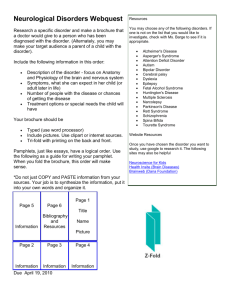
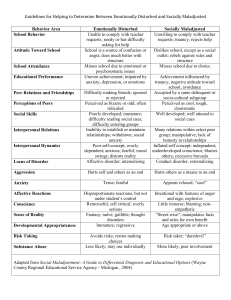
Lesson 3 - Florida Therapy Services
advertisement

Mental Health Targeted Case Management Training Lesson 22 Mental Health Terms 1. Common Terminology: These general terms are provided to give the case manager an understanding of the terms used when reading documents generated by counselors, psychologists, or psychiatrist. a. Affect; A pattern of observable behavior that is the expression of a subjectively experienced feeling state (emotion). 1) Flat: Absence or near absence of any signs of affective expression. 2) Inappropriate: Discordance between affective expression and the content of speech or ideation. 3) Labile: Abnormal variability in affect with repeated, rapid and abrupt shifts in affective expression. b. Agitation: Excessive motor activity associated with a feeling of inner tension. The activity is usually nonproductive and repetitious and consists of such behavior as pacing, fidgeting, wringing of hands, pulling of clothes, and inability to sit still. c. Delusion: A false belief based that is firmly sustained despite what almost everyone else believes and despite what constitutes incontrovertible and obvious proof to the contrary. 1) Bizarre: Involves a phenomenon that the person’s culture would regard as totally implausible. 2) Delusional Jealousy: A perception that one’s sexual partner is unfaithful. 3) Grandiose: Inflated worth, power, knowledge, identity, or special relationship to a deity or famous person. 4) Of being controlled: Feelings, impulse, thoughts, or actions are experienced as being under the control of some external force rather that being under one’s own control. 5) Of reference: Events, objects or other persons in one’s immediate environment have a particular and unusual significance (usually of a negative nature). 6) Persecutory: The individual (or someone to who they are close to) is being attacked, harassed, cheated, persecuted, or conspired against. 7) Somatic: Main content pertains to the appearance or functioning of one’s body. 8) Thought broadcasting: One’s thoughts are being broadcast aloud so that others can perceive them. 9) Thought insertion: One’s thoughts are not one’s own, but rather are inserted into one’s mind. Mental Health Targeted Case Management Training d. Disorientation: Confusion about the time of day, date, or season (time), where one is (place), or who one is (person). e. Flight of Ideas: A nearly continuous flow if accelerated speech with abrupt changes from topic to topic that are usually based on understandable associations, distracting stimuli, or plays on words. f. Hallucination: A sensory perception that has the compelling sense of reality of a true perception but that occurs without external stimulation of the relevant sensory organ. Examples are: 1) Auditory: Perception of sound, most commonly of voices. 2) Somatic: Perception of a physical experience localized with the body. 3) Tactile: Perception of being touched or of something being under one’s skin. 4) Gustatory: Involving the perception of taste (usually unpleasant) 5) Visual: Perception of sight, which may consist of formed images, such as of people, or of unformed images, such a flashed of light. g. Mood: A pervasive and sustained emotion that colors the perception of the world. Common examples include depression, elation, anger and anxiety. 1) Dysphoric: An unpleasant mood, such as sadness, anxiety, or irritability. 2) Euphoric: An exaggerated feeling of well-being, or euphoria or elation. 2. Other Mental Health Terms: You may see these terms used during your review of client documents related to history. a. Anorexia nervosa: is an eating disorder characterized by unusual eating habits such as avoiding food and meals, picking out a few foods and eating them in small amounts, weighing food, and counting the calories of all foods. Individuals with anorexia nervosa may also exercise excessively. b. Anxiety disorders: range from feelings of uneasiness to immobilizing bouts of terror. Most people experience anxiety at some point in their lives and some nervousness in anticipation of a real situation. However if a person cannot shake unwarranted worries, or if the feelings are jarring to the point of avoiding everyday activities, he or she most likely has an anxiety disorder. c. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: sometimes called ADHD, is a chronic condition and the most commonly diagnosed behavioral disorder among children and adolescents. It affects between 3 and 5 percent of school-aged children in a 6-month period (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 1999). Children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder have difficulty controlling their behavior in school and Mental Health Targeted Case Management Training d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. social settings. They also tend to be accident-prone. Although some of these young people may not earn high grades in school, most have normal or above-normal intelligence. Autism: also called autistic disorder, is a complex developmental disability that appears in early childhood, usually before age 3. Autism prevents children and adolescents from interacting normally with other people and affects almost every aspect of their social and psychological development. Bi-Polar Disorder: Extreme mood swings punctuated by periods of generally even-keeled behavior characterize this disorder. Bipolar disorder tends to run in families. This disorder typically begins in the mid-twenties and continues throughout life. Without treatment, people who have bipolar disorder often go through devastating life events such as marital breakups, job loss, substance abuse, and suicide. Borderline Personality Disorder: Symptoms of borderline personality disorder, a serious mental illness, include pervasive instability in moods, interpersonal relationships, self-image, and behavior. The instability can affect family and work life, long-term planning, and the individual's sense of self-identity. Delusions: are bizarre thoughts that have no basis in reality. Dementia: is a problem in the brain that makes it hard for a person to remember, learn and communicate; eventually is becomes difficult for a person to take care of himself or herself. This disorder can also affect a person's mood and personality. Depression: is a mood disorder characterized by intense feelings of sadness that persist beyond a few weeks. Two neurotransmitters-natural substances that allow brain cells to communicate with one another-are implicated in depression: serotonin and norepinephrine. Mental Health: How a person thinks, feels, and acts when faced with life's situations. How people look at themselves, their lives, and the other people in their lives; evaluate their challenges and problems; and explore choices. This includes handling stress, relating to other people, and making decisions. Mental health problems: They affect one's thoughts, body, feelings, and behavior. Mental health problems are not just a passing phase. They can be severe, seriously interfere with a person's life, and even cause a person to become disabled. Mental health problems include depression, bipolar disorder (manicdepressive illness), attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder, anxiety disorders, eating disorders, schizophrenia, and conduct disorder. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: is a chronic, relapsing illness. People who have it suffer from recurrent and unwanted thoughts or rituals. The obsessions and the need to perform rituals can take Mental Health Targeted Case Management Training m. n. o. p. q. r. s. t. over a person's life if left untreated. They feel they cannot control these thoughts or rituals. Outcome: The results of a specific health care service or benefit package. Panic Disorder: People with panic disorder experience heartpounding terror that strikes suddenly and without warning. Since they cannot predict when a panic attack will seize them, many people live in persistent worry that another one could overcome them at any moment. Paranoia Disorder: Symptoms of paranoia include feelings of persecution and an exaggerated sense of self-importance. The disorder is present in many mental disorders and it is rare as an isolated mental illness. A person with paranoia can usually work and function in everyday life since the delusions involve only one area. However, their lives can be isolated and limited. Performance Measures: A measure that describes the health care being provided. Current performance measures indicate whether a health plan or provider has appropriately provided certain services expected to lead to desirable outcomes. Phobias: are irrational fears that lead people to altogether avoid specific things or situations that trigger intense anxiety. Phobias occur in several forms, for example, agoraphobia is the fear of being in any situation that might trigger a panic attack and from which escape might be difficult; social phobia is a fear of being extremely embarrassed in front of other people. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: is an anxiety disorder that develops because of witnessing or experiencing a traumatic occurrence, especially life threatening events. PTSD can cause can interfere with a person's ability to hold a job or to develop intimate relationships with others. Schizophrenia: is a mental disorder characterized by "positive" and "negative" symptoms. Psychotic, or positive, symptoms include delusions, hallucinations, and disordered thinking (apparent from a person's fragmented, disconnected and sometimes-nonsensical speech). Negative symptoms include social withdrawal, extreme apathy, diminished motivation, and blunted emotional expression. School-Based Services: School-based treatment and support interventions designed to identify emotional disturbances and/or assist parents, teachers, and counselors in developing comprehensive strategies for addressing these disturbances. School-based services also include counseling or other schoolbased programs for emotionally disturbed children, adolescents, and their families within the school, home and community environment. Mental Health Targeted Case Management Training u. Wraparound Services: A unique set of community services and natural supports for a child/adolescent with serious emotional disturbances based on a definable planning process, individualized for the child and family to achieve a positive set of outcomes.