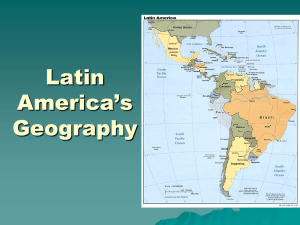
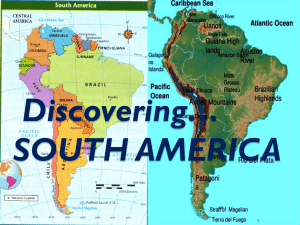
Geography of South America
advertisement
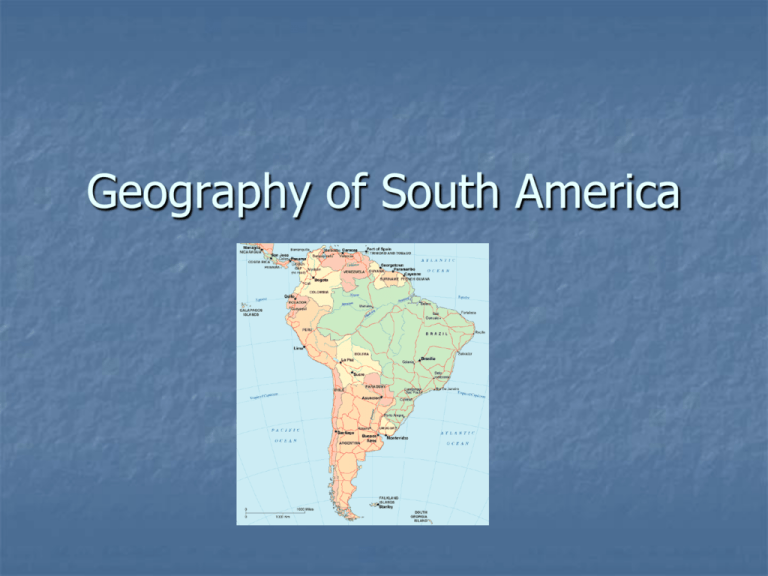
Geography of South America I. Andes Mountains A. Longest (and one of the youngest) mountain range(s) in the world, more than 5,000 mi (8,000 km) long, B. Extend from Venezuela, to Tierra del Fuego and the Falkland Islands. C. The Andes go through seven South American countries— Argentina, Chile, Bolivia , Peru, Ecuador, Colombia , and Venezuela . II. Altiplano A. High plateau near the border between Peru and Bolivia. B. Very high altitude, between 12,500 ft to over 15,000 ft. C. Few trees, plants, or native animals live here. D. However, 70% of Bolivia’s population lives in or around the Altiplano. E. Lake Titicaca- worlds highest navigable lake. Survival on the Altiplano To live at such a high altitude with little oxygen, many people living on the Altiplano chew coca leaves. The coca leaves allow people to slow their breathing down and relieve head-aches and hunger pangs. III Atacama Desert The _____ Desert in the world Lays in Northern Chile and Southern Peru Averages Less that .004 inches of rain a year! What is so unique is that the desert is bordered by the ocean. IV. Patagonia A. The Patagonia region, located in the _________ end of South America, embraces the countries of Argentina and Chile. B. This is a ___________________ dry plateau. C. Difficult to support an abundance of life V. Gran Chaco A great, low-lying plain in South America. The Chaco has a tropical climate with alternate wet and dry seasons. The Chaco is sparsely settled and largely underdeveloped by humans. Dry season. Tree’s store water in their trunks. Wet season. Tropical environment. VI. Pampas A. Pampas , wide, flat, fertile grassy plains, 300,000 sq. miles particularly in Argentina and extending into Uruguay B. Chief crop is _________ C. livestock are the main source of income. D. Eastern part is humid and receives over ____inches of rain E. Western part is dry because of the Mountains. Rain blows over the mtns. and hit the eastern part of the pampas. VII. Gaucho A. gaucho , __________ of the Argentine and Uruguayan Pampas (grasslands). B. The typical gaucho, a familiar figure in the 18th and 19th cent., was a daring, skillful horseman and plainsman, and sometimes soldier. IV. Geography of the Andes A. What is the climate like in the Northern Andes? B. What is the climate like in the Central Andes? C. What is the climate like in the Southern Andes and Argentina? VIII. Brazilian Highlands A. The Brazilian Highland region is a steep coastal ridge rising along ______miles of shoreline in Southern and Southeastern Brazil. Average elevation is _______feet. B. The range clings closely to the coast, and reappears in spots as offshore _i______. IX. Guiana Highlands A. Located in Guyana, Suriname, and ____________. B. Tepuis rise one after another, like gargantuan steps, in sheer ___________ hundreds to thousands of feet high. C. Numerous rivers, fed by heavy rainfall, rise in the highlands and pour over the edges to create deep gorges and magnificent waterfalls. D. _________________ Highest waterfall in the world (3,312 ft) X. Amazon River Basin A. The Amazon river basin is located mainly in _____________. It also stretches into some of Peru. B. Contains Amazon river and forest. C. The largest in the world, covered by more than 2 ___________square miles in the form of dense tropical forest. D. For centuries, this has protected the area and the animals residing in it. Amazon River Basin is Like Folsom Field Guiana Highlands Andes Mountains AMAZON RIVER Brazilian Highlands XI. Amazon River A. The _________ river in the world in amount of water. The river ranges from 11/2 to 6 miles wide for most of its course. It widens to about 90 miles at its mouth. The Amazon's depth averages about 40 feet Discharge rate- average, 209000 m3/s (7381000 cu ft/s) B. It flows east, across northern Brazil and into the Atlantic Ocean at the Equator. http://www.mbarron.net/Amaz on/factfile.htm