Meiosis HW 1 Answer Key - Holding
advertisement

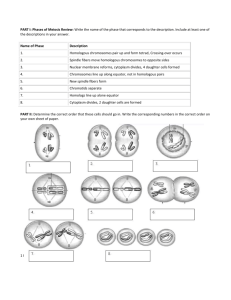
Name: _____________________________________________ Period: _____ Date: __________ Meiosis HW 1 Living Environment Matching Match the terms in column A with those is column B 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. A __D__ Somatic cell __F__ Homologous chromosome __C__ Gamete __G__ Sexual reproduction __E__ Haploid __A__ Fertilization __B__ Meiosis __H__ Diploid B a. Egg + sperm = zygote b. Creates four haploid cells c. A egg or sperm cell d. Any cell besides an egg or sperm cell e. A cell with n chromosomes f. Chromosomes same in size and content g. Creates genetically different individuals h. A cell with 2n chromosomes NOTE: morning classes had a few typos in the above section please notice these changes Multiple Choice Chose the best answer for each question below. 9. When two cells with n number of chromosomes fuse, what type of cell results? a. Zygote with 2n chromosomes b. A cell with n chromosomes c. A genetic copy of the original parent cell d. A fertilized egg produced by asexual reproduction 10. What process results in an exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes? a. Synapsis b. Crossing over c. Disjunction d. Asexual reproduction 11. Which is not a characteristic of homologous chromosomes? a. Have the same length b. Have the same centromere location c. Have the same type of information at the same location d. Cannot exchange information between chromatids of the tetrad 12. Compared to the number of chromosomes in a normal human body cell, the number of chromosomes in a normal sperm cell is a. The same b. Twice as great c. Half as great d. Four times as great 13. The process of meiotic cell division in a human male usually forms a. One diploid cell, only b. Four diploid cells c. One haploid cell, only d. Four haploid cells 14. Each body cell of a chimpanzee contains 48 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would normally be present in a gamete produced by this chimpanzee? a. 24 b. 36 c. 48 d. 96 15. The greatest degree of genetic variation would be found in offspring that result from a. Binary fission b. Regeneration c. Fertilization d. Vegetative propagation Short Answer Answer the following below using COMPLETE sentences. 16. Describe the differences between somatic cells and gametes. Where do each occur, what processes do they involve, what is different, what is the same. Somatic cells: body cells, diploid, undergo mitosis, exact copies of original cell Gamete: sex cells (egg/sperm), haploid, undergo meiosis, genetically different cells 17. Relate the terms meiosis, gametes and fertilization in one or two sentences. Meiosis produces eggs and sperm, also known as gametes. Fertilization is the fusion of the nuclei between an egg and sperm cell to create a zygote. 18. What is synapsis? When does it occur? Synapsis: homologous chromosomes line up together during prophase I of meiosis resulting in crossing over of DNA segments 19. What is disjunction? When does it occur? Disjunction: homologous chromosomes separate to opposite ends of the cell during anaphase I of meiosis 19. Compare diploid versus haploid cells. Diploid cells, also known as somatic (body) cells, contain 2n chromosomes (total number of chromosomes for that specific species) Haploid cells, also known as gametes (egg/sperm cells), contain n chromosomes (half of the total number of chromosomes for that specific species)