Workshop 4 - Before During After Reading
advertisement

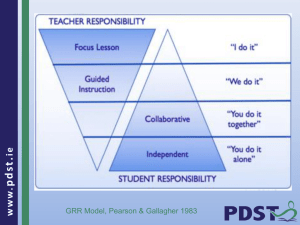
BEFORE READING ACTIVITIES Talk about the topic of the book Predict from an illustration Predict from a word Reader Questions Sequencing illustrations Ask questions about the topic of the book Develop word banks and display vocabulary about the book and about the topics you are studying Story Telling Before and After Chart Picture Flick Graphic Overlay - text organisation for nonfiction. Skimming and scanning Workshop 4 - Support Resource - APPLLS Discuss the topic of the text with students – adult shares their own experience of the topic of the text. If possible use the same tense as the text uses. e.g. Cat on the Roof: Does anyone have a cat? My friend had a cat and it was a very naughty cat. One day it climbed up a tree and my friend thought it was stuck. What do you think she did? Talk about the illustration on the front cover, or a key illustration from the book Ask the children to work in groups to think about what the story might be about Use some of the vocabulary of the book that children might find difficult, and explain where necessary Read the title of the book Ask what the children think the story is going to be about Ask the children to think of some questions they would like answered by reading the text Give groups/ pairs of children a set of pictures from the book and ask them to sequence them, prior to reading Ask questions about the topic of the book, but relating to the children’s own experiences. E.g. Possum Magic What do you like to eat? What do you eat at home? Use a semantic web to display these words Tell the story, using the illustrations or diagrams you draw, before you read the book Piece of paper with 2 columns, brainstorm all you know about the topic, list in before column, What I know about ..... After reading add to second column What we have learnt. Can be completed over time. Before reading, skim through the illustrations and get a sense of contents, characters or setting. Look at the front cover, skim through text browsing at pictures, predict the story, Read the text, and discuss the difference between the prediction and what happened. Teaches students about text organisation for nonfiction. Create a visual representation of the layout or organisation of the page, label boxes e.g. heading, title, subtitle, picture, text information model skimming talk about how this is used to predict the content of the text DURING READING Modelled reading Model reading strategies Oral Cloze Pause and predict Reread for detail Matching words Shadow Reading Echo Reading Buddy Reading Diagrams flow charts or story maps Word Masking Beat the Buzzer Quiz Hunt the Text Challenge Jigsaw reading Scaffolding Language Scaffolding Learning Pauline Gibbons Reading aloud Scaffolding Language Scaffolding Learning Pauline Gibbons Interesting word chart an activity to clarify new or unknown vocabulary Workshop 4 - Support Resource - APPLLS Read the text aloud. Try and bring the book alive, use expression, and pausing to add interest. Read the book more than once. use hard words and difficult phrases to talk about/ show the children how you read the text. leave out words while reading the book to the children and they fill in the gap, good way of gauging comprehension stop reading the book ask the children What might happen next? What a character might be thinking? Feeling? re-read the text for detail, to make sure the reading is understood. use word cards around the room, and ask the children to find the words you read from the text Record yourself reading the text, allow small groups of children to read along, with the text. Read text sentence by sentence, students read the same sentence after the teacher Reading to younger buddies provides opportunities for older readers to model fluent reading. It gives weaker older readers opportunities to practise on easier books Children can draw diagrams flow charts or story maps to show structure of the book Cover words in big book, (both content and functional words) and children predict the word. Discuss alternatives. This strategy can be used to build vocabulary. Practise scanning to locate specific details to answer quiz questions Reading Resource Book, First Steps Quiz to scan the text to locate specific information. Create challenge cards to encourage scanning of the text Have 3 or 4 different readings at different levels to cater for different abilities in the class, about the same topics. In groups children read one reading, and become experts about that reading. They share the information with members of other groups. This provides a real purpose for reading, and authentic context for summarising, as the experts decide what information they share. Listening to a good reader helps children recognise that good readers make meaning, for both young and older readers. Read aloud both fiction and non-fiction books. as you are reading, add interesting words and the page number, use contextual clues to show students how to gain meaning AFTER READING ACTIVITIES Purpose: These activities assume the children know the text and have no comprehension difficulties and use the text as a springboard and may fulfil any of these three purposes 1. Use the familiar text as basis for language study. 2. Allow students to respond creatively to what they have read. 3. Focus students more deeply on the information of the text. 1. Use the familiar text as basis for language study Jumbled text/sentence exercises Text reconstruction Consonant groups Phonic families Cloze activities in groups or pairs, children justify why they have chosen their answer Ask children true/false questions OR fact/ opinion statements related to the text, Cut up paragraph into sentence strips and mix them up, reorder into paragraph, cut up sentences into words and mix them up, reorder into sentences Cut an excerpt of text into paragraphs or sentences, students to put into order and explain their answer Sort objects, or pictures of objects into groups using the beginning sound (Pencil, pen, paper, box, ball, lid, leaf) Build word lists using words in the book, that contain the same sounds, spelt the same way Traditional – every 7th word, syntactic- structure words, semantic- content words oral cloze –children fill in the missing words, while they read along with the teacher Monster cloze – This consists of only the title, and gaps. Students guess words which are written in and as more words are added it becomes easier to complete the cloze. Vanishing cloze – Choose a part of the text, or a summary. Write it all on the board, read together, then rub out one word, reread, putting in the missing word, then erase another word and repeat the process. Continue until all the words are removed and the students are “Reading” from memory. Cut up paragraph into sentence strips and mix them up, reorder into paragraph, cut up sentences into words and mix them up, reorder into sentences 2. Allow students to respond creatively to what they have read. Innovate on the text- Innovate the ending Sensory chart Allows children to see, feel and hear characters, settings or events. Cartoon strip Readers theatre Wanted posters Freeze frames A drama activity that show a tableaux of key stages of the story. Workshop 4 - Support Resource - APPLLS change the story, but keep the same story line e.g. different characters, main events, Write a new ending, in groups or as a whole class. Children read text, or passage add information about what it might look like, sound like or feel like Turn the story into a cartoon strip, using the dialogue as words in speech bubbles, in groups or individually, Children each have a copy of the book, choose a child for each character’s dialogue, the other children read narration. Practise the reading for the performance. Children could script their own text based on the story. (innovate the text) Design a wanted poster for a character in the book, incorporate as much as the information from the story as possible. The group needs to decide the main events, and then how they will be shown, and then how to move quickly from one to the next. No talking is required. Preparation of the tableaux allows discussion of the main elements characters and events of the story Audience close their eyes the group prepares the tableaux, using their bodies and simple props, after 10 seconds, the audience close their eyes again and the group arrange for the next tableaux and so on until the story is told. 3. Focus students more deeply on the information of the text Timelines Hot seat Story map Retell the story Picture sentence matching Questioning the text Book discussion groups Summarising and paraphrasing the text Venn Diagrams Retrieval chart What’s your story? Famous five key word search Very Important points Main idea pyramid Workshop 4 - Support Resource - APPLLS Texts that incorporate passage of time lend themselves to a timeline. Children can create and illustrate time lines Children sit in a circle and one child is chosen as a character from the book. Other students ask questions to find out more about the character’s life. These questions should be consistent with the story. Move back, or forwards in time Its seventy years ago and the old woman is now only a child.... and continue to ask questions of the person in the hot seat. This gives children lots of ideas for stories of their own. As a group draw the story, on a wall chart, sequence the main actions and record with illustrations children use the pictures to retell the story (Gives information about their understanding of the story) Take about 6 pictures and 6 matching sentences, children to match up. Focus on the pictures and on the characters, ask questions that show children that what is in the book is not necessarily the whole truth. What is the mother doing? What is the father doing? Do all mothers and fathers do this? Discuss what the characters are like Make lists of words or ideas that are associated with key people in the text Rewrite a well known tale, changing the characteristics of characters Talk about stereotyping What did you enjoy about this book? What are some of the major themes of this book? What did you appreciate about your favourite character? Oral summaries, in groups students read, and collectively summarise Students to write a summary, limit the number of sentences. Suggest a title for each paragraph Write 2 or 3 sentences under each paragraph heading’ With narrative, ask children to retell shorter and shorter, until as short as possible, write on the board and discuss Explain key points in less than 1 minute Groups work together to compose a sentence that summarises the text Use two or more overlapping circles to compare topics, characters, plots, or facts Chart to record information about a number of categories or topics to allow comparisons. Teach students about the structure of a text. Give students a recording sheet with headings linked to the text e.g. setting, characters, events, text type and theme. After several of these activities, students can compare texts Reading Resource Book, First Steps Reading Resource Book, First Steps Reading Resource Book, First Steps References Learning to Learn in a Second Language Pauline Gibbons Scaffolding Language Scaffolding Learning Pauline Gibbons Reading Resource Book, First Steps Workshop 4 - Support Resource - APPLLS Workshop 4 - Support Resource - APPLLS