Biology Cell reproduction Pre test 1. Most mammals have diploid
advertisement

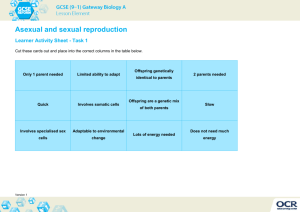
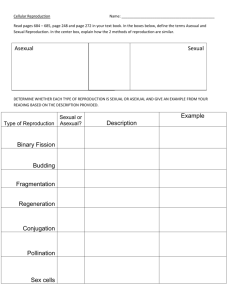
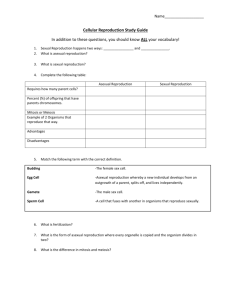
Biology Cell reproduction Pre test 1. Most mammals have diploid body cells and haploid gametes. During __________, chromosomes from haploid gametes combine, and a __________ zygote is formed. A. implantation, diploid B. fertilization, haploid C. fertilization, diploid D. implantation, haploid 2. When environmental conditions change, it is more likely that at least some members of a species will survive if A. the species reproduces asexually. B. the species requires very specific environmental conditions. C. there is variation among the members. D. the members are genetically identical. 3. The carp fish has 104 chromosomes in its body cells. When the fish's body cells divide by mitosis, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have? A. 312 B. 208 C. 104 D. 52 4. Genes can mutate through replication error or through contact with a mutagen. What can be a result of a mutation? A. The mutated gene can cause the organism to undergo speciation. B. The mutated gene is able to perform a new function. C. The mutated gene can become a separate organism. D. The mutated gene can become pathogenic to other organisms. 5. Examine the diagram below: Ciliates are protists that are able to reproduce both sexually and asexually. Both of these forms of ciliate reproduction are shown in the diagram. Which type of reproduction is represented in Process A? A. fission B. budding C. fragmentation D. sexual reproduction 6. Examine the diagram above: Ciliates are a type of protist that are able to reproduce both sexually and asexually. Both of these forms of ciliate reproduction are shown in the diagram. Which type of reproduction is represented in Process B? A. fragmentation B. budding C. sexual reproduction D. fission 7. Which of the following is a source of genetic variation in sexually-reproducing organisms? A. translation B. mitosis C. meiosis D. all of these 8. Suppose four different species live in close proximity to one another within an ecosystem. Species W reproduces through fragmentation. Species X reproduces sexually. Species Y reproduces through budding. Species Z reproduces through fission. Which species will most likely have the most genetic diversity among their offspring? A. Species X B. Species Z C. Species Y D. Species W 9. What is occurring in the diagram below? A. Genes are replicating. B. Alleles are independently assorting. C. Sister chromatids are separating. D. Segments of DNA are crossing over. 10. Suppose a person found a starfish and cut the starfish up into several pieces before throwing the starfish back into the water. Each of the pieces of the starfish grew into a new starfish. What form of reproduction did the starfish exhibit? A. fission B. sexual reproduction C. fragmentation D. budding 11. Bacteria, many plants, protists, and simple animals are able to reproduce asexually. Which of the following is an advantage of asexual reproduction over sexual reproduction? A. Asexual reproduction takes more energy to perform than sexual reproduction. B. Asexual reproduction enables a single organism to produce both eggs and sperm. C. Asexual reproduction causes the gene pool of a species to rapidly change. D. Asexual reproduction allows organisms to produce many offspring in a short period of time. 12. When a body cell divides through the process of mitosis, the chromosomes in the daughter cells A. are identical to the chromosomes of the parent cell. B. represent only the healthiest chromosomes from the parent cell. C. are only half of the chromosomes in the parent cell. D. are formed when chromosomes from the parent cell cross over. 13. Asexual reproduction takes less energy to perform than sexual reproduction. Why is this most likely the case? A. Specialized gamete cells do not need to be produced during asexual reproduction. B. Unlike sexual reproduction, there are several different types of asexual reproduction. C. Unlike sexual reproduction, parts of the parent's body are used to form the new offspring in asexual reproduction. D. Asexual reproduction occurs over a longer period of time than sexual reproduction. 14. During meiosis, each diploid parent cell divides produces haploid daughter cells. and A. twice; two B. once; two C. once; four D. twice; four 15. Offspring that are produced through sexual reproduction have more genetic diversity than offspring that are produced through asexual reproduction. Why is this the case? A. Sexual reproduction involves the mixing of genes from two separate individuals. B. Sexual reproduction involves the production of a clone. C. Sexual reproduction involves the process of mitosis. D. Sexual reproduction involves the rearranging of a single parent's genetic code. 16. How do mutations lead to genetic variation? A. by producing random changes in an organism's genetic code B. by changing the organism's appearance C. by changing the organism's behavior D. by changing the way that the organism reproduces 17. During embryonic development, cells __________ and become more __________. A. decrease in number, generalized B. decrease in number, specialized C. increase in number, generalized D. increase in number, specialized 18. Alex is studying a population of fifty organisms that belong to the same species. Some of the organisms have dark spots, some have light spots, some have no spots, and some have stripes. How does this species reproduce, most likely? A. using sexual reproduction B. using asexual reproduction C. the species does not reproduce D. using both sexual and asexual reproduction 19. Data for the hatching of sea turtle eggs is shown below. Group # Incubation temp Number of eggs Moon phase Tide Female (°C) % 1 26.0 79 New moon High 10.0 2 27.4 67 Full moon Low 15.0 3 28.5 59 First quarter High 30.0 4 29.5 42 Last quarter High 72.5 5 30.3 108 New moon Low 83.0 According to the table, what factor can be said to influence the gender of sea turtle hatchlings? A. tide B. phase of moon C. number of eggs D. temperature 20. Which of the following is a disadvantage of sexual reproduction? A. Sexually-reproducing organisms reproduce too quickly. B. Sexually-reproducing organisms are genetically-unique. C. A sexually-reproducing organism cannot reproduce without finding a mate. D. Species that reproduce sexually are unable to adapt. 21. In sexually reproducing organisms, mutations can be passed on to the organism's offspring if the mutation occurs in... A. any of the parent's cells found in the reproductive system only. B. germ cells only. C. Mutations in parent cells are never transferred to their offspring. D. any of the parent's cells. 22. Rachel grows pea plants in her backyard. Some of the pea plants have purple flowers, whereas others have white flowers. What does this indicate about Rachel's pea plants? A. The pea plants all have identical genes. B. The pea plants have genetic variation. C. The pea plants can only reproduce asexually. D. The pea plants cannot reproduce. 23. Which population is likely to have the most genetic variation among its members? A. a population whose members have many different traits B. It is impossible to identify genetic variation within a population. C. a population whose members are exactly the same D. a population whose members are very similar to each other 24. In the gastrula stage of embryonic development, shown in the diagram below, three layers of cells form—the ectoderm, the endoderm, and the mesoderm. The mesoderm cells will eventually differentiate into the A. skin and nervous system of the organism. B. organism's digestive tract lining. C. organism's muscles, blood, and reproductive organs. D. mouth and anal opening of the organism. 25. Each pair of _________ chromosomes has genes for the same trait. A. male B. sex C. homologous D. mutated Biology Cell reproduction Pre test answer sheet ____1. ____2. ____3. ____4. ____5. ____6. ____7. ____8. ____9. ____10. ____11. ____12. ____13. ____14. ____15. ____16. ____17. ____18. ____19. ____20. ____21. ____22. ____23. ____24. ____25. Answers 1. C 2. C 3. C 4. B 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. A 9. D 10. C 11. D 12. A 13. A 14. D 15. A 16. A 17. D 18. A 19. D 20. C 21. B 22. B 23. A 24. C 25. C Explanations 1. In the process of fertilization, a haploid egg cell fuses with a haploid sperm cell. The nuclei of the cells fuse, and the homologous chromosomes pair up. The result is that a diploid, one-celled zygote is formed. The zygote cell divides and becomes an embryo through normal mitotic division. 2. When environmental conditions change, it is more likely that at least some members of a species will survive if there is variation among the members. This is because the variant organisms within the species are able to respond differently to the environmental changes. 3. Body cells undergo a type of division called mitosis. During mitosis, the daughter cells produced are identical to the parent cell. So, daughter cells resulting from mitosis in a carp fish will have 104 chromosomes. 5. In Process A, the ciliate is reproducing by fission, the separation of a parent into two or more individuals of about equal size. 4. Mutations generally do one of two things. First, a mutation can lead to the loss of function of a gene. Second a mutation can lead to a new function. Mutations can have various affects on the organism. Some mutations have no affect at all. Some mutations change the morphology of the organism. Some mutations change the biochemical reactions within the organism. If the mutation is passed on to offspring and is beneficial to the offspring’s survival, eventually the descendants of the organism with the original mutation may undergo speciation. 6. In Process B, two ciliates pair and exchange genetic materials. Meiosis then occurs in the micronuclei, one of which will then develop into a zygote. Meiosis is a process that occurs in sexual reproduction. 8. Sexual reproduction allows genes from two parents to be mixed into different combinations within their offspring. This creates more genetic diversity among the members of a species. So, species X. will have the most genetic diversity among its offspring. 7. In sexually-reproducing organisms, meiosis helps contribute to genetic variation. Meiosis is the process by which sexually-reproducing organisms produce gametes, or sex cells. Meiosis produces gametes that are unique from each other and from the "parent genome". The gametes will be passed on to future offspring. 9. In the diagram, segments of DNA from homologous chromosomes are crossing over. This process, which occurs during Prophase I of meiosis, happens randomly and frequently. In fact, it can even occur at more than one place along the same chromosome. Meiosis and crossing-over are important processes because they contribute to the genetic variation found in organisms that undergo sexual reproduction. 10. Fragmentation is a type of reproduction in which the body breaks into several pieces. Some or all of these fragments then develop into complete adults when missing parts are regrown. 11. Asexual reproduction takes less time and energy to perform than sexual reproduction. However, asexual reproduction results in populations with little genetic diversity. 12. Body cells divide through the process of mitosis. In mitosis, the daughter cells produced are identical to the parent cell. In particular, they have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, and these chromosomes are identical copies of the chromosomes in the parent cell. In contrast, gametes (sex cells) are produced through the process of meiotic cell division. In meiosis, the daughter cells are different from the parent cell. The daughter cells not only have only half of the chromosomes present in the parent cell, but the process of crossing over during Prophase I creates new, nonidentical chromosomes. 13. Asexual reproduction takes less energy than sexual reproduction because the organism does not have to expend energy to find a mate or produce specialized reproductive cells. 14. There are two stages of nuclear division during meiosis. During the first stage (meiosis I), the number of chromosomes in the diploid parent cell double. Then, homologous chromosomes pair with one another and split into two daughter cells. During the second stage (meiosis II), the sister chromatids separate to produce four haploid daughter cells. Since the assortment of alleles during meiosis is independent and random, over 8 million different combinations of chromosomes are possible in humans. (Humans have 46 chromosomes. The possible number of combinations is given by the formula 2 n, where n = 23, the haploid number of chromosomes.) 15. Individuals produced through sexual reproduction are more genetically diverse than individuals produced through asexual reproduction because sexual reproduction occurs from the fusing of two specialized cells that each contains different genetic material. The fusing of the cells, called fertilization, produces a unique combination of genes not found in any other organism (except in the case of identical twins). 16. A mutation is a random change in a cell's genetic code due to a variety of causes. The change can be small and insignificant, or it can be major. Mutations can be passed on to offspring through reproduction, thus increasing the genetic variation within a population. 17. After an egg cell fuses with a sperm cell, a zygote forms. The zygote begins to divide, and the number of cells increases. Although the zygote cell undergoes mitotic division, no cell growth occurs between divisions. Where there was once one cell, many cells develop. However, the volume does not change, so the cell size decreases upon each division. When the embryo enters the gastrula stage, cells begin to specialize. Three different layers of cells develop—endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm. These cells later differentiate further into the highly specialized types of cells that make up a complete organism—muscle, nerve, blood, bone, and skin cells. 18. Since sexual reproduction results in genetic variation, populations of sexuallyreproducing organisms usually have a variety of different traits. In this case, the organisms have a variety of color patterns, so the species most likely uses sexual reproduction. 19. In sea turtles, development of embryos is influenced by temperature. The gender of many invertebrate animals is determined by sex-determining chromosomes. However, the gender of sea turtle offspring is determined by the sand temperature during incubation. When the sand is below 29 degrees, more males are produced. When the sand temperature is above 29 degrees, more females are produced. 20. Sexual reproduction combines the genetic material of two individuals. As a result, a sexually-reproducing organism cannot reproduce if it cannot find a mate. 21. In sexually reproducing organisms, mutations can be passed on to the organism's offspring if the mutation occurs in germ cells (i.e. egg and sperm). 22. Genetic variation occurs when alleles are randomly sorted during sexual reproduction. Since each offspring receives a different combination of alleles from the parent organisms, phenotypic diversity results. Rachel's pea plants are exhibiting phenotypic diversity because some of the plants have purple flowers, whereas others have white flowers. This indicates that the pea plants have genetic variation. 23. The array of physical traits within a population is generally a good indicator of the amount of genetic variation within the population. So, the greater the variety of observable features within a population, the greater the genetic variation within the population. 24. Ectoderm cells differentiate to form the skin and nervous system of the organism. Endoderm cells eventually become the organism's digestive tract lining. Mesoderm cells become the organism's muscles, blood, and reproductive organs.