Web Design Notes (01)
advertisement

HKCEE CIT (Mod D)
Web Design
Web Design (9)
Learning CSS
Soft copies of this handout and related demo web pages can be found at:
http://www.clsmss.edu.hk/~whlau/10CIT/#webdesign
What is CSS (Cascading Style Sheet)?
1. Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a simple mechanism for adding style(s) to web documents.
Styles define how to display HTML elements. Examples include (but not limited to):
a) Setting the text color and background color of the whole page or some elements.
b) Setting fixed background image that does not scroll with the page.
c) Changing font size, font family, font color, character spacing, text alignment, etc.
d) Adding font styles (e.g. bold, italic, underline, etc) to text.
e) Adding border to different elements.
f) Setting width, height, margins and padding of block elements.
g) Changing the opacity of different elements.
Ref: http://www.w3.org/Style/CSS/
http://www.w3schools.com/css/css_examples.asp
2.
There are three methods to add style to a web document:
a) Inline: adding a style attribute.
Example:
<p style="text-align: center; font-size: 16px" /> ... </p>
(Center this paragraph, and set the font size in this paragraph is to be 16px)
Note:
i. This method is not recommended, as it is difficult to maintain the styles.
ii. Every element has its own style attribute, and we must look into the HTML codes to
update styles of all elements.
iii. It is only a quick way to add a few styles to a specific element.
b) Embedding a style sheet by inserting a style element in head element.
Example:
<style type="text/css">
body { background: #ffffcc; font-family: Arial }
p { text-align: center; font-size: 16px }
</style>
(Set a pale yellow background color; Use the Arial font; Center ALL paragraphs, etc.)
Note:
i. It provides the flexibility of adding the same set of styles to more than one elements
ii. It is suitable for adding styles to a single web page.
iii. Every web page has its own embedded style sheet. If there are several web pages,
each HTML document must be modified when some styles are to be updated.
Supplementary Notes – Web Design (9)
P.1/6
HKCEE CIT (Mod D)
c)
Web Design
Linking an external style sheet by using a link element in head element.
Example:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css"
type="text/css" media="all" />
Refer to Web Design (7) for more details of the syntax.
Ref: http://htmlhelp.com/reference/css/style-html.html
Note:
i. It is suitable for adding styles to a group of web pages.
ii. Since the styles are stored in an external file, the file size of the HTML file can be
reduced. The download time is reduced for downloading multiple web pages with
the same CSS file.
iii. It is easy to maintain the styles, as they are stored in a single file.
iv. It is easy to keep the design (including color scheme and layout) consistent across all
the web pages in the same web site.
3.
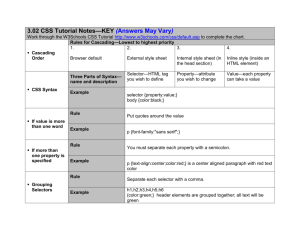
CSS Syntax:
a) A style sheet contains a list of rules;
b) Each rule-set consists of one or more selectors and a declaration block;
c) Declaration block, enclosed by curly braces { }, contains one or more declarations.
d) Each declaration consists of a style property with its values, separated by colon (:);
e) Declarations are separated by semi-colons (;).
Ref: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cascading_Style_Sheets
Example:
Colon between
property and value
Separated by
semi-colon
body { background: #ffffcc; font-family: Arial }
Selector
Property
Value
Another property and value
Why CSS?
4. What are the advantages of using CSS?
a) CSS provides more formatting features than HTML.
b) It is more flexible to set styles for a group of elements at a time.
c) It is easier to maintain because we can apply one style sheet to several web pages.
d) We can separate the content (in HTML) from its presentation (by using CSS)
e) See the demonstrations at CSS Zen Garden: http://csszengarden.com/
5.
Semantic HTML is a way of writing HTML to reinforce the meaning of information rather
than to define its presentation. In an HTML file, we focus on the information and its structure
(headings, sections, etc.), and the presentation is left to CSS to handle. It is not recommended
to use presentation markup tags (e.g. b) but to use semantic markup tags (e.g. strong).
Ref: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semantic_HTML
Supplementary Notes – Web Design (9)
P.2/6
HKCEE CIT (Mod D)
Web Design
How to Write CSS
6. Different CSS Selectors:
a)
Element
body { background: #ffffcc; font-family: Arial }
h3 { color: #0c2; border-bottom: 1px dashed #0c2 }
b) Class
.warning { color: red; font-weight: bold }
To define the class of an element, add a class attribute. Different elements can have
the same class value.
<span class="warning"> ... </span>
c)
Identifier (ID)
#copyright {
font-size: 80%;
text-align: center;
border-top: 1px #00f solid
}
It is easier to
read it we write
in multiple lines.
To define the ID of an element, add an id attribute. No two elements can have the same
id value.
<div id="copyright"> ... </div>
d) Combinations of the above:
Selector
div#A
span.X
div#B .Y
.X , .Y , .Z
div.X img
a:hover
div.Z a:hover
Matching
a div element of ID “A”
a span element of class “X”
Any element of class “Y” inside a div element of ID “B”
Any element of class “X”, “Y” or “Z”
Any img element inside a div element of class “X”
Any a element when mouse is over it
Any a element when mouse- over inside a div element of class “Z”
Ref: http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS2/selector.html
7.
Common CSS Units:
a) Measurement:
i.
%: percentage
ii.
em: current font size
iii.
px: pixel
b) Color:
i.
#rrggbb: HTML color code (short form: #rgb)
ii.
rgb(x, x, x): RGB value with x ranges from 0 to 255
iii.
rgb(x%, x%, x%): RGB value with x ranges from 0 to 100
Ref: http://www.w3schools.com/css/css_units.asp
Supplementary Notes – Web Design (9)
P.3/6
HKCEE CIT (Mod D)
Web Design
CSS properties
8. Background:
Property
background-color
background-image
background-repeat
background-attachment
background-position
background
Values
Color code or Color name
none or url('path')
repeat or repeat-x or repeat-y or no-repeat
fixed or scroll
top or center or bottom
left or center or right
x% or y%
xpos or ypos
Specifying all the above properties in one declaracion
Ref: http://www.w3schools.com/css/css_background.asp
Example: Setting background color of a web page
body {
background-color: #fff;
background-image: url(flower.jpg);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
background-position: top right
}
The above lines can be combined to:
body { background: #fff url(flower.jpg) no-repeat fixed top right }
9.
Text formatting (color, alignment and other styles):
Property
color
text-align
text-decoration
text-indent
text-transform
font-style
font-weight
font-size
font-family
font
Values
Color code or Color name
left or center or right or justify
none or underline or overline or line-through
Length (in px, em, etc.) or Percentage (for first line only)
none or capitalize or uppercase or lowercase
normal or italic
normal or bold
Length (in px, em, etc.) or Percentage or xx-small to xx-large
Font family name (e.g. Arial, Serif, Sans-serif, etc.)
Specify the above font properties in one declaracion (at least size and family)
Ref: http://www.w3schools.com/css/css_text.asp
http://www.w3schools.com/css/css_font.asp
Examples:
body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif }
h1 { text-align: center; text-transform: uppercase }
h2 { text-decoration: underline; text-transform: capitalize }
p { text-align: justify; text-indent: 3em }
p.test { font: italic 20px Arial }
p#copyright { text-align: center; font-size: 80%; font-weight: bold }
Supplementary Notes – Web Design (9)
P.4/6
HKCEE CIT (Mod D)
Web Design
10. List (for UL or OL):
Property
Values
list-style-type
For UL: disc or circle or square;
For OL: decimal or lower-roman or upper-roman or
list-style-position
list-style-image
list-style
lower-alpha or upper-alpha
inside or outside
none or url('path')
Specify the above list properties in one declaracion
Ref: http://www.w3schools.com/css/css_list.asp
Examples:
ul { list-style-type: square }
ul ul { list-style-type: circle }
11. Border / Margin / Padding / Width / Height:
a) If not set, border is zero.
b) Margin is the space outside the border.
c) Padding is the space between the border and the content.
d) Each element has its own default margin and padding.
CSS Box Model
Property
border-width
border-style
border-color
border
margin
padding
width
height
Values
Length (in px, em, etc.) or thin or medium or thick
none or dotted or dashed or solid or double or grove or
ridge or inset or outset
Color code or Color name
Specify the above border properties in one declaracion
Length (in px, em, etc.) or Percentage or auto
Length (in px, em, etc.) or Percentage
Length (in px, em, etc.) or Percentage
Length (in px, em, etc.) or Percentage
Note:
margin and padding can have one to four values, for top, right, bottom and left respectively.
Each of border, margin, padding can be added “-top”, “-right”, “-bottom” and “-left”.
Ref: http://www.w3schools.com/css/css_border.asp
Examples:
p#copyright { border-top: 1px solid blue }
h1 { border-bottom: 2px dotted #f00 }
img { margin: 5px 10px }
img { padding: 1px 2px 3px 4px; }
Description:
The paragraph element (p) with ID “copyright” has a blue solid top border of 1px width.
The heading 1 element (h1) has a red dotted bottom border of 2px width.
All image (img) have 5px-thick top and bottom margins, 10px-thick left and right margins.
All div elements have padding of: top=1px, right=2px, bottom=3px and left=4px.
Supplementary Notes – Web Design (9)
P.5/6
HKCEE CIT (Mod D)
Web Design
Special Notes
12. An element can have more than one class:
<div class="A B C"> ... </div>
13. CSS pseudo-classes are used to add special effects to some selectors:
a) Anchor pseudo-classes (for hyperlinks):
a:link
{ color: blue }
/* Unvisited Link */
a:visited { color: green }
/* Visited Link */
a:hover { backgrond: yellow}
/* Mouse over Link */
a:active { color: red }
/* Selected Link */
b) The “:hover” pseudo-class can also be applied to other elements, such as div.
c)
However, IE does not support it.
div.test
{ opacity: 0.5 } /* Semi-transparent */
div.test:hover { opacity: 1.0 } /* Opaque when mouse over */
The “:first-child” denotes and element which is the first child of the parent element.
Note: for IE to support it, DOCTYPE must be declared.
div.main p:first-child { background: #ffcccc }
The above matches the first p in the following HTML code:
<div class="main">
<p> ... </p>
<p> ... </p>
</span>
Ref: http://www.w3schools.com/css/css_pseudo_classes.asp
Browsers Compatibility Issue
14. Some browsers may not follow the CSS standard to render web pages. For example, IE
includes padding and border in the width and height. To fix it, declare DOCTYPE.
Ref: http://www.w3schools.com/css/css_boxmodel.asp
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_Explorer_box_model_bug
15. ie7-js is a JavaScript library to make MS Internet Explorer behave like a standards-compliant
browser. It fixes many HTML and CSS issues.
<!--[if lte IE 8]>
<script src="http://ie7-js.googlecode.com/svn/version/2.0(beta3)/IE8.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<![endif]-->
Ref: http://code.google.com/p/ie7-js/
Useful Links
CSS Tutorial at W3C School
http://www.w3schools.com/css/
CSS Reference at W3C School
http://www.w3schools.com/CSS/CSS_reference.asp
CSS 2.1 Specfication
http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS21/
Next Topic: Opacity, Display property, Overflow Control, Styling Table, etc.
Supplementary Notes – Web Design (9)
P.6/6