abundance of oligosaccharide products released by lichenase digestion of AIR material from M. furcata, C. turpini, P. trabecula and C.
atmophyticus. Hordeum vulgare flour MLG was used as a standard and a buffer only treated sample was included in order to identify any peaks not corresponding to MLG oligomers.
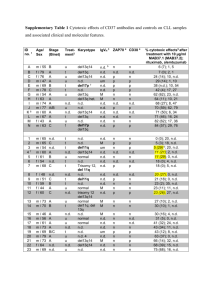
Table S1. Glycosyl-linkage compositions (mol %) of the charophycean green algae cell walls [AIR?].
Table S2. EST sequences, annotations and accession numbers.
Table S3. Non-cellulosic glycosyl residue compositions of the AIR from the CGA and from red wine
RG-II.
Table S4. Thioacidolysis monomer yields and G/S molar ratios.
2
Table S5. The epitopes recognized by antibodies used in glycan microarray and immunolabelling studies.
3