CHART: CHARACTERISTICS OF A CIVILIZATION OR - Salz-APWH
advertisement
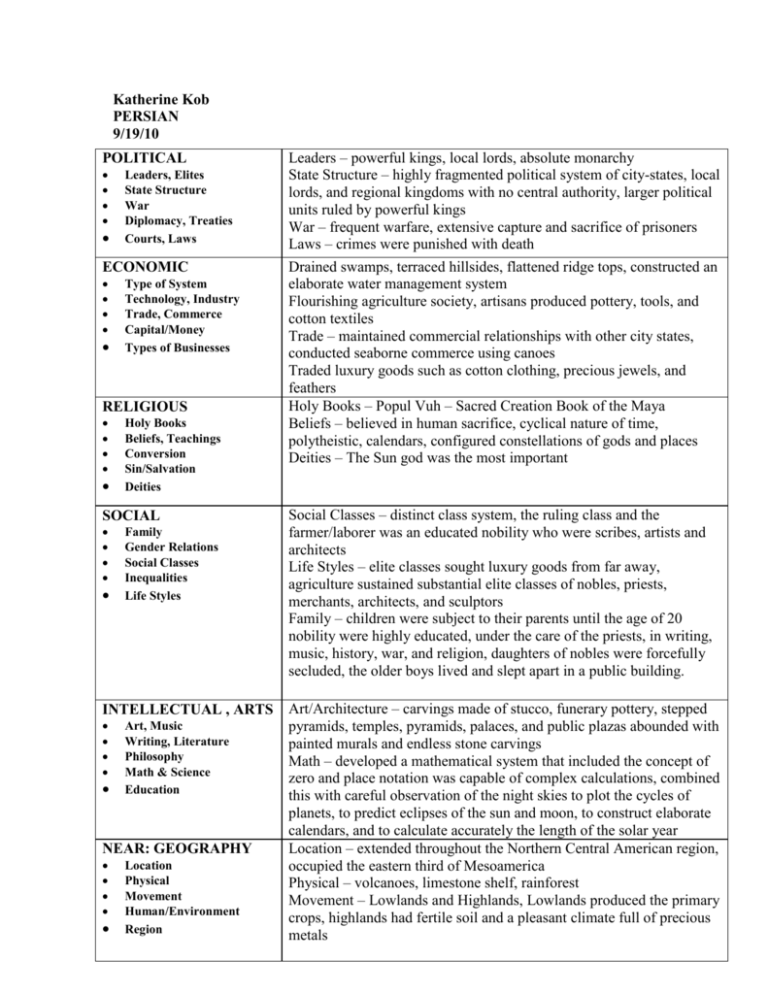
Katherine Kob PERSIAN 9/19/10 POLITICAL Leaders, Elites State Structure War Diplomacy, Treaties Courts, Laws ECONOMIC Type of System Technology, Industry Trade, Commerce Capital/Money Types of Businesses RELIGIOUS Holy Books Beliefs, Teachings Conversion Sin/Salvation Deities SOCIAL Family Gender Relations Social Classes Inequalities Life Styles INTELLECTUAL , ARTS Art, Music Writing, Literature Philosophy Math & Science Education NEAR: GEOGRAPHY Location Physical Movement Human/Environment Region Leaders – powerful kings, local lords, absolute monarchy State Structure – highly fragmented political system of city-states, local lords, and regional kingdoms with no central authority, larger political units ruled by powerful kings War – frequent warfare, extensive capture and sacrifice of prisoners Laws – crimes were punished with death Drained swamps, terraced hillsides, flattened ridge tops, constructed an elaborate water management system Flourishing agriculture society, artisans produced pottery, tools, and cotton textiles Trade – maintained commercial relationships with other city states, conducted seaborne commerce using canoes Traded luxury goods such as cotton clothing, precious jewels, and feathers Holy Books – Popul Vuh – Sacred Creation Book of the Maya Beliefs – believed in human sacrifice, cyclical nature of time, polytheistic, calendars, configured constellations of gods and places Deities – The Sun god was the most important Social Classes – distinct class system, the ruling class and the farmer/laborer was an educated nobility who were scribes, artists and architects Life Styles – elite classes sought luxury goods from far away, agriculture sustained substantial elite classes of nobles, priests, merchants, architects, and sculptors Family – children were subject to their parents until the age of 20 nobility were highly educated, under the care of the priests, in writing, music, history, war, and religion, daughters of nobles were forcefully secluded, the older boys lived and slept apart in a public building. Art/Architecture – carvings made of stucco, funerary pottery, stepped pyramids, temples, pyramids, palaces, and public plazas abounded with painted murals and endless stone carvings Math – developed a mathematical system that included the concept of zero and place notation was capable of complex calculations, combined this with careful observation of the night skies to plot the cycles of planets, to predict eclipses of the sun and moon, to construct elaborate calendars, and to calculate accurately the length of the solar year Location – extended throughout the Northern Central American region, occupied the eastern third of Mesoamerica Physical – volcanoes, limestone shelf, rainforest Movement – Lowlands and Highlands, Lowlands produced the primary crops, highlands had fertile soil and a pleasant climate full of precious metals NOTES: Collapsed mysteriously in about 909 CE, foreign invasion nor internal rebellion does not seem to be the case