MGLO7210 Economic Mineral Deposits and Management of

1
MAKERERE UNIVERSITY
DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY
1.
Course Name: Economic Mineral Deposits and
Management of Resources
2.
Course Code: MGLO 7210
3.
Course Description
This is an advanced course taught to Master of Science in Geology students.
It is an in-depth treatment of economic mineral deposits world-over. The course is divided into four parts. Part 1 dwells on general fundamental principles of formation of ore deposits, exploration techniques, ore sampling and mining and environment. Part II handles different types of ore deposits and classic examples around the world. Part III is the practical component of the course. Part IV is a seminar topic a student researches upon.
The major topics of the course are:
Fundamental Principles of Ore Genesis
Mineral Exploration Techniques
Ore Sampling, Reserve Calculations and Mineral Economics
Mining and the Environment
World-Class Ore Deposits
Seminar on Research Topic
2
4.
Course Objectives
These are:
To inculcate the knowledge of ore formation into students involving advanced studies such as fluid inclusions and isotopes.
To furnish the students with information concerning the distribution of mineral deposits around the earth.
To impart the knowledge of mineral exploration to the students to prepare them for independent projects of their own.
To train students in research methods in the discipline of mineral deposits and their exploration.
5.
Teaching and Assessment Pattern
Duration of Course:
The course is taught to the MSC 1 students in one 15-week semester. It is a
3 credit unit course with two hours of lectures and 1 contact hour for practicals per week.
Mode of Instruction
Instruction by lectures
Weekly quizzes to the students to enable them to be participatory.
Both oral and written quizzes are given to the students.
Weekly practicals that will be assessed. Practicals will involve library and internet search on the beneficiation methods, uses and world-class examples of the handspecimen sample being investigated.
3
Assignments will be given to students after every major topic.
One day trip in Migadde area on Bombo road to practice mineral exploration and sampling methods.
Students will sit a course test after part I and another course test after part II.
Each student will be assigned a seminar topic for library and internet research. Towards the end of the semester the findings will be presented in form of a lecture by the student. Both the oral presentation and write-up will be assessed.
Assessment Pattern
The assessment of the students will be based on the following:
Contribution Requirements a) Assignments b) Tests c) Practicals
No. of units
4
2
14 d) Seminar topic e) Final examination
Total
1
1
(a-d) 40%
60%
100%
4
All the scores will be converted to letter grades as follows:
Marks %
80-100
Letter Grade Grade Point
A 5
75-79.9
B+
70-74.9
B
4.5
4.0
65-69.9
B- 3.5
60-64.9
55-59.9
50-54.9
45-49.9
40-44.9
35-39.9
Below 35
C+
C
C-
D+
D
D-
E
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
6.
Reading List
Amstutz, G.C., El Goresy, Frenzel, G., Kluth, C., Moh, Wausch,
Küln, A. and Zimmermann, R.A. (Eds.), 1982. Ore genesis, the state of art; Springer Verlag.
Evans, A.M., 1980. An introduction to ore geology, vol. 2
Elsevier.
Hutchison, C.S., 1983. Economic deposits and their tectonic setting; The MacMillan Press ltd.
Jensen, M.L. and Bateman, A.M., 1981. Economic mineral deposits, 3 rd Edition; John Wiley, New York.
Nielson, J.M. (Ed), 1982. Strategies of small scale mining and mineral industries; AGID, Rep. No. 8.
5
Petters, W.C., 1987. Exploration and mining geology, 2 nd Ed.,
John Wiley and Sons.
Sawkins, F.J., 1984. Metal deposits in relation to plate tectonics;
Springer Verlag.
Thomas, L.J., 1979. An introduction to mining; Methuen of
Australia.
Evans, A.M., 2000. Ore geology and industrial minerals; An introduction, 3 rd Edition; Blackwell Science.
7.
Course Outline
Fundamental Principles of Ore Genesis
Definition of some terminologies, ore reserves, theories of ore genesis, classification of ore deposits, modes of ore formation, fluid inclusions, geothermometry and geobarometry, wall rock alteration, regional metallogeny.
Mineral Exploration Techniques
Sequential exploration model, feasibility studies
Ore Sampling, Reserve Calculations and Mineral Economics
Principles of sampling, channel sampling, spacing the channels, reducing of bulk samples, chip samples, muck samples and car samples, pitting, trenching and drilling (auger, banka, diamond). Reserve calculations, mineral economics.
6
Mining and the Environment
Mining methods, impact of mining to environment, Environment Impact
Assessment (EIA)
World-Class Ore Deposits
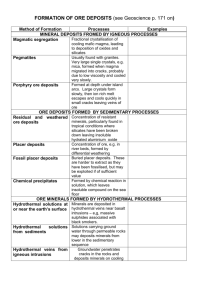
Archaean style mineralisation (greenstone belts), carbonatites, kimberlites, volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits, granophyre and batholith associated mineralisation, granite mineralisation, pegmatites, greisens, porphyry deposits, Kuroko-type of deposits, alkali granites, skarn deposits, surface processes deposits, sedex deposits, banded iron formations, sedimentary carbonate deposits.
Practicals
Handspecimens, their physical characteristics, diagnostic features, worldclass examples, beneficiation methods, annual production figures (if possible) and uses. Occurrence in Uganda and/or East Africa.
Seminar Research Topic
Research on a topic pertinent to economic mineral deposits. Make a public presentation and finally write-up.
8.
Suggested Teaching Programme
I. Fundamental Principles of Ore Genesis 3 weeks Assignment 1
Definition of some terminologies
Ore reserves
Theories of ore genesis
Classification of ore deposits
Modes of ore formation
Fluid inclusions
Geothermometry and geobarometry
Wall rock alteration
Regional metallogeny
II. Mineral Exploration Techniques 2 weeks Assignment 2
Sequential exploration model
Feasibility studies
III. Ore Sampling, Reserve Calculations and Mineral Economics
3 weeks
Principles of sampling
Channel sampling
Spacing the channels
Reducing of bulk samples
Chip samples
Muck samples and car samples
Pitting
Trenching and drilling (auger, banka, diamond)
Reserve calculations
Mineral economics
7
IV. Mining and the Environment 2 weeks Assignment 3
Mining methods
Impact of mining to environment
Environment Impact Assessment (EIA)
Test 1
V. World-Class Ore Deposits 5 weeks Assignment 4
Archaean style mineralisation (greenstone belts)
Carbonatites
Kimberlites
Volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits
Granophyre and batholith associated mineralisation
Granite mineralisation
Pegmatites
Greisens
Porphyry deposits
Kuroko-type of deposits
Alkali granites
Skarn deposits
Surface processes deposits
Sedex deposits
Banded iron formations
Sedimentary carbonate deposits
8
9
Test 2
VI. Practicals
Overlap starting from 2 nd Week of the semester up to the 15 th week.
VII. Seminar Research Topic
Overlaps starting from the 7 th week of the semester up to the 15 th week.
9.
Responsibility of the Student
Regular attendance, do all the assignments, practicals, attend all the field demonstrations participate in field excursions and write field reports.
Consult supervisors’ to develop research proposal.
10.
Responsibility of the Course Lecturer
Constant and punctual teaching, guide students during practicals, accompany and explain issues during field demonstrations and outer fieldwork, accurate and prompt grading of assignments, practicals, field reports, tests and examinations. Assist students after formal lectures. Guide students to develop a research proposal.