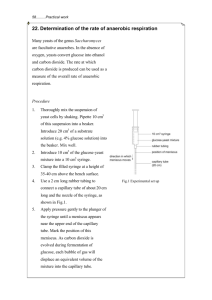
The effect of different concentration of ethanol solution on anaerobic
advertisement

The effect of different concentration of ethanol solution on anaerobic respiration of yeast Why do we choose to conduct this experiment? Alcoholic fermentation is the basis of brewing and wine making. But ethanol is toxic to yeast. We conduct this experiment to investigate the effect of concentration of ethanol on anaerobic respiration of yeast. Hypothesis Since ethanol is toxic to yeast, as the concentration of ethanol solution increase, the yeast is inhibited to carry our respiration, so we estimated that the anaerobic respiration rate of yeast will decrease as the concentration of ethanol solution increase. Principle •As yeast will carried out anaerobic respiration in the absence of oxygen, ethanol is given out which is poisonous to yeast and respiratory rate of yeast is then slow down. This can be shown by drops in the increase in air pressure in each syringe the volume of the syringes are constant. •As carbon dioxide is produced during anaerobic respiration, air pressure inside syringe is increase which can be detected by the low pressure sensor. Apparatus and Materials needed •Syringes x 6 •Beakers x 6 •Short rubber tubing x1 •Computer x 1 •Data logger and low pressure sensor x 1 •Electronic balance x 1 •2g of yeast •10 cm3 of glucose •Distilled water •10 cm3 of pure ethanol Procedure 1. Set up the computer and Science Workshop was got ready. 2. 6 syringes and 6 beakers are prepared and labelled1 to 6. 3. Weigh 0.25g of yeast in electronic balance for each syringe4. Mix X cm3 pure ethanol and Y cm3 distilled water, 1.25cm3 glucose, 0.25g of yeast into each beaker according to the table below Syringe 1 2 3 4 5 6 % of ethanol solution X cm3 of water 0 1.5 3 6 12 15 18.75 18.45 18.15 17.55 16.35 15.75 Y cm3 of ethanol 0 0.3 0.6 1.2 2.4 3 Volume of glucose solution 3 Total volume (cm ) 3 (cm ) 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.25 20 20 20 20 20 20 • Take syringe 2 as an example: The ethanol solution concentration is 1.5% total volume = 20 cm3 volume of ethanol added: = 20 x 1.5% = 0.3 cm3 •volume of glucose solution added = 1.25cm3•volume of water added = (20-1.25-0.3)cm3 = 18.45cm3 6. The syringes are filled by the mixture in the beaker through the nozzle by the plunger.7. A free end of rubber tubing is attached to the nozzle of the syringe, another end is attached to the low pressure sensor connected to the data logger. 8. Data is then recorded as a graph.9. The above steps are repeated in order to obtain result for 6 syringes 10. The slope of the graph of each syringe was taken.The change in pressure / change in time = slope = rate of anaerobic respiration11. After all the slopes of the 6 graphs was taken, a graph was then plotted on rate of anaerobic respiration of yeast against concentration of ethanol solution by using Excel. This is the set-up of our experiment