MOLECULAR IDENTIFICATION OF NAEGLERIA SPP
advertisement

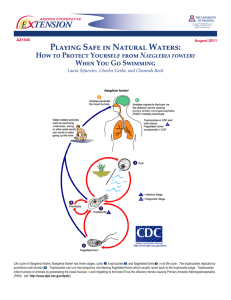
MOLECULAR IDENTIFICATION OF NAEGLERIA SPP. ISOLATED IN MEXICO Fernando Lares Villa1, Eunice Guzmán Fierros1, and Johan F. De Jonckheere2 1. Department of Agronomic and Veterinary Sciences, Technological Institute of Sonora. 5 de febrero 818 Sur, Cd. Obregón, Sonora, 85000, Mexico. flares@itson.mx 2. Scientific Institute of Public Health, B-1050 Brussels, Belgium. Mode: Poster Thematic: Environment and Public Health Key words: amoebae, Naegleria, isolation Introduction. There have been several cases of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) caused by Naegleria fowleri in Mexico. Identifications of the genus Naegleria were mainly on morphological basis but sometimes isoenzymes were used. In Mexico, two high temperature tolerant Naegleria australiensis and Naegleria lovaniensis could be identified by this method amongst the isolates. However, several Naegleria isolates of these studies could not be identified. Strains of N. fowleri have also been isolated from the environment and PAM cases in Mexico (1). Objective. To identify as much different Naegleria species as possible from different sites in Sonora and from other five states of Mexico. Material and Methods. The sampling area covered the states of Sonora, Sinaloa, Jalisco, Michoacán, Estado de México, and Distrito Federal. Water bodies sampled were ponds, rivers, lakes, and a water reservoir. The samples were kept for a week at room temperature, before been processed in triplicate and incubated at 20ºC, 37ºC and 42ºC, respectively. Only isolates that showed typical Naegleria morphology were further investigated. Flagellate formation was tested in distilled water at room temperature. DNA was isolated from pelleted trophozoites using the UNSET method (2). The ITS1, 5.8S and ITS2 rDNA were PCR-amplified using an ITS forward primer and an ITS reverse primer, corresponding to the 3’ end of the SSU rDNA and the 5’ end of the LSU rDNA, respectively (3). The PCR product was sequenced with the amplification primers without cloning with a Beckman CEQ2000 sequencer using the CEQ Dye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Kit. Total ITS1, 5.8S and ITS2 sequences of the Naegleria isolates were aligned to those of published sequences of different Naegleria spp. (4). Results and Discussion. Except one sample from Michoacán all samples yielded amoebae. Two samples, one from Jalisco, one from the Distrito Federal, only yielded isolates at 20ºC incubation. Seven Naegleria spp. Were identified, N. lovaniensis, N. tihangensis, N. americana, N. clarki, N. pagei, N. indonesiensis, and N. byersi. The strain of N. indonesiensis differs by one substitution in the ITS2 sequence from one of the type strain, while the sequences of the N. clarki isolate is totally identical to those of the type strain. One of the two isolates of N. pagei differs a bit in the ITS2 sequence. In strains of the new N. lovaniensis isolates is unique as it is the first time a one bp deletion is observed in the ITS2 of the species. Conclusion. We have attempted to find as much different strains as possible which belong to Naegleria. While only N. fowleri, N. lovaniensis and N. australiensis had been identified in Mexico with certainty before, we are adding, six other Naegleria spp. to the list. This study is only a small survey and more elaborate studies are needed to know the dispersal and biodiversity of Naegleria spp. in Mexico. References. 1. Lares-Villa F., De Jonckheere J. F., Visvesvara G. S., Rechi-Iruretagayena A., Ferreira-Guerrero E., Fernandez-Quintnilla G. and Ruiz-Matus C. 1993. Five cases of primary amoebic encephalitis in Mexically, B.C. México: study of the isolates. J. Clin Microbiol, 31, 685688. 2. Hugo, E. R., Stewart, V. J., Gast, R. J., Byers, T. J. 1992. Purification of the amoeba mtDNA using the UNSET procedure. In Soldo A. T. and Lee J. J. (Ed.) Protocols in protozoolgy, Allen Press, Lawrence, Kansas, p. D-7.1-2. 3. De Jonckheere, J. F. 2004. Molecular definition and the ubiquity of species in the genus Naegleria. Protist 155, 89-103. 4. De Jonckheere, J. F. 1998. Sequence variation in the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer, including 5.8S, of Naegleria spp. Protist 149, 221-228.