Chapter6ReviewAnswers

Science 10
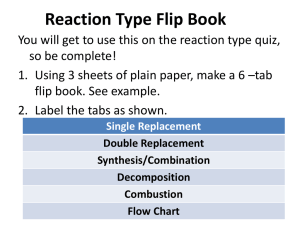
Chapter 6 Review
1.
List the six main types of chemical reactions and their general formula a) Synthesis A + B
AB
Name:______ KEY _____________
Block:____ Date:______________ b) Decomposition c) Single Replacement d) Double Replacement e) Neutralization
AB
A + B
A + XY
AY + X
AB + XY
AY + XB
Acid + Base
Water + Salt f) Combustion A + O
2
AO (oxide of A)
C x
H y
+ O
2
CO
2
+ H
2
O
2.
When a synthesis reaction occurs between a metal and a non-metal, ___ ionic ____ compounds are formed.
When a __ synthesis reaction ___ occurs between two non-metals, ___ covalent ___ compounds are formed.
3.
List all of the common elements that form diatomic molecules.
H
2
, N
2
, O
2
, F
2
, Cl
2
, Br
2
, I
2
, At
2
4.
Complete and balance the following synthesis reactions: a) _ 6 _ Na + ___ N
2
2 Na
3
N b) _ 4 _ K + ___ O
2
2 K
2
O c) _ 2 _ Mg + ___ O
2
2 MgO
5.
A decomposition reaction is the _ opposite / reverse __ of a synthesis reaction.
6.
Complete and balance the following decomposition reactions: a) _ 2 _ AuBr
3
2 Au + 3 Br
2 b) ___ CaF
2
Ca + F
2 c) _ 2 _ N
2
O
2 N
2
+ O
2
7.
When the element “A” is a metal in the single replacement reaction (A + BC
B + AC), the product “B” is a ___ metal ________.
8.
When the element “A” is a non-metal in the single replacement reaction (A + BC
C + BA), the product “C” is a ___ non-metal ________.
9.
Complete and balance the following single replacement reactions: a) ___ Cl
2
+ ___ CuBr
2
Br
2
+ CuCl
2 b) _ 2 _ Al(NO
3
)
3
+ _ 3 _ Mg 3 Mg(NO
3
)
2
+ 2 Al c) ___ PbF
4
+ _ 4 _ Na
4 NaF + Pb
10.
Complete the following double replacement reaction using just the letters A, B, C and D.
AB + CD
__ CB __ + __ AD __
11.
In the reaction you completed in question #10 above, A and C are ___ metals ____, while B and D are
__ non-metals ___.
12.
In a double replacement reaction, one of the products forms a __ precipitate ____.
13.
A precipitate is an __ insoluble ____ solid that forms from a solution.
14.
Complete and balance the following double replacement reactions: a) _ 2 _ KOH + ___ CuBr
2
Cu(OH)
2
+ 2 KBr b) ___ Al(NO
3
)
3
+ ___ FeF
3
AlF
3
+ Fe(NO
3
)
3 c) _ 3 _ CaS + _ 2 _ K
3
PO
4
3 K
2
S + Ca
3
(PO
4
)
2
15.
Write the word equation for a neutralization reaction.
Acid + Base Water + Salt
16.
Complete and balance the following neutralization reactions: a) _ 3 _ HBr + ___ Al(OH)
3
3 H
2
O + AlBr
3 b) ___ CH
3
COOH + ___ NaOH
H
2
O + NaCH
3
COO c) _ 2 _ H
3
PO
4
+ _ 3 _ Ca(OH)
2
6 H
2
O + Ca
3
(PO
4
)
2
17.
What reactant is required for all combustion reactions?
Oxygen (O
2
)
18.
Complete and balance the following combustion reactions: a) ___ C
3
H
8
+ _ 5 _ O
2
3 CO
2
+ 4 H
2
O b) _ 2 _ C
3
H
6
+ _ 9 _ O
2
6 CO
2
+ 6 H
2
O c) ___ C
6
H
12
O
6
+ _ 6 _ O
2
6 CO
2
+ 6 H
2
O
19.
Classify each of the following reactions as synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, neutralization and/or combustion: a) 2 HCl
H
2
+ Cl
2 b) C
2
H
2
+ 5 O
2
4 CO
2
+ 2 H
2
O
__
__
Decomposition
Combustion
______
________ c) H
2
SO
4
+ Ca(OH)
2
CaSO
4
+ 2 H
2
O d) SrCl
2
+ 2 NaNO
3
Sr(NO
3
)
2
+ 2 NaCl e) 3 Cl
2
+ 2 FeBr
3
2 FeCl
3
+ 3 Br
2 f) 2 Cr + 3 F
2
2 CrF
3
__
__
__
__
Neutralization
Double Replacement
Single Replacement
Synthesis
______
_
__
_______________
20.
Complete and balance the following reactions and classify them as synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, neutralization and/or combustion: a) _ 2 _ NaCl
2 Na + Cl
2
__ Decomposition ______ b) ___ CaI
2
+ ___ Na
2
CO
3
CaCO
3
+ 2 NaI c) ___ H
2
SO
3
+ ___ Mg(OH)
2
2 H
2
O + MgSO
3 d) ___ N
2
+ _ 3 _ I
2
2 NI
3 e) ___ C
2
H
4
+ _ 3 _ O
2
2 CO
2
+ 2 H
2
O f) _ 2 _ Mg + ___ O
2
2 MgO g) ___ Cl
2
+ _ 2 _ CsI
2 CsCl + I
2 h) ___ Be + ___ Fe(NO
3
)
2
Be(NO
3
)
2
+ Fe i) _ 2 _ AlBr
3
+ _ 3 _ Cu
2
SO
4
Al
2
(SO
4
)
3
+ 6 CuBr j) _ 3 _ HCl + ___ Al(OH)
3
3 H
2
O + AlCl
3
__
__
__
__
_
Double Replacement
Neutralization
Synthesis
Combustion
_
______
__________
________
Synthesis & Combustion
__
__
__
__
Single Replacement
Single Replacement
Double Replacement
Neutralization
_
_
_
______
21.
The _____ rate of reaction ______ describes how quickly or slowly reactants turn into products.
22.
__ Temperature ______, __ surface area ______, ___ concentration _____, and ____ catalysts__ ____ are the four main factors that affect reaction rates.
23.
Increasing the temperature of a reaction causes the _ particles (atoms/molecules)_ of the reactants to move more ___ quickly ____, which leads to more ___ collisions ____ and more ___ energy _____.
24.
Concentration refers to how much ___ solute _______ is dissolved in a solution.
25.
The greater the concentration, the greater the chance that ___ collisions ___ among particles will occur.
26.
__ Surface area _____ is the measure of how much area of an object is exposed.
27.
__ Increasing_ ______ the surface area results in more collisions among particles.
28.
A _____ catalyst _____ is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the reaction itself.
29.
Catalysts make it possible for reactions to occur with less ____ energy ______ than reactions would otherwise need without the catalyst present.
30.
Your body has many biological catalysts, called ___ enzymes ______, that speed up reaction in living cells.
31.
Many automobiles have ___ catalytic converters _____ located underneath the frame of the vehicle. These devices help convert carbon monoxide into __ carbon dioxide (CO
2
) _____. They also help convert hydrocarbons into _ carbon dioxide (CO
2
) _ and _ water (H
2
O) ____, and help convert poisonous nitrogen oxides into __ (N
2
) nitrogen ___ gas and ___ (O
2
) oxygen ___ gas.
32.
____ Increasing _____ temperature, concentration, and _____ surface area _____ generally leads to an increased reaction rate.
Vocabulary to Know:
Write a concise definition of each of these terms found in this chapter.
Catalyst:
Catalytic converter:
Combustion:
Concentration:
Decomposition:
Double replacement:
Enzymes:
Refer to Notes and/or Glossary of Textbook Neutralization:
Precipitate:
Rate of reaction:
Single replacement:
Solute:
Solvent:
Surface area:
Synthesis: