Teacher Notes about Adaptations to go with Plant Survival Techniques
advertisement

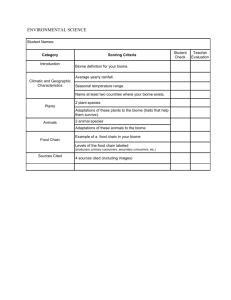
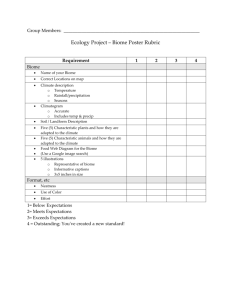
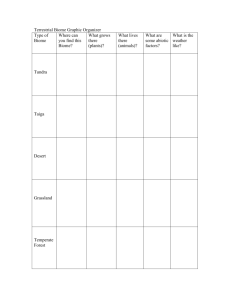
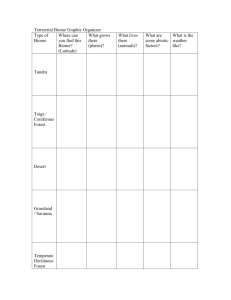
Plant Survival TechniquesName ____________________ Per. __ Date ________ 1. Adaptations Based on: Belize Biome Project PPT found in Course Documents on Blackboard What are adaptations? - Special _____________ that allow a plant or animal to live in a particular place or habitat - These adaptations make it hard for the plant/animal to survive in a __________________ place. - This explains why certain plants are found in one area but not in another. Ex.: You wouldn’t see a _____________ living in the Arctic. Teacher Notes – Presented in class on Mon., 12/14/15 to each period: Adaptations, to be successful, are characteristics of a particular plant or animal that develops that helps that organism survive BETTER in their environment, ecosystem, biome. Adaptations are the result of an accidental change in the genetic code of an organism, a change in the DNA. - These changes are called “mutations”. You will learn more about mutations next year in your Genetics unit. - Some mutations result from an environmental source such as radiation that makes the DNA change in some way. (Chernobyl, in Ukraine, was a nuclear power plant that had such a severe meltdown 30 years ago that there is still an exclusion zone around it for any but short-term exposure for humans. -Most mutations, however, result from an accident in copying the DNA strands in a single organism. Mutations can have 1 of 3 results: 1) no change – the organism is not affected in any way by the mutation 2) harmful effect – the mutation can cause the plant or animal to be less successful in surviving in its ecosystem—the result here is that the organism is less likely to survive longer and is less likely to pass its mutated genetic information done through next generations 3) positive effect – the mutation can cause the plant or animal to be MORE successful in surviving in its ecosystem A mutation that results in a benefit allows that organism to survive better in its ecosystem or biome. That organism will more likely survive longer & produce more offspring, thus handing down its mutated genes to offspring. Those offspring will also more likely live longer and produce more offspring. A number of generations later, what was a single happening could be the new normal for the entire population. That is how adaptations occur—not immediately but over generations of organisms. Plant Adaptations in different Biomes (from http://www.mbgnet.net/bioplants/adapt.html) In which biome would you likely see a plant with no leaves to help reduce water loss during photosynthesis? a __________________ biome In which biome would you likely see a plant with smooth bark and smooth or waxy flowers to help speed the run off of H2O? a _________________ _________________ biome In which biome would you likely see trees with leaves that have thin, broad, light-weight leaves to capture a lot of sunlight to make lots of food during the warm weather? A ___________________ ___________________ _________________ biome In which biome would you likely see grasses with extensive (really large) root systems to prevent grazing animals from pulling roots completely out of the ground as they feed on them? A temperate _________________ biome. In which biome would you likely see mostly evergreen trees with dark needles that droop downward to help shed excess snow without breaking branches? A ________________ biome In which biome would you likely see plants less than 12 inches tall, dark in color to help them absorb solar heat, and grow in clumps to help protect themselves from the wind and cold? A _______________ biome. In which aquatic (H2O) biome are you likely to see a plant that is flexible enough to withstand the pressures of moving water? A _______________ biome In which aquatic biome are you likely to see a plant that is very salt tolerant? A ____________ biome. Plant Survival Techniques— 2. Tropisms from Ms. McCaslin’s flipped video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5cgOwVewpPo&feature=youtu.be Plants may not be able to move, but they are able to change how they grow in ______________ to their environment. Growth toward or away from a _______________ is known as a tropism. Types of Tropism What is Stimulus That Triggers the Tropism? Phototropism _____________ Gravitropism (Geotropism) ______________ Thigmotropism ______________ Word Bank for Adaptations: features different cactus desert tropical rainforest temperate deciduous forest taiga tundra freshwater marine Word Bank for Tropisms: response stimulus touch