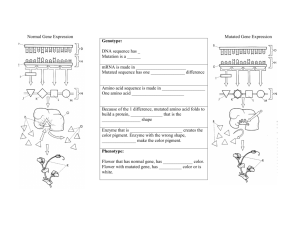
Mendelian Genetics probability table and hints
advertisement

Mendelian Genetics Probability Table* 1 Parent’s Genotypes (Cross) AA x AA 2 AA x Aa 3 4 AA x aa Aa x Aa 5 Aa x aa 6 aa x aa Children’s Genotype Children’s Phenotype 100% AA 100% Dominant 50% AA 50% Aa 100% Aa 25% AA 50% Aa 25% aa 50% Aa 50% aa 100% aa 100% dominant 100% Dominant 75% dominant 25% recessive 50% dominant 50% recessive 100% recessive *If you don’t memorize this table, then you are a fool…… Hints for solving problems: For every problem, you will either be given the genotype or the phenotype. Identify which one you have. Always, write the cross. If given the cross, calculate the children’s genotype or phenotype. i.e. give the genotypes of a cross where the parents are both heterozygous (Aa x Aa). If given the phenotypes of the parents, first find the genotypes and then calculate children’s genotype or phenotype. Two individuals who have a straight hair line (straight hair line is recessive to widow’s peak) are mated, what are the possible phenotypes of the children. The genotype of the parents will almost always include the words homozygous or heterozygous. If it does, write the cross first, then calculate. Some word problems will give you the number of children resulting from a cross and ask you to figure out the cross. First get a total number of children. Then find the percentage of each type of child (dominant or recessive). Then figure out what cross would yield that result. In genetics, the numbers DO NOT have to be exact 50% dom, 50% rec is the result of a Aa x aa cross, but if the numbers are 52% dom, 48% rec then it is also the result of the same cross. Only two crosses (#4, 5) result in something OTHER than 100% dominant or 100% recessive. They are the ones most likely to be asked on a test. Mendelian Genetics Probability Table* 1 Parent’s Genotypes (Cross) AA x AA 2 AA x Aa 3 4 AA x aa Aa x Aa 5 Aa x aa 6 aa x aa Children’s Genotype Children’s Phenotype 100% AA 100% Dominant 50% AA 50% Aa 100% Aa 25% AA 50% Aa 25% aa 50% Aa 50% aa 100% aa 100% dominant 100% Dominant 75% dominant 25% recessive 50% dominant 50% recessive 100% recessive *If you don’t memorize this table, then you are a fool…… Hints for solving problems: For every problem, you will either be given the genotype or the phenotype. Identify which one you have. Always, write the cross. If given the cross, calculate the children’s genotype or phenotype. i.e. give the genotypes of a cross where the parents are both heterozygous (Aa x Aa). If given the phenotypes of the parents, first find the genotypes and then calculate children’s genotype or phenotype. Two individuals who have a straight hair line (straight hair line is recessive to widow’s peak) are mated, what are the possible phenotypes of the children. The genotype of the parents will almost always include the words homozygous or heterozygous. If it does, write the cross first, then calculate. Some word problems will give you the number of children resulting from a cross and ask you to figure out the cross. First get a total number of children. Then find the percentage of each type of child (dominant or recessive). Then figure out what cross would yield that result. In genetics, the numbers DO NOT have to be exact 50% dom, 50% rec is the result of a Aa x aa cross, but if the numbers are 52% dom, 48% rec then it is also the result of the same cross. Only two crosses (#4, 5) result in something OTHER than 100% dominant or 100% recessive. They are the ones most likely to be asked on a test.