Polar Covalent Bonds
2.4 Polar Covalent Bonds
1. Unequal Sharing
LO: I know what is meant by a polar covalent bond.
If the atoms forming a covalent bond are the same they will have an equal pull on the shared pair of electrons.
This type of bond is a pure covalent bond.
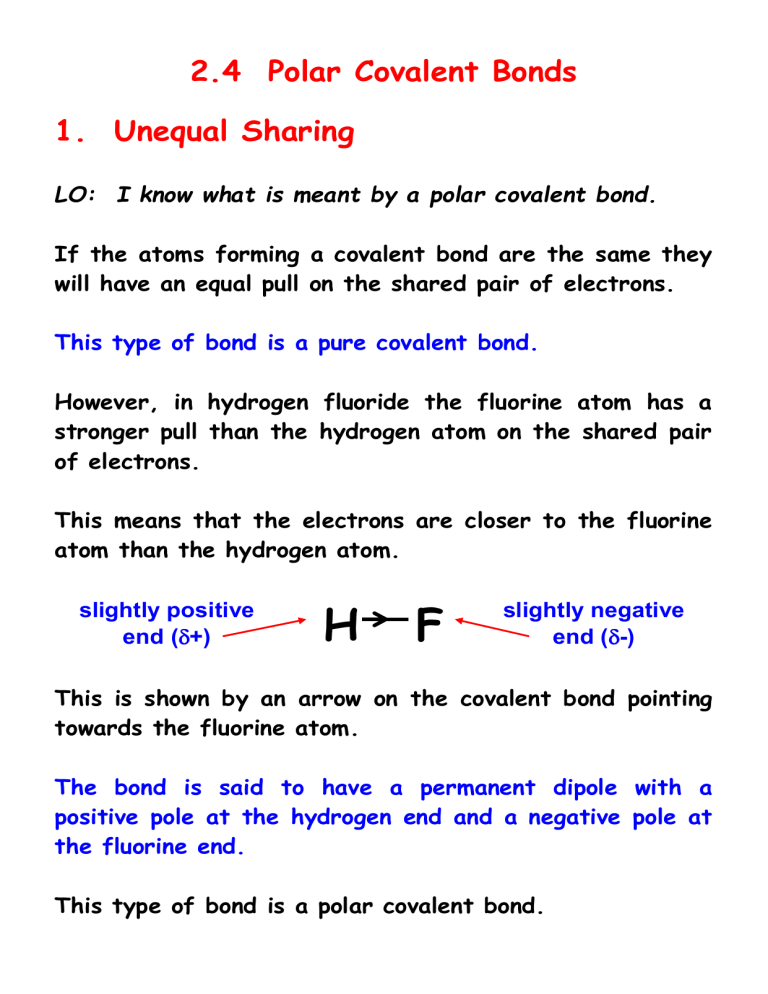
However, in hydrogen fluoride the fluorine atom has a stronger pull than the hydrogen atom on the shared pair of electrons.
This means that the electrons are closer to the fluorine atom than the hydrogen atom. slightly positive end (
+)
H F slightly negative end (
-)
This is shown by an arrow on the covalent bond pointing towards the fluorine atom.
The bond is said to have a permanent dipole with a positive pole at the hydrogen end and a negative pole at the fluorine end.
This type of bond is a polar covalent bond.
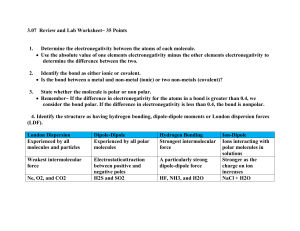
2. How Strong an Attraction?
LO: I know what is meant by electronegativity.
Electronegativity is a measure of the attraction an atom which is involved in a covalent bond has for the shared electrons of the bond.
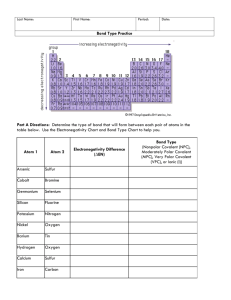
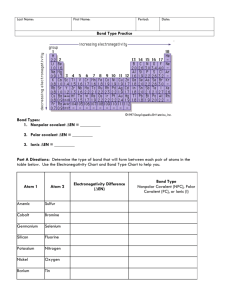
2.2
1.0
1.2
2.5
2.2
3.5 4.0
3.0
0.8 2.1
2.8
2.6
0.8
Electronegativity:
increases across a period.
decreases down a group.
In a polar covalent bond the atom with the:
highest electronegativity will be slightly negative.
lowest electronegativity will be slightly positive.
The greater the difference in electronegativity the more polar the bond.
So, will be
H Br H I than
3. Polar Molecules
LO: I understand how molecules can be polar.
A polar molecule is a molecule which has a permanent slightly positive charge on one side and a permanent slightly negative charge on the other.
Water is a polar molecule.
It has a slightly positive side and a slightly negative side.
Polar liquids can be detected by passing a fine stream past a charged rod:
Polar liquids will be attracted to the charged rod.
Non-polar liquids will flow straight past.
Examples:
Liquid Polarity
Water
Paraffin
Alcohol
White Spirit
Polar
Non-polar
Polar
Non-polar