Name Evolution TEST-Chapter 16 & 17
advertisement

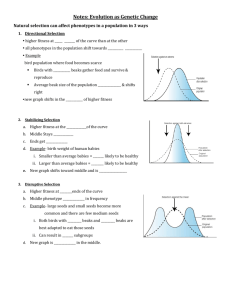
Name ____________________________ Evolution TEST-Chapter 16 & 17-4 (2 Points each) MULTIPLE CHOICE Circle the answer that best completes the statement. This bell-shaped curve of phenotype distribution is typical of ____________ traits. A. single gene traits B. polygenic traits C. founder effect D. vestigial In order for genetic equilibrium to be maintained and the Hardy-Weinberg principle to hold which of the following CAN NOT BE true? A. The population must be small B. There must be random mating C. There can be no movement in or out of the population D. No mutations E. No natural selection When a population reaches genetic equilibrium, _______________________________ A. evolution happens more quickly B. evolution doesn’t happen at all C. genetic drift can be seen D. the conditions for Hardy-Weinberg are NOT met Mutation and gene shuffling are ways to _____________________________________________________ A. introduce genetic variation into a population B. artificially select breeding organisms C. acquire traits through use D. select for the fittest adaptation Darwin believed in the idea that evolution happened slowly over a long period of time called __________ A. punctuated equilibrium B. gradualism C. symbiosis D. mass extinction A situation in which the allele frequencies change as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of individuals is know as the ___________________ A. genetic equilibrium B. founder effect C. Hardy-Weinberg principle D. polygenic evolution Any change in the relative frequency of alleles in a population is called ________________. A. punctuated equilibrium B. mutation C. evolution D. genetic equilibrium Which of the following is most likely to have caused the change in the population shown in the graphs at the left? A. a new predator prefers dark-tan crabs B. a new predator prefers light-tan crabs C. a new beach color makes medium-tan crabs the least visible D. a new beach color makes medium-tan crabs the most visible Adaptive radiation is also known as ____________. A. coevolution B. convergent evolution C. divergent evolution D. punctuated equilibrium * * * * * * * * * * * * * * SHORT ANSWER: Fill in the blanks with an answer that best completes the question NAME 3 CONDITIONS THAT MUST BE MET FOR THE HARDY-WEINBERG PRINCIPLE TO HOLD TRUE: _________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ Tell something that can happen to cause mutations or gene shuffling. __________________________________ * MATCH THE PATTERN OF MACROEVOLUTION WITH ITS DESCRIPTION You can use them more than once! _____ Whales, sharks, and penguins all have streamlined bodies and appendages for moving in water even though they belong in different classes of animals (mammals, birds, fish) A. COEVOLUTION B. ADAPTIVE RADIATION C. MASS EXTINCTION _____ Hummingbirds have a beak just the right length to reach the nectar in a cardinal flower and as they feed their foreheads bump into the pollen structure. Cardinal flowers are red which hummingbirds can see, but bees can’t, and their pollen structure is at just the right height for the hummingbird to pick up pollen as it feeds. D. CONVERGENT EVOLUTON E. PUNCTUATED EQUILIBRIUM ____ Horse evolution shows long stable periods of little evolution interrupted by brief periods of rapid change ____ The Galápagos finches evolved through natural selection from a common ancestor into a wide variety of different looking species with different kinds of beaks ____ At the end of the Cretaceous period an asteroid hit the Earth causing the loss of many species including the dinosaurs ____ Ostriches are native to the savannahs of Africa, while penguins live in the polar regions. Although ostriches and penguins are closely-related, they look very different. ____ Ostriches and giraffes are both native to the savannahs of Africa. They share the same characteristic of a very long neck. ____ In the ocean surrounding Antarctica, there are fish that survive the cold water by using a molecule made of glycoproteins that circulate the blood and keep it from freezing. In the Arctic ocean, fish also have an antifreeze protein but it is completely different from that of the Antarctica fish. _____ Bees don’t see red, but do see yellow, blue, and Ultra-violet light. Thus, bee-pollinated flowers are mostly yellow or blue with UV nectar guides (landing patterns) to guide the bee. They usually have a small, narrow floral tube to fit the tongue-length of that species of bee. MATCH THE GRAPH WITH THE PATTERN OF SELECTION; A B C ___ DIRECTIONAL SELECTION ___ DISRUPTIVE SELECTION ___ STABILIZING SELECTION _____ In which of these is the fitness of individuals at one end of the normal distribution curve higher than that of individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curve _____ In which of these is the fitness of individuals in the middle higher than that of individuals at the extreme ends _____ In which of these is the fitness of individuals at the extreme ends higher than that of individuals in the middle _____ Human babies born smaller than average are likely to be less healthy and less likely to survive. Larger than average babies are likely to have difficulty being born. The fitness of these larger or smaller weight babies is lower than average-sized babies so human babies tend to born of average size. _____ Birds with bigger, thicker beaks can feed more easily on larger, harder seeds. A food shortage causes the supply of small and medium seeds to run low, leaving only larger seeds. Birds with bigger beaks show greater fitness than birds with medium or small beaks. Over time more birds with bigger beaks survive and reproduce. _______ The orange and black pattern of a Monarch butterfly serves as a warning to sharp-eyed birds that the Monarch is poisonous to eat and tastes bad. Individuals with the brightest color pattern were More likely to warn off birds and survive to reproduce than those with a dull or medium color pattern. over time and many generations, the Monarch population became more brightly-colored. _______ In birds, feather color among males is more likely to attract a mate, but also more likely to attract a predator. Over time and many generations, the highest frequency color is for males with medium colors, while males with very dull colors and males with very bright colors became increasingly rare. _______ A population of birds lives in an area where plants with medium sized seeds are wiped out by a fungal infection. Birds with unusually large or small beaks would have higher fitness than those with medium sized beaks. Over time the population splits into two subgroups; one that eats small seeds and one that eats large seeds. MATCH THE VOCAB WORD WITH ITS DEFINITION: _____ Changes in allele frequency in a small population that are due to random chance and don’t follow the laws of probability A. GENETIC EQULIBRIUM B. FOUNDER EFFECT C. GENETIC DRIFT D. HARDY-WEINBERG PRINCIPLE E. GENE POOL F. RELATIVE FREQUENCY G. MUTATION _____ The idea that allele frequency will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change _____ A situation in which the allele frequencies in a population do not change and the population does not evolve _____ The number of times a certain allele occurs in a gene pool compared to the number of times other alleles for that same gene occur _____ A change in the DNA sequence caused by a mistake in DNA replication or exposure to radiation or chemicals _____ All the genes, including all the different alleles, in a population _____ A change in allele frequencies due to the migration of a small subgroup of a population to a new place * * * * * * * * * * * * * * BONUS Give an example of a POLYGENIC TRAIT in humans _______________________________ * Name ____________________________ Evolution TEST-Chapter 16 & 17-4 (2 Points each) MULTIPLE CHOICE Circle the answer that best completes the statement. This bell-shaped curve of phenotype distribution is typical of ____________ traits. A. polygenic traits B. single gene traits C. founder effect D. vestigial In order for genetic equilibrium to be maintained and the Hardy-Weinberg principle to hold which of the following CAN NOT BE true? A. No mutations B. There must be random mating C. There can be no movement in or out of the population D. The population must be small E. No natural selection When a population reaches genetic equilibrium, _______________________________ A. evolution doesn’t happen at all B. evolution happens more quickly C. genetic drift can be seen D. the conditions for Hardy-Weinberg are NOT met Mutation and gene shuffling are ways to _____________________________________________________ A. select for the fittest adaptation B. artificially select breeding organisms C. acquire traits through use D. introduce genetic variation into a population Darwin believed in the idea that evolution happened slowly over a long period of time called __________ A. punctuated equilibrium B. symbiosis C. gradualism D. mass extinction A situation in which the allele frequencies change as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of individuals is know as the ___________________ A. founder effect B. genetic equilibrium C. Hardy-Weinberg principle D. polygenic evolution Any change in the relative frequency of alleles in a population is called ________________. A. punctuated equilibrium B. evolution C. mutation D. genetic equilibrium Which of the following is most likely to have caused the change in the population shown in the graphs at the left? A. a new predator prefers dark-tan crabs B. a new predator prefers light-tan crabs C. a new beach color makes medium-tan crabs the most visible D. a new beach color makes medium-tan crabs the least visible Adaptive radiation is also known as ____________. A. coevolution B. convergent evolution C. punctuated equilibrium D. divergent evolution * * * * * * * * * * * * * * SHORT ANSWER: Fill in the blanks with an answer that best completes the question NAME 3 CONDITIONS THAT MUST BE MET FOR THE HARDY-WEINBERG PRINCIPLE TO HOLD TRUE: _________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ Tell something that can happen to cause mutations or gene shuffling. __________________________________ * MATCH THE PATTERN OF MACROEVOLUTION WITH ITS DESCRIPTION You can use them more than once! _____ Whales, sharks, and penguins all have streamlined bodies and appendages for moving in water even though they belong in different classes of animals (mammals, birds, fish) A. MASS EXTINCTION B. ADAPTIVE RADIATION C. CONVERGENT EVOLUTON _____ Hummingbirds have a beak just the right length to reach the nectar in a cardinal flower and as they feed their foreheads bump into the pollen structure. Cardinal flowers are red which hummingbirds can see, but bees can’t, and their pollen structure is at just the right height for the hummingbird to pick up pollen as it feeds. D. PUNCTUATED EQUILIBRIUM E. COEVOLUTION ____ Horse evolution shows long stable periods of little evolution interrupted by brief periods of rapid change ____ The Galápagos finches evolved through natural selection from a common ancestor into a wide variety of different looking species with different kinds of beaks ____ At the end of the Cretaceous period an asteroid hit the Earth causing the loss of many species including the dinosaurs ____ Ostriches are native to the savannahs of Africa, while penguins live in the polar regions. Although ostriches and penguins are closely-related, they look very different. ____ Ostriches and giraffes are both native to the savannahs of Africa. They share the same characteristic of a very long neck. ____ In the ocean surrounding Antarctica, there are fish that survive the cold water by using a molecule made of glycoproteins that circulate the blood and keep it from freezing. In the Arctic ocean, fish also have an antifreeze protein but it is completely different from that of the Antarctica fish. _____ Bees don’t see red, but do see yellow, blue, and Ultra-violet light. Thus, bee-pollinated flowers are mostly yellow or blue with UV nectar guides (landing patterns) to guide the bee. They usually have a small, narrow floral tube to fit the tongue-length of that species of bee. MATCH THE GRAPH WITH THE PATTERN OF SELECTION; A B C ___ DIRECTIONAL SELECTION ___ DISRUPTIVE SELECTION ___ STABILIZING SELECTION _____ In which of these is the fitness of individuals at one end of the normal distribution curve higher than that of individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curve _____ In which of these is the fitness of individuals in the middle higher than that of individuals at the extreme ends _____ In which of these is the fitness of individuals at the extreme ends higher than that of individuals in the middle _____ Human babies born smaller than average are likely to be less healthy and less likely to survive. Larger than average babies are likely to have difficulty being born. The fitness of these larger or smaller weight babies is lower than average-sized babies so human babies tend to born of average size. _____ Birds with bigger, thicker beaks can feed more easily on larger, harder seeds. A food shortage causes the supply of small and medium seeds to run low, leaving only larger seeds. Birds with bigger beaks show greater fitness than birds with medium or small beaks. Over time more birds with bigger beaks survive and reproduce. _______ The orange and black pattern of a Monarch butterfly serves as a warning to sharp-eyed birds that the Monarch is poisonous to eat and tastes bad. Individuals with the brightest color pattern were More likely to warn off birds and survive to reproduce than those with a dull or medium color pattern. over time and many generations, the Monarch population became more brightly-colored. _______ In birds, feather color among males is more likely to attract a mate, but also more likely to attract a predator. Over time and many generations, the highest frequency color is for males with medium colors, while males with very dull colors and males with very bright colors became increasingly rare. _______ A population of birds lives in an area where plants with medium sized seeds are wiped out by a fungal infection. Birds with unusually large or small beaks would have higher fitness than those with medium sized beaks. Over time the population splits into two subgroups; one that eats small seeds and one that eats large seeds. MATCH THE VOCAB WORD WITH ITS DEFINITION: _____ Changes in allele frequency in a small population that are due to random chance and don’t follow the laws of probability A. MUTATION B. RELATIVE FREQUENCY C. GENE POOL D. HARDY-WEINBERG PRINCIPLE E. GENETIC DRIFT F. FOUNDER EFFECT G. GENETIC EQULIBRIUM _____ The idea that allele frequency will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change _____ A situation in which the allele frequencies in a population do not change and the population does not evolve _____ The number of times a certain allele occurs in a gene pool compared to the number of times other alleles for that same gene occur _____ A change in the DNA sequence caused by a mistake in DNA replication or exposure to radiation or chemicals _____ All the genes, including all the different alleles, in a population _____ A change in allele frequencies due to the migration of a small subgroup of a population to a new place * * * * * * * * * * * * * * BONUS Give an example of a POLYGENIC TRAIT in humans _______________________________ *