PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION LAB
advertisement

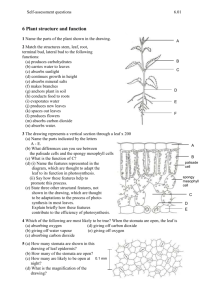
PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION LAB Page 584 may also be helpful. I. Roots: Neatly draw and label a monocot and dicot root cross-section. Use page 585 in the book. Label: xylem, phloem, epidermis and parenchyma. MONOCOT ROOT DICOT ROOT II. Types of roots: Draw a tape root and give an example and draw a fiberous root and give an example. TAPROOT FIBEROUS ROOT III. Leaf: Draw each type of leaf. SIMPLE LEAF PALMATELY COMPOUND PINNATELY COMPOUND IV. Stomata and Guard Cells: Neatly sketch and label stomata and its guard cells in a leaf. Use page 596-pick one picture to draw. Label: stoma, guard cell, epidermal cells and chloroplast. 1-Where does photosynthesis occur in the leaf? 2-What is transpiration? 3-What are stomata? 4-What gases are exchanged through the stomata? V. Stems: Neatly draw and label an herbaceous monocot and dicot stem. Use: epidermis, xylem, phloem, and vascular bundles. Use page 589. Do not draw woody stems. MONOCOT STEM VI. Monocot vs. Dicot Chart Venation DICOT STEM Arrangement of vascular bundles # of Flower parts Monocot Dicot VII. Flowers: (Pg. 612) Neatly draw and label a flower. Label: pistil, stigma, style, ovary, stamen, anther, filament, sepals and petals. VIII. Plant Cell: Neatly draw and label a plant cell. Label: mitochondria, nucleus, cytoplasm, ER, chloroplast, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cell wall, cell membrane, vacuoles, and nucleolus. PLANT COLLECTION Tape the following types of plant parts. Lay them flat after collection and before taping in your collection. MONOCOT LEAF DICOT LEAF Pinnately, palmately cmpd or simple leaf Pinnately, palmately cmpd or simple leaf MONOCOT LEAF DICOT LEAF Pinnately, palmately cmpd or simple leaf Pinnately, palmately cmpd or simple leaf EVERGREEN LEAF DECIDUOUS LEAF HERBACEOUS STEM FLOWER-monocot/dicot? WOODY STEM