Environmental Sciences
advertisement

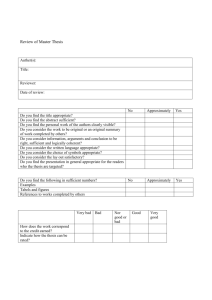
Environmental Science (BS) Intended Program Outcomes Specific Content Knowledge Students will demonstrate: Basic competencies in chemistry, physics, biology and mathematics; awareness of their relevance to environmental processes; and knowledge of their applications to environmental analyses. Understanding of: the interactions between systems, living or non-living, and their surrounding environments; and the influence of such interactions on the functioning of the systems, and on the quality of the environment. A working knowledge of the structure of Earth’s environment, including the composition, essential properties and functioning of its principal components; the cycling of materials between those components; and the causes and processes of environmental change. Ability to analyze and to predict the environmental effects of human societal activities such as: urbanization, transportation, industrial production, agriculture, waste management, generation and utilization of energy, and land development. Up-to-date knowledge of the hazards of adverse environments, and of available remedies, including remediation techniques as well as preventive public policies, and legislation, for environmental management or protection of natural resources. Ability to approximate complex environmental systems with simpler models that are amenable to mathematical, graphical or qualitative analyses. Application of the scientific method in a research project that includes: the generation, analysis and interpretation experimental data; and documentation of the research findings in written reports, in a senior thesis, or in poster or oral presentations. Direct and Indirect Measures Criteria for Success Direct Criteria for Success: 100% of Core Course syllabi will clearly articulate an emphasis on specific course content in Environmental Sciences 100% of graduating seniors will demonstrate content mastery of a specific research area through the research, preparation, presentation, and evaluation of a senior thesis. Indirect Criteria for Success: 80% of ESI students will report that they have attained requisite specific content knowledge upon completion of each of the ESI core courses based on course evaluations and/or a course exit survey. Analysis of focus group data conducted at the end of the freshman, sophomore, Junior, and senior years will report student consensus that proficiency and progression in specific content knowledge were achieved since the prior academic year. Methods of Assessment Direct Assessment Method(s): Syllabus Analysis Curriculum Analysis Final Projects Senior Thesis Indirect Assessment Method(s): Course Evaluations Exit Surveys Focus Groups Intended Program Outcomes Effective Oral and Written Communication Students will demonstrate an ability to: discuss environmental science topics, orally and in writing, without ambiguity or errors in fact, grammar or reasoning; communicate ideas about the environment, with clarity, to audiences with different levels of education or training in environmental science; present, environmental science information in different forms, as necessary: oral, graphical, pictorial, or mathematical; Direct and Indirect Measures Criteria for Success Direct Criteria for Success: 100% of Core Course syllabi will clearly articulate an emphasis on written and/oral communication in Environmental Sciences through inclusion of at least one (1) communication-specific assignment 80% of freshmen enrolled in EVS 2920 (Environmental Forum &Colloquium) will demonstrate effective communication skills through the preparation and presentation of a portfolio 100% of graduating seniors will demonstrate the ability to effectively communicate content in a specific research area through the research, preparation, presentation, and evaluation of a senior thesis 25% graduating seniors will make oral or poster presentations at local or national scientific meetings. 10% of graduating seniors will have manuscripts accepted for publication in peer reviewed journals. Indirect Criteria for Success: 80% of ESI students will report that they have improved their communications skills upon completion of each of the ESI core courses based on a course evaluations and/or a course exit survey. Analysis of focus group data conducted at the end of the freshman, sophomore, junior, and senior years will report student consensus that proficiency and progression in oral and written communication skills were achieved since the prior academic year. Methods of Assessment Direct Assessment Method(s): Syllabus Analysis Curriculum Analysis Portfolio Senior Thesis Professional Presentation Inventory Student Publication Inventory Indirect Assessment Method(s): Course Evaluations Exit Surveys Focus Groups Intended Program Outcomes Critical Thinking Students will demonstrate an ability to: Identify the crucial elements of an environmental problem situation, and to determine their relative importance. Objectively examine all facts, theories and other information they encounter, determine their soundness and assess their credibility; Identify the fallacies, inconsistencies or baseless assumptions in their own arguments, and in the statements of others; Maintain an open mind and to examine alternative viewpoints in drawing conclusions, attributing causes or formulating solutions to environmental problems; Satisfactorily answer questions relating to any aspect of their senior thesis research, including uncertainties in their data and interpretation of their results. Quantitative Reasoning Students will demonstrate the ability to: Solve problems by analyzing the relevant facts and/or numerical data, and applying the correct environmental science principles, logical reasoning, mathematical concepts, and creative imagination Assess real life or hypothetical environmental problem situations, identify the crucial elements therein and determine their relative importance; Select the appropriate environmental science principles and procedures to use in solving problems devise strategies and specific steps for systematic solution of problems; Plan and perform environmental problem analyses, using principles and methods of diverse environmental science courses and those of other disciplines. Direct and Indirect Measures Criteria for Success Direct Criteria for Success: 100% of Core Course syllabi will clearly articulate an intentional emphasis on critical thinking in Environmental Sciences 80% of freshmen enrolled in EVS 2920 (Environmental Forum &Colloquium) will demonstrate critical thinking skills through the preparation and presentation of a portfolio 100% of graduating seniors will demonstrate their critical thinking skills their ability to integrate various crossdisciplinary content and perspectives in the effective preparation and communication, and evaluation of a senior thesis 100% of ESI students will apply critical thinking in the design, execution and reporting of their thesis research projects, as documented by their advisors. Indirect Criteria for Success: 80% of ESI students will report that they have improved their critical thinking skills upon completion of each of the ESI core courses based on course evaluations and/or a course exit survey. 80% of juniors and seniors enrolled in EVS 4643 (Environmental Policy & Risk Management) will demonstrate the ability to think critically through the integration of crossdisciplinary information and worldviews in the presentation of a rubric-graded case study Analysis of focus group data conducted at the end of the freshman, sophomore, Junior, and senior years will report student consensus that their critical thinking skills increased since the prior academic year. Direct Criteria for Success: Analysis of the syllabi in EVR 3028 (Environmental Modeling Principles), EVR 3235 (Atmospheric Processes), EVS 3395 (Contaminant Hydrogeology), and EVR 4140 (Environmental Chemistry with Lab) will clearly articulate an intentional emphasis on quantitative reasoning Juniors and seniors completing EVR 3028 (Environmental Modeling Principles) will score 80% or higher on an exit examination Indirect Criteria for Success: 80% of ESI students will report that they have improved their quantitative reasoning skills upon completion of EVR 3028 (Environmental Modeling Principles), EVR 3235 (Atmospheric Processes), EVS 3395 (Contaminant Methods of Assessment Direct Assessment Method(s): Syllabus Analysis Curriculum Analysis Portfolios Senior Thesis Indirect Assessment Method(s): Course Evaluations Exit Surveys Case Studies Focus Groups Direct Assessment Method(s): Syllabus Analysis Curriculum Analysis Exit Examination Senior Thesis Indirect Assessment Method(s): Course Evaluations Exit Surveys Observation Reports Thesis Committee Report Direct and Indirect Measures Intended Program Outcomes Solve problems by analyzing the relevant information and selectively applying scientific and mathematical principles, logical reasoning, and creative imagination. Criteria for Success Ethical Values Students will demonstrate the ability to : Identify and consider the implications of ethical issues in environmental problems Develop and articulate their own environmental ethic and contributions to that ethic Methods of Assessment Hydrogeology), and EVR 4140 (Environmental Chemistry with Lab) based on a course evaluations and/or a course exit survey. Juniors and seniors completing EVR 3028 (Environmental Modeling Principles) will score 80% or higher on an observation report. 100 % of ESI students will receive satisfactory advisor and thesis committee reports on their problem solving skills. Direct Criteria for Success: Analysis of the syllabi in EVR 3033 (Environmental Regulations), EVR 4032 (Environmental Ethics), and EVS 4643 (Environmental Policy & Risk Management will clearly articulate an intentional emphasis on ethical values 80% of juniors and seniors enrolled in EVR 3033 (Environmental Regulations) will demonstrate consideration of ethical perspectives through the research, preparation and presentation of a final project (regulatory analysis briefing) by achieving a grade of 80% or better on an rubric which includes measures their ability to include ethical considerations in their analysis of environmental policy problems 80% of juniors and seniors enrolled in EVR 4032 (Environmental Ethics)will demonstrate consideration of ethical perspectives through the research, preparation and presentation of a final project by achieving a grade of 80% or better as graded using rubric which measures their ability to include ethical considerations in their analysis of environmental policy problems. Indirect Criteria for Success: 80% of ESI students will report that they have improved their ethical reasoning skills upon completion of each of the ESI core courses based on course evaluation and/or a course exit survey. 80% of juniors and seniors enrolled in EVS 4643 (Environmental Policy & Risk Management) will demonstrate the ability to include ethical considerations through the analysis and integration of cross-disciplinary information and worldviews in the presentation of a rubric-graded case study Analysis of focus group data conducted at the end of the freshman, sophomore, junior, and senior years will report student consensus that their awareness of ethical issues has increased since the prior academic year. Direct Assessment Method(s): Syllabus Analysis Curriculum Analysis Final Projects Indirect Assessment Method(s): Course Evaluations Exit Surveys Case Studies Focus Groups Direct and Indirect Measures Intended Program Outcomes Criteria for Success Methods of Assessment