Western Civilization Cultural Diffusion Timeline
advertisement
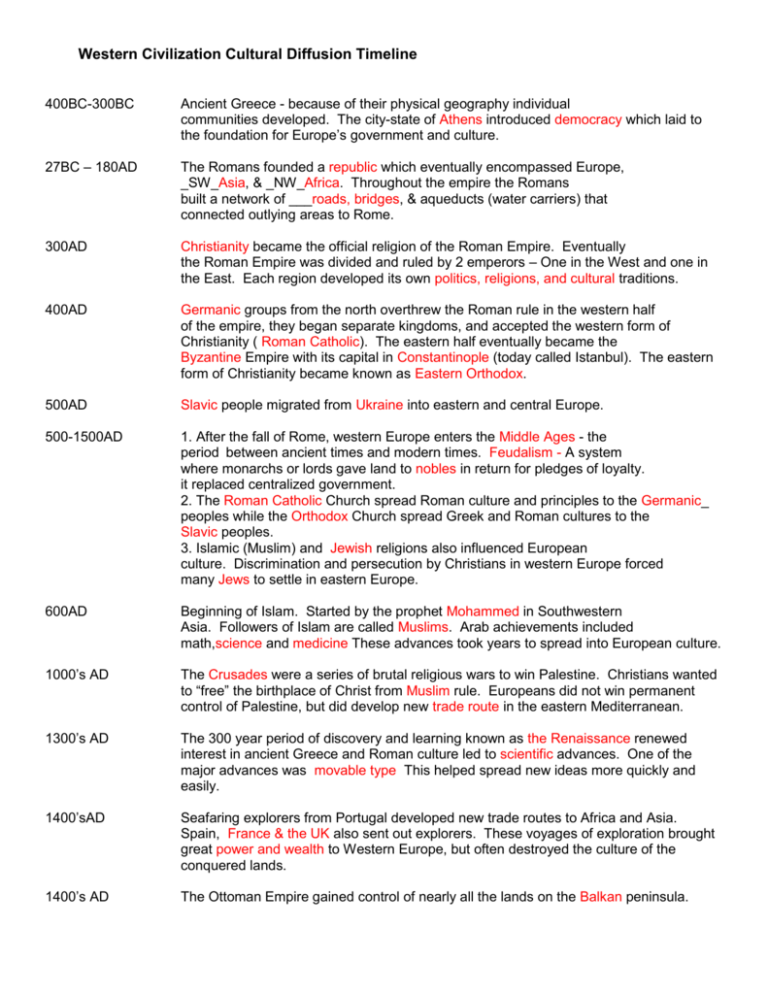
Western Civilization Cultural Diffusion Timeline 400BC-300BC Ancient Greece - because of their physical geography individual communities developed. The city-state of Athens introduced democracy which laid to the foundation for Europe’s government and culture. 27BC – 180AD The Romans founded a republic which eventually encompassed Europe, _SW_Asia, & _NW_Africa. Throughout the empire the Romans built a network of ___roads, bridges, & aqueducts (water carriers) that connected outlying areas to Rome. 300AD Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire. Eventually the Roman Empire was divided and ruled by 2 emperors – One in the West and one in the East. Each region developed its own politics, religions, and cultural traditions. 400AD Germanic groups from the north overthrew the Roman rule in the western half of the empire, they began separate kingdoms, and accepted the western form of Christianity ( Roman Catholic). The eastern half eventually became the Byzantine Empire with its capital in Constantinople (today called Istanbul). The eastern form of Christianity became known as Eastern Orthodox. 500AD Slavic people migrated from Ukraine into eastern and central Europe. 500-1500AD 1. After the fall of Rome, western Europe enters the Middle Ages - the period between ancient times and modern times. Feudalism - A system where monarchs or lords gave land to nobles in return for pledges of loyalty. it replaced centralized government. 2. The Roman Catholic Church spread Roman culture and principles to the Germanic_ peoples while the Orthodox Church spread Greek and Roman cultures to the Slavic peoples. 3. Islamic (Muslim) and Jewish religions also influenced European culture. Discrimination and persecution by Christians in western Europe forced many Jews to settle in eastern Europe. 600AD Beginning of Islam. Started by the prophet Mohammed in Southwestern Asia. Followers of Islam are called Muslims. Arab achievements included math,science and medicine These advances took years to spread into European culture. 1000’s AD The Crusades were a series of brutal religious wars to win Palestine. Christians wanted to “free” the birthplace of Christ from Muslim rule. Europeans did not win permanent control of Palestine, but did develop new trade route in the eastern Mediterranean. 1300’s AD The 300 year period of discovery and learning known as the Renaissance renewed interest in ancient Greece and Roman culture led to scientific advances. One of the major advances was movable type This helped spread new ideas more quickly and easily. 1400’sAD Seafaring explorers from Portugal developed new trade routes to Africa and Asia. Spain, France & the UK also sent out explorers. These voyages of exploration brought great power and wealth to Western Europe, but often destroyed the culture of the conquered lands. 1400’s AD The Ottoman Empire gained control of nearly all the lands on the Balkan peninsula. 1492 Christopher Columbus reached the Americas (New World). This era known as the Age of Exploration brought great power and wealth to Western European nations. By mid 1500’sAD Availability of printed material spread the ideas of the Reformation. These new ideas weakened the power of the Roman Catholic Church and led to the rise of Protestantism. This movement is known as the Protestant Reformation. Religious wars engulfed Europe and enabled monarchs to strengthen their power over nobles and church leaders. Late 1600AD to early 1700sAD The Age of Reason was also called the Enlightenment. Europeans began to question long standing values and traditions. This movement led to political and economic revolutions. Late 1600’sAD English Parliament passes the English Bill of Rights. which limited the power of the monarch. 1700’sAD Industrial Revolution (Capitalism) begins in England. Power driven machines and new methods of production transformed life in Europe. New social groups emerged: the middle class of merchants and factory owners and the working class of factory laborers. Late 1700’s AD The French Revolution overthrew the monarch and spread the ideas of democracy. 1800’s -1900s The rule of monarchs was challenged across Europe. By 1900, most European countries had Constitutions that limited the monarch’s power and guaranteed rights to citizens 1805 – 1815 The Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon Bonaparte led France in its quest for territorial gain in Europe. Napoleon’s allies were Holland, Italy, Naples, Warsaw, Bavaria, Saxony, and Denmark. The Allies of the United Kingdom were Austria, Portugal, Prussia, Russia, Spain and Sweden. Early victories led Napoleon to believe he could invade Russia. Napoleon was eventually defeated at Waterloo Mid 1800’s AD Inequality in the industrial work place led to the birth of communism – a philosophy that called for a society based on economic equality in which the workers controlled the factories and all industrial production. 1912 – 1913 AD The Balkan Wars ended the Ottoman Empire 1914-1918 Rivalries among European powers for colonies and for economic power (Imperialism) led to World War I. In Russia, the people were not prepared to fight. The high cost of the war in human life and money forced the czar to abdicate - step down from the throne. Outcomes of WWI 1917 Bolshevik overthrow - Communist Revolution led by V.I. Lenin. He wanted to base the government on the teachings of Karl Marx - a 19th Century German philosopher. Marx believed in the government owning and managing everything. No capitalism (free enterprise) 1918 The Slavic people united to form the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. In 1929 this Kingdom was renamed Yugoslavia 1919 The peace treaty that ended WWI (known as the Treaty of Versailles) found Germany guilty of starting WWI. As punishment they had to pay reparations (payment for damages) to the victorious countries. 1919-1939 Monarchies collapsed in Germany, Austria – Hungary, and Russia. Several Central and Eastern European nations gained independence. Unresolved political problems and widespread economic depression enabled dictators such as Benito Mussolini (Italy) and Adolph Hitler (Germany) to gain power. 1921 Bolsheviks (Communists) win the civil war in Russia. The country is renamed the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) or Soviet Union. WWII 1939 Germany invaded Poland (Sudetenland) that was an ally of the UK. The United Kingdom declares war on Germany which caused the start of World War II 1939-1945 The Axis Powers were Germany, Italy and Japan. The Allied Powers were the US, the UK, France, and Soviet Union. During WWII - 6 million European Jews and others were killed by Germany’s Nazi leaders. This horror is known as the Holocaust. 1941 Japan attacked the US at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii and brought the US into WWII. 1945 Aftermath of WWII 1945 – 1950 US dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan to end WWII. Cold WAR 1949 Europe is ruined and divided. Eastern Europe came under communist control led by USSR. Western Europe’s democracies received millions of dollars and military aid to rebuild under the Marshall Plan. The victorious Allied Powers divided Germany into 4 zones. The 3 western zones (US, UK, and France) became West Germany and the eastern zone (USSR) became East Germany. Many people in Eastern Europe fled communism to Western Europe. The Cold War begins. 1949 – 1989 Eastern European countries led by communist USSR were ideologically opposed to Western European countries that were led by the US. This ideological conflict is known as the Cold War 1950 – 1980 Eastern European nations tried to revolt against communist power, but were not successful because the USSR had a strong military. 1951 Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany formed the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) 1957 The ECSC added the European Economic Community (EEC) and the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC) for its members. 1960’s East Germany built the Berlin Wall and other barriers. Western European democracies became more productive and economically secure, but communist Eastern Europe had a low standard of living and little economic growth. The Berlin Wall was constructed by the German Democratic Republic (GDR, East Germany) that completely cut off West Berlin from surrounding East Germany and from East Berlin. The barrier included guard towers placed along large concrete walls, which was erected served to prevent the massive emigration and defection that marked Germany and the communist Eastern Bloc during the post-World War II period. Both borders came to symbolize the "Iron Curtain" that separated Western Europe and the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War. 1973 Denmark, The UK, and Ireland joined the EEC 1979 First direct elections of members to the European Parliament 1980 Polish workers formed Solidarity - the first free labor union in the Communist World. Solidarity worked toward reform and economic change. 1981 Greece joins the EEC 1986 Spain and Portugal join the EEC 1989 Public demonstrations and the Soviet leader’s refusals to reform led to the fall of communist power in Eastern Europe and the USSR. The Berlin Wall came down. 1990 Germany reunited and the USSR broke up into 15 independent republics. 1990’s Free elections brought democratic leaders and the rise of market economies in much of Eastern Europe and Russia. 1991-1992 Several Yugoslav republics declared independence; civil war broke out and ravages areas of the Balkan Peninsula 1992 The Maastricht Treaty was signed and formed the European Union. The member countries voted to have a central bank and common currency (known as the Euro). Goods, workers, and services move across borders of member nations without passports or tariffs. 1993 Czechoslovakia split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia in a revolution known as the Velvet Revolution. 1995 Austria, Finland, and Sweden joined the EU 2004 Czech Republic, Estonia, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovenia, Slovakia, and Hungary joined the EU. These members are different from prior members because most are former communist countries of Eastern Europe 2007 Bulgaria and Romania joined the EU bringing the number of members to 27. The EU is the largest trading entity in the world and a major competitor of the US on world markets.