Pharmacology MCQs: July 2nd
advertisement

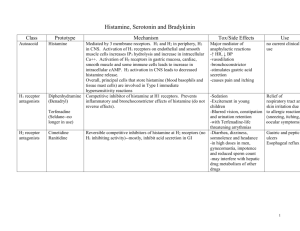
Pharmacology MCQs: July 2 nd 1. Regarding histamine a. b. c. d. e. 2. Histamine a. b. c. d. e. 3. d. e. Cisapride Sucralfate Metaclopromide Bethanechol Neostigmine Regarding drugs which act on the colon a. b. c. d. e. 7. They can be used to treat systemic mastocytosis They are capable of >90% reduction in gastric acid secretion after a single dose Up to 20% of ulcers may fail to heal with 4 weeks of conventional H2 antagonist/antacid treatment Cimetidine may cause reversible gynaecomastia and confusional states as side effects All of the above are true Agents promoting GI motility (i.e are prokinetic) include all of the following EXCEPT a. b. c. d. e. 6. Diphenhydramine Cyproheptadine Pyrilamine Loratadine Promethazine Regarding H2 antagonists a. b. c. 5. Causes increased BP via potent vasoconstricting effects Stimulates gastric acid secretion Is produced by bacteria in ciguatera fish causing GI upset and cvascular effects Has insignificant effects on nerve endings All of the above are correct All of the following H1 antagonists may cause moderate- marked sedation EXCEPT a. b. c. d. e. 4. H1 receptors occur in cardiac muscle H2 receptor blockers include promethazine Adrenaline is a physiologic antagonist of histamine Histamine works on bronchiolar smooth muscle to bronchodilate it Brain H3 receptors are predominantly postsynaptic Lactulose is a stimulant laxative Diphenoxylate is a weak analogue of fentanyl Loperamide is safe for use in patients with diarrhoea from ulcerative colitis Senna has a delayed onset of action Kaolin is an adsorbent and is more effective in treatment of diarrhoea than loperamide or diphenoxylate All of the following drugs / diseases cause prolonged QT interval / potentially lethal ventricular arrhythmias when combined with astemizole EXCEPT a. b. c. d. e. Rifampicin Patients with liver disease Ketoconazole Erythromycin Itraconazole 8. H2 antagonists a. b. c. d. e. 9. Irreversibly compete with histamine at H2 receptor sites Also bind to H1 receptors Famotidine inhibits the cytochrome P450 system Ranitidine may increase bioavailability of ethanol by >40% in normal individuals Ranitidine is 7 times more potent than famotidine in treatment of duodenal ulcers Cimetidine may increase the pharmacologic effect of all of the following EXCEPT a. b. c. d. e. Lignocaine Ketoconazole Warfarin Phenytoin Barbiturates 10. Regarding drugs affecting serotonin a. b. c. d. e. Sumatriptan is a serotonin antagonist Buspirone is a 5HT1a agonist Cyproheptadine is a competitive serotonin blocker in doses of 120 to 160 mg/day Ketanserin blocks 5HT receptors and B receptors Ondansetron is a 5 HT 2 antagonist 11. Regarding the ergot alkaloids a. b. c. d. e. Bromocriptine has profound effects on uterine smooth muscle stimulation Methysergide is a peptide alkaloid Ergotamine constricts most human blood vessels and is short acting PCP is an ergot alkaloid Ergotism may be defined as a spectrum of hallucinations, convulsions and “fiery limb pains” 12. All of the following drugs stimulate renin release EXCEPT a. b. c. d. e. Clonidine Nitroprusside Isoproterenol Alpha antagonists Thiazides 13. All of the following vasoconstrict EXCEPT a. b. c. d. e. Vasopressin Ergotamine Angiotensin 2 Substance P Endothelin 14. Regarding NSAIDs a. b. c. d. e. Aspirin reversibly acetylates and blocks platelet cyclo oxygenase Piroxicam has the shortest half life of all the NSAIDS Serious haematological problems have occurred with indomethacin use Ibuprofen is excreted predominantly unchanged in the urine Naproxen = selective COX 2 inhibitor 15. Methyxanthines (theophylline) a. b. c. d. e. Have negative chronotropic/inotropic effects Have antidiuretic effects Inhibit the enzyme phosphodiesterase at high concentrations Theophylline has less selective smooth muscle effects compared with caffeine Have no effect on skeletal muscle 16. All of the following pairings are correct EXCEPT a. b. c. d. e. PGE1 = vasodilation PGE2 = relaxes gut longitudinal muscle PGF 2 alpha = bronchoconstricts PGF2alpha = oxytocic actions PGI 2 = inhibits platelet aggregation 17. PGE 1 has all of the following effects EXCEPT a. b. c. d. e. Maintains patent ductus in some congenital heart disease Contracts intestinal smooth muscle Vasodilates Inhibits platelet aggregation Decreases water and sodium excretion by the kidney 18. Regarding drugs used to treat asthma a. b. c. d. e. Antimuscarinic agents are much more potent than B2 agonists in reversing asthmatic bronchospasm Salmeterol has a duration of action of 4 – 6 hours Isoproterenol is a potent bronchodilator but may cause cardiac arrhythmias Cromolyn sodium is an excellent agent for treatment of an acute asthma attack Aminophylline contains 66 % theophylline by weight Answers Pharm 2nd July 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. C B D E B D A D E B E A D C C B E C Physiology MCQs: July 2 nd Respiratory 1. Regarding the lung a. b. c. d. e. 2. All of the following pairings are correct (assuming normal person at rest) EXCEPT a. b. c. d. e. 3. Metabolic alkalosis Respiratory alkalosis with partial renal compensation Metabolic acidosis Respiratory acidosis Mixed respiratory/metabolic alkalosis All of the following states decrease lung compliance EXCEPT a. b. c. d. e. 7. Decreased pH Increased temperature Carbon monoxide Increased 2.3 DPG Increased pCO2 This blood gas picture reveals which of the following? PH = 7.52, pCO2 = 20 mmHg, pO2 = 120 mmHg, bicarb = 16 mmol/l a. b. c. d. e. 6. Bradykinin Serotonin Noradrenaline Angiotensin 1 Vasopressin All of the following shift the oxygen dissociation curve to the right EXCEPT a. b. c. d. e. 5. Tidal volume = 500 ml Alveolar ventilation = 7500 ml Pulmonary blood flow = 5000 ml/min Functional residual capacity = volume of gas in lung after normal expiration Physiologic dead space = 150 ml Which of the following substances is activated by passage through the pulmonary circulation? a. b. c. d. e. 4. There are about 300 million alveoli in the human lung The terminal bronchioles are the smallest airways without alveoli Anatomic dead space = 150 ml Alveoli are about 0.3 mm in diameter All of the above are true Lung fibrosis Increased pulmonary venous pressure Long period of time where the lung is unventilated Emphysema Alveolar oedema Regarding airway resistance a. b. c. d. e. The Poiseulle equation denotes pressure volume characteristics for turbulent flow The very small bronchioles are the major site of resistance to airflow Decreased pCO2 in alveolar gas causes an increase in airway resistance As lung volume reduces, airway resistance reduces also Contraction of bronchial smooth muscle by stimulation of adrenergic receptors increases airway resistance 8. Regarding control of ventilation a. b. c. d. e. 9. The apneustic centre lies in the medulla The central chemoreceptors respond to changes in oxygen concentrations The chemoreceptors in the aortic bodies respond to a fall in arterial pH Peripheral chemoreceptors respond to decreases in arterial pO2 The most important factor in control of ventilation under normal conditions is the pO2 of the arterial blood Alveolar ventilation in a male with a respiratory rate of 10/min and tidal volume of 600 ml is a. b. c. d. e. 1000ml 1750 ml 3000ml 4500ml 6000ml 10. At high altitudes all of the following things occur in an effort to acclimatise EXCEPT a. b. c. d. e. Hypoventilation Polycythaemia Increased numbers of capillaries per unit volume in peripheral tissues O2 dissociation curve shifts to right Pulmonary vasoconstriction 11. With respect to regional gas exchange in the upright lung a. b. c. d. e. Ventilation is greater at the top of the lungs Perfusion is much greater at the top of the lungs compared with the bases Ventilation/perfusion ratio is abnormally high at the top of the lungs PO2 is highest at the bases of the lungs PH is highest at the bases of the lungs 12. Regarding ventilation a. b. c. d. e. Normal FEV1 is 70% of FVC FEV1 is decreased much more than FVC in patients with lung fibrosis FEV1 is dependent on expiratory effort FVC in an average healthy person is about 3100 ml FEV1 is about 42% of FVC in a patient with obstructive lung disease 13. You are up very high where barometric pressure is 447 mmHg. What is the partial pressure of oxygen in the air up there? a. b. c. d. e. 0.5 mmHg 40 mmHg 80 mmHg 120 mmHg 150 mmHg 14. Regarding oxygen transport a. b. c. d. e. The predominant way oxygen is transported in the blood is as dissolved oxygen 1 gram of pure Hb can combine with 1.34 - 1.39 ml of oxygen An anaemic patient has a lowered arterial pO2 because the Hb is low CO2 is 200 times more soluble than oxygen The CO2 dissociation curve is less steep than that of oxygen Answers: Physiology July 2nd 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. E B D C B D C D D A C E C B