Antibodies, chemical reagents and serratamolide (AT514)

EB04-LEU-0431R Supplementary Information
Materials and Methods
Antibodies, chemical reagents and serratamolide (AT514)
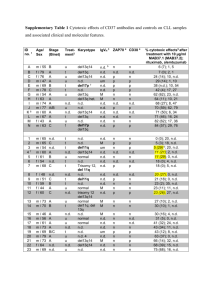
Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) to CD5 and CD19 were from Diaclone Research (Besançon,
France); mAb to CD3 was from Serotec (Oxford, UK).
mAb to CD40 was from Calbiochem-Merck
Biosciences (Darmstadt, Germany). mAbs to poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP, sc-8007); p53
(sc-099); actin (sc-8432); and rabbit polyclonal antibodies (RpAb) to Bcl-2 (sc-492), Bax (sc-526),
Bid (sc-11423), and Akt1 (sc-5298) were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc. (Santa Cruz, CA,
USA). mAb anti-cytochrome c was purchased from Pharmingen (San Diego, CA, USA). RpAb to caspase-9 and caspase-3 were purchased from BD Biosciences (Bedford, MA, USA). RpAb to phospho-Akt (Ser473) was from Cell Signalling Technology, Inc. (Beverly, MA, USA). Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled goat Ab to mouse or rabbit Ab were from Dako A/S (Glostrup,
Denmark). Fludarabine (9-
-D-arabinosyl-2-fluoroadenine) and LY294002 were purchased from
Sigma-Aldrich Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). Bisindolylmaleimide I (BisI) and U0126 were from
Calbiochem. The detailed procedure for AT514 purification will be described elsewhere.
MTT cell viability assay
B-CLL cells or PBL (20x10 4 /well) were incubated in 96-well plates with increasing concentrations of
AT514 (ranging from 0-25
M). Control cells were cultured in medium containing aliquots of DMSO equivalent to those added with the AT514 peptide. The final volume in all cases was 100
l/well.
After 24 h, 10
l of MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazolyl-2)-2,5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromide) (Sigma) at 5 mg/ml in PBS, was added to each well and cells further incubated for an additional 4 h period. The blue MTT formazan precipitate was dissolved in 100
l of isopropanol:1M HCl (24:1) and the absorbance at 540 nm was determined on a Multiskan Bichromatic microplate reader (Labsystems,
Helsinki, Finland). B-CLL cells were also incubated with various concentrations of fludarabine for
48 h, and cell viability determined by the MTT assay.
1
Analysis of apoptosis by flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy
B-CLL cells were treated with 20
M AT514 and suspended at 10
6
/ml in 1x binding buffer (Bender
Medsystems, Vienna, Austria) containing 3
l of FITC-Annexin V and 50
g of propidium iodide
(PI). After 10 min, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry on a Coulter Epics XL (Miami, FL, USA).
For Hoechst staining, cells were added to glass coverslips previously coated with 10
g/ml poly-Dlysine; after 1 h cells were fixed, permeabilized and coverslips placed on drops of DakoCytomation fluorescence mounting medium (Dako). Cells were observed on an epifluorescence Axioplan microscope (Zeiss, Germany) and photographed with a Leica DC 350F CCD camera (Leica
Microsystems Ltd, Heerbrugg Switzerland).
Plasmid constructs and cell transfection
The NF-
Bluc reporter plasmid was kindly provided by Dr. Eduardo Muñoz (Universidad de
Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain) (17). The control D3005 plasmid was provided by Dr. Daniel G. Tenen
(Harvard Medical School, Cambridge, MA, USA). Exponentially growing Raji cells (10x10 6 ) were suspended in 400
l of cold OptiMEM (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), mixed with 20
g of DNA and transfection performed on a Gene Pulser (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) at 210 v and 960 mf.
Transfection efficiency (20-25% after 18 h) was monitored by co-transfecting with the pEGFP-C1 vector and analysis by flow cytometry.
Preparation of nuclear and cytosolic extracts
10x10 6 B-CLL cells with or without previous incubation with 20
M AT514 were harvested, washed and resuspended in 400
l of cold buffer A (10 mM HEPES pH 7.6, 10 mM KCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM EGTA, 0.75 mM Spermidine, 0.75 mM Spermine, 1 mM DTT) with 1mM MoO
4
Na
2
, 1mM NaF, and protein inhibitors (aprotinin, leupeptin, pepstatin, PMSF). After 15 min on ice, 10% Nonidet-
P40 was added and lysates vortex for 10 s and centrifuged. The supernatant (cytosol) was removed and 50
l of cold buffer C (20 mM HEPES pH 7.6, 400 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM
2
EGTA) with all inhibitors as in buffer A, was added to the pellet (nucleus) and incubated on a rotary shaker at 4 0 C for 20 min. Lysates were centrifuged and protein content was determined in both cytosolic and nuclear fractions using the Dc Protein Assay kit (Bio-Rad).
Western blotting
Cells (6-10x10 6 /well) were incubated in 6-well plates with or without 20
M AT514. After 24 h cells were lysed in 10 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, 1% NP-40, 0.1% SDS, 1% deoxycholate, 1 mM Na
3
VO
4
,
1 mM NaF, 1 mM PMSF, 5
g/ml leupeptin, and 10
g/ml aprotinin, pH 7.4. For Akt phosphorylation analyses, 20x10 6 cells were lysed in the same buffer without SDS and containing
1 mM NaPPi and 10% glycerol. Equal protein amounts were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting. Protein bands were developed using the enhanced chemiluminiscent detection method
(ECL; Amersham, Buckinghamshire, UK) and quantified on a densitometer (Bio-Rad). Protein load was corrected using actin as an internal standard.
Statistical analyses
Significance of the difference between means was determined by the Student´s non paired t test. A
P -value <0.05 was considered significant. Analyses were performed using the GraphPad InStat
V2.04a software (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
3