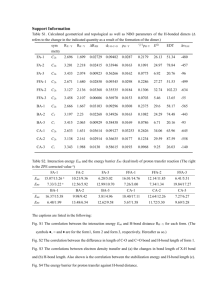
Animal Production and Health
advertisement

Animal Production and Health STUDENTS’ INFORMATION HANDBOOK in the Department of Animal Production and Health Faculty of Agricultural Sciences Ladoke Akintola University of Technology P.M.B. 4000, Ogbomoso, Nigeria. PROF. A. A. Odunsi Dean, Faculty of Agricultural Sciences Dr. I. O. Oladunjoye Head of Department 1 Animal Production and Health FOREWORD The handbook provides general and useful information on the philosophy and objectives of programmes available in the department, admission requirements, course contents, regulations and list of personnel in the departments. The department offers both undergraduate (B.Tech) and Post Graduate (PGD, M. Tech, M.Phil and Ph.D) degrees in different areas of specialization in the field of Animal Sciences. The Departments are endowed with highly qualified and experienced academic staff members. There is a well-equipped laboratory and farm facilities for sound academic pursuit at undergraduate and post graduate levels. Students should note that there is a body called the Nigerian Institute of Animal Science (NIAS) established by Act No 26 of 2007. NIAS regulates the practice of the profession for Animal Scientists. The department of Animal Production and Health and indeed LAUTECH was the first university in Nigeria to present graduates for induction into the Institute in 2009,Our second set were inducted in May 2010. Students are implored to carefully peruse the contents of the handbook and abide by the rules and regulations contained there-in. Best wishes. Dr. I. O. Oladunjoye Head, Department of Animal Production and Health 2 Animal Production and Health TRAIN OF HEADSHIP 1. Professor J. O. Akinola Head of Department, 1991 – 1997 2. Professor G. O. Farinu Ag. Head of Department, 1997 – 2001 Head of Department, 2002-2005 3. Dr. J. A. Akinlade Ag. Head of Department, 2005 – 2007 4. Professor A. A. Odunsi Head of Department. 2007 – 2010 5. Prof. A. A. Akingbade Ag. Head of Department, 2010 – 2011 Head of Department 2011 – 2014 6. Dr. I. O. Oladunnoye Ag. Head of Department, 2014 – till Date 3 Animal Production and Health BRIEF HISTORY OF THE DEPARTMENT The Department of Animal Production and Health started as one of the three foundation Departments in the Faculty of Agricultural Sciences during the 1990/1991 Session. Members of the academic staff then numbered five and composed of a Professor and Head of Department, a Senior Lecturer, two Assistant Lecturers and a Graduate Assistant. The Department also had, at inception, one technologist and five junior members of staff. With reference to admission, 24 students were registered for the Department, although the Department shared in the responsibility for the training of all the fifty 100-level students admitted to read Agriculture. As the department continued in its staff recruitment and development efforts, the academic staff strength had, by 2010 risen to 30 (Professor 4, Associate Professor – 2, Senior Lecturer – 5, Lecturer 1 – 9, Lecturer II – 3, Assistant Lecturer – 5, and Teaching Assistants – 2, Administrative Staff members are three (Senior Confidential Secretary, Principal Data Management Officer and one Senior Office Assistant) and five Technical Staff members (Chief Technologist – 1, Technologist II – 1, Senior Assistant Technologist – 1, Laboratory Assistant – 2) See Table 1. The student’s population has also risen considerably. In 2009/2010, the Department of Animal Production and Health was carved out and like other new departments in the Faculty and start, functioning fully in the 2010/2011 academic session. The various courses taught cover all aspects in the field of Animal Sciences. OUR VISION Serving animal agriculture through dynamic networks of discovery and education. OUR MISSION To promote training in sustainable animal agriculture, set global production and research standards, and produce versatile and globally competitive graduates. UNIVERSITY PHILOSOPHY The Philosophy of the University, which applies to the Faculty of Agricultural Sciences and indeed the Department of Animal Production and Health, is reproduced as follows: The Ladoke Akintola University of Technology should relate to the requirement of dev elopement in a country 4 like Nigeria with its complex social and economic problems. The circumstances of Nigeria call for men and women with knowledge and skill and the capacity to create opportunities for themselves and others. Oyo and Osun States established the University of Technology defining Technology in an all-encompassing sense of the applicative use of various types of knowledge and professional skills for the optional development of human and material resources of its environs. In addition to the orientation of University generally, the Ladoke Akintola University of Technology is geared forwards the social, cultural and technological needs of the country in general and of the Oyo and Osun States in particular. The University combines the ideas of excellence in learning and research with a large dose of practical application in development. Its strength lies in its orientation towards productivity in all aspect of its programmes. In essence, the University is both a centre of academic excellence and a training ground for productive, self-employable, self-sustaining and self-reliant individuals passing through it. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES: (A) The provision of excellent and functional education in the science and technology of animal production and health at the degree and post graduate levels, (B) The provision of continuing education relevant to natural needs for animal production and health and allied experts in forestry, agricultural engineering, farm management and extension. (C) The improvement of animal production and health potentials of local farmers by providing extension services, short term training and opportunities for reciprocal visit and exchange. (D) Conducting appropriate goal oriented research in animal production and health. (E) Collaboration with the states, national and international institutions in the different aspects of research in animal production and health. (F) The Production of animal protein to meet the needs of the University its immediate environment and the Oyo and Osun State through the highly mechanized University farm. (G) Cooperation with other faculties of the University to achieve the set goals and objectives of the University. ADMISSION REQUIREMENTS JME/UME Entry Requirement Five “O” Level credits in Chemistry, Mathematics, Biology/Agric Science, Physics and English Language. Admission is also through Pre-Degree Science Programme of the University (PDS) 5 JAMB Subjects Chemistry, Biology/Agricultural Science and Physics Direct Entry I. Two A level passes or equivalent in Chemistry and one Biology/Botany/Zoology/Agric. Science/ Geography. II. NCE/OND Certificate holders will spend four years, i.e. they will not participate in the 400 level internship years. III. HND certificate holders will be admitted to 200 level and will not participate in the internship programme of 400 level i.e. HND holders will offer courses at 200, 300, and 500 levels. THE COURSE UNIT SYSTEM AND REGULATIONS GOVERNING THE AWARD Description of the Course Unit System The course unit system is an operational system in which the entire programme of course required by a student for a particular degree is packaged into a number of modules each consisting of a prescribed number of units. Usually, one module is to be offered in one semester. Thus, the unit represents one hour of lecture or one hour of tutorials or two or three hours of practical work per week throughout the semester normally of fifteen weeks duration. Mechanisms of the Course Unit System 1. Registration for Course This is normally at the beginning of each semester. Registration guidelines shall be distributed to the students before registration begins. 2. (a) Submission of Registration Form Harmattan Semester The Submission of registration forms for the harmattan semester shall end before matriculation in the case of freshmen and two weeks after the University official date of resumption in the case of returning undergraduates. (b) Rain Semester A maximum of two weeks from commencement shall be allowed for the acceptance of registration forms. 3. Registering/Dropping of Course Registering for a course at the beginning of a semester shall automatically mean registration for the course and the examination shall be carried out. However, a student may drop a course, provide he/she formally applied to do so within five weeks of the commencement of lecturer in the course, and obtain the approval of the Head of Department. 6 4. Penalty for Late Registration Students who failed to submit their registration forms within two weeks after the stipulated period shall pay a late registration fine as prescribed by the university. EXAMINATION AND GRADING SYSTEM 1. Continuous Assessment Assessment of students’ performance shall be continuous. The final examination for each course shall normally be at the end of the semester in which the course is offered. The final grade will be made up of the students’ score in the continuous assessment as well as the end of course examination. The continuous assessment shall carry a maximum mark of 40%. 2. Attendance In order to qualify for examination in a course, a student shall be required to achieve 75% attendance of all the scheduled classes (Lectures, Field Practical and laboratory work) for the courses. 3. Absence From Examination A student who is absent from a course examination without the permission of the Head of department during or at the end of the semester, will receive a grade of F. Permission may be granted only on substantial compassionate or medical grounds as approved by Director University Health Service. 4. Terminologies (a) The Unit of a Course: is defined in relation to the semester duration; this is equivalent to a lecture duration of one hour weekly for one semester of about 15 teaching weeks or three to four hours every week, in the laboratory for one semester of same duration (15 weeks) or the equivalent in workshop or field work time. The size of course shall, as much as possible, be a maximum of four units and its duration shall be one semester except for projects and design courses which may carry more than tree units and may last more than one semester. (b) A core course: is one which must be registered for and passed by a student to get the degree, and is counted towards the classification of his/her degree. (c) An elective course: is either compulsory or optional (d) A compulsory elective: shall be counted towards the classification of students’ degree. For the purpose of determining the class of degree, the CGPA shall cover 100 to 500 level courses for UME students and 200 – 500 level for Direct Entry students. 5. Grading system: A five-point grading system is currently adopted as shown. 7 Mark Range (%) 70-100 60-69 50-59 45-49 40-44 0-39 Letter Grade Grade Point A B C D E F 5 4 3 2 1 0 Interpretation Excellent Very Good Good Satisfactory Poor but passing Failure COMPUTATION OF RESULT The following terminologies and abbreviations are commonly used in the progressive computation of students’ result throughout his/her four/five-year stay in the University. i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. Total Loading Units (T.L.U.): This is the total number of course units carried by student in a particular semester. It is the summation of the load units on all course carried during the semester, for example, a student who is taking 8 courses of 2 units each has a T.L.U. of 8 x 2 = 16 for that semester. Cumulative Load Units (.L.U.): This is the summation of total load units over all the semester from the beginning to date. A student who is prone to repeating courses will finish (if he does not drop out) with a higher C.L.U. than his non-repeating colleagues, and will most likely require a longer time to complete requirements for the award of a degree. Total Credit Point (T.C.P.): This is the sum of the product of course units and rating in each course, for the entire semester. For example, consider a student who took 6 courses of 3 units each, suppose the grade he obtained in the six courses were A, B, C, D, E, and F respectively. The TCP of this student is obtained as (3 x Grade point) = 15 + 12 + 9 + 6 + 3 + 0 = 45.0 Cumulative Grade Point (CGP): This is summation of Total Credit Point over all semesters from the beginning to date. Grade Point Average (GPA) This is the Total Credit Point (TCP) divided by the Total Load Units (TLU), for example, consider the student’s score referred to in section (iii), his T.C.P. is 45.0 and has T.L.U. of 18 (i.e. 6 courses of 3 units each for the semester, his G.P.A is therefore 45/18 – 2.50. The highest possible GPA that can be earned is 5.0 and that is when a student has earned an “A” grade in every course during the semester. The lowest GPAS obtainable is 0.00, signifying an “F” grade all through. Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA): This is not the summation of GPA’s for all semester, rather it is the summation of TCP for all the semester to date divided by the summation of TLU for the said semester. Like the GPA, CGPAs obtainable range from 0.00 to 5.00 in effect, CGPA = CCP/CLU where CCP is Cumulative Credit Point and CLU is the Cumulative Load Unit. 8 Final Assessment and Class of Degree Class First Class 2nd Class Upper Division 2nd Class Lower Division 3rd Class Division Pass vii. viii. ix. CGPA 4.50-5.00 3.50-4.49 2,40-3.44 1.50-2.39 1.00-1.49 Academic Probation: A student whose CGPA at the end of any semester is less than 1.00 shall be placed on academic probation during subsequent semester. Withdrawal from the University: Any student who is on academic probation in a semester and fails to achieve a CGPA at the end of that semester shall be asked to withdraw from the university. Repetition of Courses: Any course failed by a student must be repeated until passed. A student may repeat only those courses in which he has obtained a grade of F. The grade earned for a repeated course shall be recorded and used in the computation of the GPA and CGPA in the usual way. 6. Requirements for the Award of a Degree For the award of a degree, a candidate must satisfactorily complete the minimum number of units prescribed for the degree. He/she must, in addition, complete successfully all compulsory courses as well as the special and five electives for the degree as prescribed. To be eligible for Bachelor of Technology in Animal Production and Health, a student must pass a total of at least 198/220 units. (a) UNIVERSITY REQUIREMENTS 1. Basic Science 2. General Studies 3. Computer Studies 4. FAA 101 5. LIB 101 Sub Total (b) 38 units 12 units 1 unit 2 units 0 unit 53 units FACULTY/DEPARTMENTAL REQUIREMENTS 1. Faculty Courses 2. Departmental Sub Total 132 units 35 units 167 units 9 Examination Offences and Sanctions Student involved in University examination malpractices or violate examination regulations shall be referred for disciplinary action. Listed below are the examination offences and the prescribed corresponding sanctions as recommended by the University Senate. S/N 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. EXAMINATION OFFENCES Involvement in leakages of examination question/marking scheme: (a) Student(s) involved (b) Staff involved Illegal possession of answer script(s) by student: (a) Blank answer script (b) Script containing answers Possession of answer script(s) filled with more than one handwriting (a) Student(s) involved (b) Staff complicity in multiple handwriting malpractices Possession of unauthorized text(s) and illustration(s) of any form that aid examination malpractices Impersonation in any form Student(s) assault or harassment on invigilators/personnel Harassment of co-students for non-cooperation in examination malpractices Falsification of identity, such as names, matriculation number, etc. by a student. Giraffing Exchange of scripts or information during examination Failure to submit examination answer scripts 12. Transfer or receipt examinations 13. Failure to obey invigilator’s instructions during examination Insubordination 14. 15 of information during Failure to appear before the Examination Malpractices Panel after an invitation. 10 SANCTIONS Expulsion Dismissal Suspension for two Semester/Expulsion Expulsion/Dismissal Suspension for four (4) Semesters Expulsion/Dismissal Expulsion Suspension for two (2) Semesters Suspension/Expulsion for four (4) Semesters Suspension for two (2) Semesters Suspension for four (4) Semesters Suspension for two (2) Semesters Suspension for two (2) Semesters for all parties involved Suspension for four (4) Semesters Suspension for four (4) Semesters Suspension for four (4) Semesters after which the student will then face the panel on original offence Code of Conduct for Students in the Departments 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Punctual and regular attendance at lectures, tutorials seminars and practical classes is compulsory. Student who has a genuine reason to be absent from any of the activities listed above must first obtain permission from the lecturer(s) or personnel in charge. Student must consult with their level advisor or such persons that may be knowledgeable about the operation of the course unit system for necessary information. students should learn how to compute their semester GPA as well as CGPA and keep accurate records of their academic performance Students should not disturb the peace and order of the department through noise making, operating musical instruments or drumming Handset must be switched off during lectures, tutorials, seminars, practical classes and examinations, Students should shun fighting and other violent acts Students must treat one another with respect. Students should maintain an honest life Students should work hard, recreate and pray. Students are advices to dress moderately and decently. 11 DEPARTMENT OF ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH RESOURCE PROFILE ACADEMIC STAFF S/NO NAME RANK QUALIFICATION DISCIPLINE AREA OF SPECIALISATION 1. Prof. A. A. Akingbade Professor B.Agric (Ife), M.Sc. (Aberdeen), Ph.D Natal Animal Nutrition Small Ruminant Nutrition (HOD) 2. Prof. J. O. Akinokun Professor B.Sc., M.Sc. (Kansas State), Ph.D. (Ibadan) Breeding and Genetics Breeding and Genetics 3. Prof. J. A. Akinlade Professor B.Sc., (Maiduguri) M.Sc; Ph.D (Ibadan) Ruminant Production and Management Ruminant Production/Croplivestock Interaction and organic agriculture 4. Prof. V. A. Togun Professor 4. Dr. I. O. Oladunjoye Reader Monogastric Nutrition Monogastric Nutrition 5. Dr. (Mrs.) F.G. Sodeinde Senior Lecturer B.Tech. (LAUTECH), M.Sc., Ph.D (Ibadan) Ruminant Production Ruminant Production 6. Dr. Aderinola O. A. Reader B.Agric, M.Agric (FUTA), Ph.D (LAUTECH) Ruminant Production Pasture Utilization 7. Dr. T. A. Adedeji Reader B. Agric, M.Sc, Ph.D (UNAAB) Breeding and Genetics Breeding and Genetics 8. Dr. (Miss) G. O. Tona Senior Lecturer Dairy Science Ruminant Nutritional 9. Dr. (Mrs) C. O. Olaniyi Senior Lecturer B.Sc., Kumasi, M.Sc. Ph.D (Ibadan) B.Agric, M.Sc, Ph.D (Ibadan) Aquaculture Aquaculture 10. Dr. S. A. Ameen Senior Lecturer Veterinary Medicine Vet Physiology B.Sc., M.Sc. Ph.D. (Ibadan) DVM, M.Sc., Ph.D (Ibadan) 12 11. Mr. T. B. Olayeni Lecturer I B. Agric. (Ife). M.Tech. (LAUTECH), 12. Dr. T. A. Rafiu Lecturer I B. Agric (UNAAB) M.Tech,Ph.D (LAUTECH) 13. Dr (Mrs). Binuomote R. T. Lecturer II B.Tech (LAUTECH) M.Agric (UNAAB) 13. Mr. Shittu D. Assistant Lecturer B.Tech (LAUTECH) S/N TECHNICAL STAFF Name Rank 1 Mr.Alabi Wasiu Senior Technologist 2 Mr. S. A. Oyeleye 3 Mr.Kareem I O Technologist II NISLT (ND) NISLT (HND) Assistance NISLT (ND), Technologist NISLT (HND) Monogastric Nutrition Monogastric Nutrition Monogastric Production Monogastric Nutrition and Management Ruminant Production Ruminant Nutrition Animal Nutrition Monogastric Nutrition Qualification Specialization Status Diploma Sci. Lab Tech., ANISLT (Ibadan) Microbiology Cum Viyrology Technologist II Chemistry/Biochemist ry Chemistry/Biochemist ry Laboratory Assistance Senior Laboratory Assistance ADMINISTRATIVE STAFF LIST S/N 1 Name Mrs. R. M. Adeniran 2 Mrs. E. O. Oyerogba 3 Mrs. Adisa Rank/Designation Senior Confidential Secretary Trainee Data Management Officer Clerical Officer 13 CURRICULUM AND COURSE CONTENT A LIST OF ACADEMIC COURSES HARMATTAN SEMESTER 100LEVEL HARMATTAN SEMESTER Course Codes Course Titles Hours T 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 Units BIO 101 BIO 103 CHM 101 CHM 191 FAA 101 GNS 101 LIB 101 MTH 101 PHY 101 PHY 103 L 2 0 3 0 2 2 1 4 3 0 BIO 102 BIO 104 CHM 102 CHM 192 CSE 100 L 2 0 3 0 1 Hours T 1 0 1 0 0 P 0 3 0 3 0 2 2 4 3 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 3 General Biology I Experimental Biology I General Chemistry I Experimental Chemistry I Fundamental of Drawing Use of English I Use of Library Elementary Mathematics I General Physics I Experimental Physics I Sub total RAIN SEMESTER Course Codes Course Titles GNS 102 GNS 110 MTH 102 PHY 102 PHY 104 General Biology II Experimental Biology II General Chemistry II Experimental Chemistry II Introduction to Computer Technology Use of English II History of Settlement Elementary Mathematics II General Physics II Experimental Physics II Sub total Total for 100 Level 14 P 0 3 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 1 4 1 2 2 0 5 4 1 23 Units Units 3 1 4 1 1 2 2 5 4 1 24Units 47 Units 200 LEVEL HARMATTAN SEMESTER Course Codes Course Titles AEC 201 ANB 201 APH 201 ARD 201 CEP 201 CEP 203 CPS 201 CPS 203 CPS 205 APH 203 *GNS 207 *GNS 209 FTP 201 Introduction to Agricultural Economics I Agricultural Chemistry Introduction to Animal Agriculture Introduction to Agricultural Extension Introduction to Environmental Mgt. and Toxicology Introductory Pesticide Science Introductory Crop Taxonomy, Anatomy and Physiology Introductory Soil Science Principle and Practice of Horticulture Introduction to Fisheries and Wildlife Management History of Science Citizenship Farm Practical Training I Sub total 15 L 2 Hours T 0 Units P 0 2 2 2 0 0 3 3 2 2 3 0 0 2 2 0 0 2 1 1 0 0 3 3 1 2 1 1 0 0 3 3 2 2 2 0 0 2 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 9 2 2 0 21units. RAIN SEMESTER Course Codes Course Titles AEC 202 ANB 202 APH 202 ARD 202 CEP 202 Introduction to Agricultural Economics II Animal Anatomy & Physiology Livestock Environment Introduction to Rural Sociology and Rural Development Introduction Insect Science L 2 Hours T 0 Units P 0 2 1 0 3 2 2 2 0 0 0 0 2 2 1 0 0 1 . CEP 204 CPS 202 Introductory Plant Pathology 1 0 3 Principles and Practices of 1 0 3 Crop Husbandry CPS 204 Introductory Agricultural 1 0 0 Meteorology CPS 206 Introduction to Agro-forestry 2 0 0 AES 202 Entrepreneurial Studies in 2 0 0 Agriculture I GNS 206 Family, Marriage system and 2 0 0 kinship FPT 202 Farm Practical Training II 0 0 9 Sub total Total for 200 Level *Students to register for only one GNS Course in Harmattan Semester. 16 2 2 1 2 2 2 0 21units 42units 300 LEVEL HARMATTAN SEMESTER Course Codes AEC 301 AEC 303 Course Titles MEE 301 Statistics and Biometrics Principles of Agricultural Economics I Principles of Animal Production I Animal Health I Introduction to Animal Biotechnology Feeds and Feeding Stuff Introduction to Training Techniques for Agricultural and Rural Development Introductory Pesticides Chemistry Toxicology and Integrated Pest Management Entrepreneurial studies in Agriculture II Introductory Soil Pedology, Classification and Physics Introduction to Computers Aquatic and Terrestrial Ecosystem Agricultural Mechanization FPT 301 Farm Practical Training III APH 301 APH 303 ANB 301 ANB 303 ARD 301 CEP 301 AES 301 CPS 301 CSE 201 APH 305 L 2 2 Hours T 0 0 P 0 0 Units 2 2 2 1 2 0 0 0 0 3 0 2 2 2 2 2 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 0 0 2 2 0 0 2 1 0 3 2 2 1 0 0 0 0 2 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 9 0 Sub Total 23 units RAIN SEMESTER Course Codes Course Titles AEC 302 AEC 304 APH 302 APH 304 ANB 302 ANB 304 ARD 302 CEP 302 CEP 304 CPS 302 CPS 304 Introduction to farm Management Principles of Agricultural Economics II Principles of Animal Production II Pasture Management Basic reproduction and digestive physiology Basic Animal Nutrition Leadership for Agricultural and Rural Development Principle of Crop Protection (Entomology) I Principles of Plant Pathology Introductory to Tropical Crops Agricultural Genetics and Breeding 17 L 3 2 Hours T 0 0 Units P 0 0 3 2 2 0 0 2 2 1 0 0 3 3 2 2 1 2 0 0 3 0 2 2 1 0 3 2 1 2 21 0 0 0 3 0 3 2 1 2 CPS 306 APH 306 FTP 302 Introductory Soil Micro Biology and Chemistry Fish and Wildlife stock Assessment and Population Dynamics Farm practical Training Sub total Total for 300 Level 1 0 3 2 2 0 0 2 0 0 9 400 LEVEL INTERNSHIP/SIWES PROGRAMME HARMATTAN SEMESTER Course Codes Course Titles AEC 401 AEC 403 APH 401 APH 403 ANB 401 ANB 403 ARD 401 ARD 403 CEP 401 CEP 403 CEP 405 CPS 401 CPS 403 CPS 405 Farm Records, Accounting and Management Farm Management /Study Trip Poultry and Feed Mill Management Aquaculture and Fish Farming Poultry and feed mill management Livestock Toxicology and Biotechnology On-Farm Demonstration/Field Trips Extension Applications of Audio Visual in Training Farmers Environmental Monitoring System and Techniques Principles and Practices of Crop Protection Apicultural Management Crop Production Techniques and Nursery Operations Soil Survey and Land Use Planning Mechanization and Workshop Practices Sub total 18 L 0 Hours T 0 0 24 units 47 units 0 0 Units 2 3 9 1 3 0 0 P 6 0 0 0 0 6 6 2 2 0 0 3 1 0 0 3 1 0 0 3 2 0 0 6 1 0 0 6 2 0 0 0 0 3 6 1 2 0 0 3 1 0 0 3 1 24 units RAIN SEMESTER Course Codes AEC 402 AEC 404 APH 402 APH 404 APH 406 ANB 402 ANB 404 ARD 402 CEP 402 CEP 404 CPS 402 CPS 404 Course Titles Seminar in Farm Business Planning and Management Problem Solving Report writing Agricultural Economics Cattle, Sheep and Goat Management Disease and Health Management Processing Techniques and utilization of animal and fish products Special Techniques in animal livestock production Rabbit and Swine Production Report writing and record keeping in Agriculture Experimental Pesticides, Chemistry and Residue Analysis Mushroom Production Technology Processing and Storage of Agricultural Products Soil Testing, Fertilizer Application and Soil Conservation Techniques Sub total Total for 400 Level 19 L 0 Hours T 0 Units P 3 1 0 0 6 2 0 0 6 2 0 0 0 0 6 6 2 2 0 0 6 2 0 0 0 9 3 3 1 6 2 0 0 0 0 0 3 1 0 0 3 1 0 0 6 2 20 units 42 units 500 LEVEL HARMATTAN SEMESTER Course Codes Course Titles APH 501 APH 503 APH 505 APH 507 ANB 501 ANB 503 AEC 505 Poultry, Swine and Rabbit Production Small Ruminant Production and Management Seminar, Animal Experimentation, Feed lot Operation and Research Techniques Applied Animal Breeding and Genetics Monogastric Animal Nutrition Reproductive Physiology and Artificial Insemination Agricultural Development and Policy Total No of Unit L 3 Hours T 0 P 0 3 3 0 0 3 3 0 0 3 2 0 0 2 3 3 0 0 0 0 3 3 2 0 0 2 20 Units 500 LEVEL RAIN SEMESTER Course Codes Course Titles APH 502 APH 504 APH 506 APH 508 APH 510 ANB 502 ANB 506 ANB 510 APH 598 Beef and Dairy Cattle Production Animal Health and Disease Special Topics in Domestication & Production of other Small Animals Animal Products and Processing Range Management Ruminant Animal Nutrition Environmental Physiology and Lactation Aquaculture Project Total No of Unit 20 Units L 3 Hours T 0 P 0 Units 3 2 2 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 0 0 2 2 3 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 3 2 2 0 0 2 4 22 Units COURSE CONTENTS Course codes, title and descriptions 200 Level AEC 201 Introduction to Agricultural Economics I 2-0-0 (2units) Introduction to Agricultural Economics – Scope and method, Price Theory and the Function of the market with particular reference to agriculture. Theory of agricultural production. Cost Analysis with respect to agricultural production. Theory of distribution. AEC202 Introduction to Agricultural Economics II 2-0-0 (2 units) Macro Economics Theory as it relates to agriculture emphasizing the components of agriculture in National Income and in International trade; fiscal and monetary policies as hey affect agriculture, inflation and the rural sector. AES 202 Entrepreneurial Studies in Agriculture 2-0-0 (2 units) Definition of entrepreneurship and entrepreneur, savings and Investment, Professionalism and job creation potentialities, recent economic developmental issues and coping methods. APH 201 Introduction to Animal Agriculture 2-0-0 (2 units) Man and the history and development of animal agriculture. Common breeds of cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, poultry, rabbits and general principle of their husbandry including housing record keeping, feeding, breeding and health management, processing and marketing of animal products. APH 202 Livestock Environment 2-0-0-2 (2 units) Livestock housing. Use of local materials in construction and fabrication of housing facilities. Feeding and management facilities for swine, poultry and rabbits construction of facilities in range and feed lots for ruminant animals. Waste management and disposal in commercial livestock operation waste cycling APH 203 Introduction to Fisheries And Wildlife Management 2-0-0(2unit) Classification, microphology, evolution and lifecycle of principle species of animals involved in fisheries, wildlife and range management. ANB 201 Agricultural Chemistry 1-0-3 (2 units) The composition of living matter, chemistry of meat, milk, eggs, herbicides, insecticides and fumigants. The composition, structure function and metabolism of carbohydrates lipids, proteins, enzymes and nucleic acids, chlorophyll, photosynthesis, respiration, nitrogen metabolism and their biochemical relationships. 21 ANB 202 Animal Anatomy and Physiology. 2-0-3 (3 units) Normal functions of higher animals with particular emphasis on mammalian and avian digestive, reproductive, skeletal, nervous, sensory, circulatory and endocrine system. Anatomy of cattle, sheep goats, pigs, poultry and rabbits. Stress, ecology and adaptation of the various species. ARD 201 Introduction to Agricultural Extension 3-0-0 (3 units) Meaning, definition, problems and importance of Agricultural Extension. History of extension in Nigeria. Farm family extension, gender, status role in farm-family units (e.g. youth, children, men and women in extension). Definition, types and importance of local groups and local leaders in extension programme. History of training and visit extension systems in Nigeria. Meaning and structure of T & V extension. Extension supporting institutions- research-Extension; Farmer-Input Liaison Services (REFILS), Research Institutes, Agricultural. Development Programme (ADP), Credit Institutes; Banks and Credit Corporation; input Supply Companies; Agroallied industries; and non-governmental Organizations (NGO). ARD 202 Introduction to Rural Sociology and Rural Development 2-0-0(2units) Definition of rural development. Basic concepts and principles of rural sociology to an understanding of rural situation. Development of rural community. The nature, problems and prospects of community development in Nigeria. Government involvement in rural development. Local participation in rural development. CEP 201 Introductory Environment Management & Toxicology 1-0-0 (1 units) History and Development of toxicology, General principles of environmental management, Classification of monitoring techniques of the environment, Ecosystem, environment and environmental factors, Elements of environmental pollution. The fate and effects of different toxicant in the environment Future of environmental management and toxicology in developing nations. CEP 202 Introductory Insect Science 1-0-3 (2 units) Morphology and anatomy of insect: physiology; life cycle and variations Systematic and classification. Origin of insect pests situations and ecological basis for insect pests control. Social insects CEP 203 Introductory Pesticide Science 1 – 0 -0 (1 units) Historical development, uses, scope and classification. Mode of action of insecticides herbicides, and fungicides. Fate of selected pesticides in soil, water and soil. Pesticide degradation: Extraction and clean up process. Pheromones; introduction and chemistry of few selected ones. Implication of pesticide, precautions and management. 22 CEP 204 Introductory Plant Pathology 1-0-3 (2 units) Classification, nomenclature, structure, mode of transmission, properties, life cycle, infection process of plant pathogenic fungi, bacteria, virus, mycoplasma-like organism, and nematodes of agricultural importance Methods of controlling plant pathogenic diseases in the tropics Interaction between different pathogens. CPS 201 Introductory Crop Taxonomy, Anatomy and Physiology 1-0-3 (2units) Parts of the crops; basic definition of terms; Cell biology, cell types. Development of cells and tissues. Comparative anatomy of major plant organs. Introduction to plant taxonomy: Characteristics distribution, economic importance and local examples of leguminoseae graminacea, composite, dioscoreacea, rutacease etc. Use of plant keys. Enzymes; meaning, classification and mechanisms; Photosynthesis and translocation; pollination, respiration and energy utilization. Seed dormancy and germination; Seedling development. Water relations, plant mineral requirements and nutrition, Environmental factors in crop growth and development. Plant growth substances and their role in crop production. Concepts of ecosystem: food chain, webs, interaction between plants and animals. Production in ecosystems. Energy flow and nutrient cycling. Dynamic of population and communities. Climatic, biotic and topographic factors affecting distribution of plants in an ecosystem. Ecological groups: hydrophytes, halophytes, epiphytes and mesophytes. CPS 202 Principles and Practices of Crop Husbandry 1-0-3 (2 units) Crop production and its development. The principles, problems, and prospects of crops production. Importance of crop production. Cultural practices: land clearing, land preparation, packing, burning, seeding/planting; weeding, fertilizer application, etc. Cropping systems, tillage practices – conventional, minimum, no tillage. Farm tools and machinery. Agronomic groupings of crop plants; cereals, legumes, roots crops, tuber crops, oil crops, forage crops, fibre crops, sugar crops, etc. Types and characteristics of arthropods, micro-organisms and other pests affecting crops. Insect pests and diseases of arable and permanent crops. Management of pests, diseases and weeds. World, African and Nigerian food production problems and potential solutions. CPS 203 Introductory Soil Science 1-0-3 (2 units) Soils, their origin and formation, soil mineralogy, soil formation factors and processes, soil profile, physical properties of soils-soil texture, soil structure, soil moisture, air and temperature. Soil colloids, soil reactions, soil organic matter and soil organisms. Soil and water conservation nutrient requirements and mineral nutrition of plants. Meaning and scope of soil fertility. Essential nutrient elements and their roles in crop growth and development. Physical, chemical and biological factors affecting nutrients availability and supply. Fertilizers; sources, forms, manufacture, 23 application, methods, rates, ratio, filler, recommendation, timing handling and storage. Soil fertility in the tropics. Avenues of nutrient losses. Ways of improving soil fertility. CPS 204 Introductory Agricultural Meteorology 1-0-0 (1 units) The principles, aims and scope of climatology and biogeography. The elements and control of climate and weather and the dynamics of the earth’s atmosphere. Radiation and heating of the atmospheric systems Condensation and precipitation processes. Seasonal variations in temperature, day length, radiation, rainfall and evapotranspiration. Equipment and maintenance of standard meteorological stations. The tropical climate: relationship between agriculture and climate with reference to crops, livestock, irrigation, pests and diseases. CPS 205 Principles and Practices of Horticulture 1-0-3 (2 Units) Meaning, importance and scope of horticulture. Horticultural production systems. Problems and practices of nursery operations. Green house management. Propagation methods in horticultural plant production. Growth regulators. Important flowers and their propagation methods Landscaping flowers management in residential, commercial and public parks and places. CPS 206 Introduction to Agroforestry 2-0-0 (2 units) Define agro-forestry. Identify the scope and objectives of agro-forestry . state the essential features of an agro-forestry system. List and describe the various land use systems that are related to agro-forestry. Identify the soil and other management problems involved in the system. Outline the economic basis of agro-forestry in Nigeria. Outline the factors that led to the development of the agroforestry concept. FTP 201 Farm Practical Training I 0-0-9 (0 Unit) CTC and vegetable production, training in Apiary, sheep and goats, poultry, feed mill, rabbitry and nursery practices, Special unit and farm supermarket. FTP 202 Farm Practical Training II 0-0-0 (0 Unit) Students to be introduced to practices of arable and permanent crop production, floriculture, horticultural practices, forestry (including seed collection and processing) pasture establishment and management and fisheries. 24 300 LEVEL AEC 301 Statistics and Biometrics 2-0-0 (2 units) The nature of statistical Method; Methods of data collection. Sampling and Presentation; Measure of Association, Regression Analysis, Analysis of variance; Elementary design of experiments. AEC 302 Introduction to Farm Management 3-0-0 (2 units) Nature and scope of farm managements, management functions is traditional agriculture organization of the farm set-up, farm records and accounting, farm business analysis capital budgeting, farm and enterprise budgeting, farm decision and long term investment, linear ;programming (maximization). Analysis of various food crops interpolated with cocoa; reasons for interplant in, density of interplant food crops, costs and returns in agro forestry, Evaluation of alternative technologies in livestock production. AEC 303 Principles of Agricultural Economics 1 2-0-0 (2 units) Theories of production (resource allocation), consumer behaviour and price determination with emphasis on agriculture. AEC 304 Principles of Agricultural Economics II 2-0-0 (2 Units) Theory of income determination with emphasis on the inpact of the product, money and employment markets and macro economic policies on agriculture AES 301 Entrepreneurial studies in Agriculture II 2-0-0 (2units) Business Ideals, critical success factors in enterprise management, objectivity, integrity, discipline, priotisation, provision of excellent and distinctive goods/Services, markeing, Accounting/Finance, Human Resources management. Business conception. Distinction between feasibility and viability studies, simple formant and case study for feasibility studies. business management (planning and organizing) stages/procedure for planning; what is organizing; the seven basic resources to be managed in business; Money, man, materials, method, moment (time), method (technology) and machine. APH 301 Principles of Animal Production I 1-0-3 (2 units) Characteristics of livestock production in Nigeria. Breed of pigs, poultry and rabbits. Production and management practices including housing, feeding, reproduction, disease and health management. Livestock economics processing and marketing of pigs, poultry and rabbits. APH 302 Principles of Animal Production II 2-0-0 (2 units) Characteristics and breeds of ruminant animal (sheep, goats, beef and dairy cattle). Ruminant animal energy and protein feeds and their utilization; vitamins, minerals and water requirements; reproduction, 25 housing, disease and health management processing and marketing of sheep, goats, beef and dairy cattle. APH 303 Animal Health I 1-0-3 (2 units) The causes and economic impact of diseases of livestock; environmental factors in relation to major livestock diseases. Introductory parasitology – helminthes parasites, ectoparasites protozoa and fungi. Introductory bacteriology and virology. APH 304 Pasture Management 2-0-0 (2 units) Pasture in Nigeria agriculture. Classification and botany of grasses and legumes. Nigerian grasslands. The agronomy of sown grass, legume and mixed (grass + legume) pastures. Tree-grass mixtures and management. Grazing systems: forage conservation and utilization. Pasture seed production. APH 305 Aquatic And Terrestrial Ecosystem 1-0-0 (1unit) Physical and chemical properties of both inland and sea water. Hydrology and water cyclo, properties of natural and man-make lake. Thermal properties and stratification. Study and identification of the characteristics flora and fauna of importance in the fresh water and coastal swamps of the tropics. The ecology, utilization and management of aquatic flora and fauna. Control of aquatic weeds in ponds – chemical, biological. APH 306 Fish Stock Assessment And Population Dynamics 2-0-0 (2units) Evaluation of the fisheries resources of selected project areas, fishermen catch per unit effort. Distribution of commercial landings and the relative constancy in the concentration of fishing boats. Evaluation of wildlife resources in selected game reserves and national parks; ground and aerial censoring methods. ANB 301 Introduction to Animal Biotechnology 2-0-0 (Units) Basic concepts, current knowledge in the rapidly growing technologies that underpin human and veterinary medicine, livestock and natural resources management. ANB 302 Basic Reproductive and Digestive Physiology 2-0-0 (Units) Introduction to animal reproduction, reproductive efficiency and profitable livestock production. Sexual development in various farm animal and reproductive systems. Pregnancy and Infertility in animals. Digestive system. Nutrition and reproduction interface in various farm animals. ANB 303 Feeds and Feeding Stuffs 2-0-0 (2 Units Classification, proximate composition and characteristics of feedstuffs. Introductory nutritional and metabolic processes. Nutritional requirements for maintenance and production. Importance of water in nutrition. Feeding 26 standards, ration composition and formulation. Utilization of agroindustrial byproducts. Economics of livestock feeding. ANB 304 Basic Animal Nutrition 1-0-3 (3 Units) Digestion and utilization of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids nucleic acids, vitamins and minerals. Nutrient requirements of various livestock species and symptoms of nutrient deficiencies. Factors affecting nutritional needs of animals. Methods of feed analysis. ARD 301 Introduction to Training Techniques for Agricultural and Rural Development 3-0-0 (2 units) Definition of Training, Training Techniques, Methods of Training, Types of Training. Analysis of Training needs, Identification of training Needs, Techniques for determining training needs. ARD 302 Leadership for Agricultural and Rural Community Development 2-0-0 (2 units) The meaning of leadership. Types of leaders. Leadership in rural communities. Role and functions of rural community. Rural community development. What is Rural community, Problems of Rural Community, Development of Rural Community, The Nature of Local Government. Local Government in Community Development, Extension in Rural Community Development, Nature of Extension. The Extension Agent and Nigeria perspective, Functions of Extension, Problems of Extension. CEP 301 Introductory Pesticides Chemistry, Toxicology and Integrated Pest Management 2- 0 -0 (2 units) Role of pesticides in agriculture, size and scope of pesticide market, economic aspects of pesticides. Groups of pesticides: parathyroid, natural, synthetic. Mode of action, metabolism of parathyroid in insect, in vivo, in vitro. Toxicology of pesticides: occupational exposure, dermal toxicity, eye toxicity, inhalation toxicity and evaluation of oral toxicity. Biochemical background and fate of pesticides. Formulation, handling and storage of pesticides. Quality assessment. Definition, importance and factors determining the use of integrated pest management. CEP 302 Principles of Crop Protection (Entomology) 1-0-3 (2 units) Types of insect damage based on classification with examples, crop enemies including storage pests; bionomics distribution of major insect pests of tropical crops by chemical and non-chemical methods. Hazards of pesticide use for man and the ecosystem. CEP 304 Principles of Plant Pathology 1-0-3 (2 units) Fundamentals of phytopathology, etiology, epidemiology, and control of diseases of economic plants with emphasis on diseases found in West Africa. Techniques for isolation, inoculation, and culturing of plant 27 pathogens. Effects of environmental factors on disease; nature of hostpathogen interaction; effects of plant pathogens on growth, morphology and physiology of plant; Different methods of measuring rate, spread, yield loss, fundamentals of plant resistance to plant diseases CPS 301 Introductory Soil Pedology, Classification and Physics 1-0-3 (2 units) Soil forming rocks and minerals, weathering of rocks and minerals, factors and processes of soil formation, soil morphological characteristics, profile description. Soil profile approaches to soil classification systems Land capability classification: Land suitability classification, fertility capability classification, Bulk density, particle size analysis, soil structure, aggregate stability; porosity, soil water relations, infiltration –pF curve, infiltration rate, and the hydraulic cycle. CPS 302 Introduction to Tropical Crops 2-0-0 (2 units) Climate, economic and social conditions as factors affecting crop distribution and growth. Climate, temperature- minimum, maximum, and optimum. Optimum, water supply: rainfall and water requirement of plants; hydrophytes, mesophytes, xerophytes. Light effect on plant growth and development, Agronomy of majour tropical crops; cereals, including grasses; root and tuber crops, fibre crops, Legumes (grain and forage); horticultural crops, including tree crops (cocoa, oil palm, coconut palm, rubber, coffee and citrus). Current trend in the production of some of these tropical crops. CPS 304 Crop and Animal Breeding and Genetics 2-0-0 (2 units) Cell structure and components, chromosomes structure, number and variations, linkage and crossing over, mutation and genes in population. Multiples alleles, mitosis and meiosis. The origin, organization and transmission of biological variations. Theory of evolution. Fundamental principles of inheritance, Mendelian genetics. Introduction to population and quantitative genetics. Objectives and general principles of crop breeding, their application to self-pollinated, cross pollinated and vegetative propagated crops. General and special methods of selection in in-breeding. Compatibility, male sterility, heterosis, and polyploidy in crop breeding. Mutation breeding. Methods of crop improvement. Development, multiplication and distribution of improved crop varieties. CPS 306 Introductory Soil Microbiology and Chemistry 1-0-3 (2 units) Introduction to soil microbiology; kinds and classes of soil micro organisms. Importance of soil microbes in the tropics. Soil organic matter and factors affecting its transformation in the soil. General decomposition process. Chemical composition of soils; soil colloids, silicate mineral chemistry. Cation and anion exchange phenomena and base saturation. Soil reaction (active and reserved acidity, alkalinity buffering capacity, liming, sodicity, salinity). Biochemistry of nutrient elements in the soil 28 with emphasis on P, N and S cycles. Microbial ecology. The Nitrogen cycle to include the biochemistry and microbiology of nitrification, symbiotic and non-symbiotic N-fixation; the phosphorus cycle, microbial transformation of Sulphur, iron and other mineral elements. CSE 201 Introduction to Computers 2-0-0 (2 Units) History of computers. Functions of computer. Characteristics of a computer. Problem solving, flow charts, algorithms, computer programming statements, symbolic names, arrays, subscript expressions and control statements. Introduction to basic or fortran programming language. Computer applications. MEE 301 Agricultural Mechanization 1-0-0 (1 unit) The importance of Agricultural Engineering and its relation to the agricultural industry and to the engineering profession. Agriculture surveying: types of surveys, leveling, angles and directions. Agriculture mechanization – problems of farm mechanization, primary and secondary tillage, seedbed preparation and planting equipment. Cultivation and pestcontrol equipment. Farm powers. Development of the tractor, internal combustion engine. Engine cycles, efficiencies and operations. Constructional features and coupling of tractor engine. Farm buildings and structures. Farm machinery, equipment and housing. Livestock processing facilities and storage. FPT 301 Farm Practical Training III 0-0-0 (0 Unit) Students shall to be grouped and each group will expected to come up with a commercializable project. Such may include seedling production, broiler/cockerel production etc. FPT 302 Farm Practical Training III 0-0-0 (0 Unit) Students shall to be grouped and each group will expected to come up with a commercializable project. Such may include seedling production, broiler/cockerel production etc. 400 LEVEL AEC 401 Farm Accounting and Management 0-0-6 (2 units) Definition of farm records, types of farm records, e.g. inventory, payroll, production, farm operations, farm receipts, crop and livestock summaries and their importance. Systems of farm accounting – cash analysis. Farm trading and balance sheet statements. Uses of farm records. Capital budgeting and partial budgeting of farm business. AEC 402 Seminar on Farm Business Planning and Managerial Problem Solving 0-0-3 (1 unit) 29 AEC 403 Market and Marketing of Agricultural Produce 0-0-3 (1 unit) Visitation to market place, identification of types of mark and channels, evaluation off market prices of crop and animal produce, trends in market prices, influence of marketing functions on market prices, identification of market segmentation and branding, advertisement and sales promotion, spatial equilibrium, strategies in agricultural marketing, problems of agricultural marketing and suggested solutions. APH 401 Pasture Management 0-0-6 (2 units) Identification and classification of various pastures species. Establishment and management of sown grass, legume and mixed grass + legume pastures. Hay and silage making processes. Weed control, fences and fencing. Fire use and control. APH 402 Cattle, Sheep and Goat Management 0-0-6 (2 units) Animal judging and selection of initial stocks; Synchronization of oestrus; preparation of colostrums, care of dam and her litter, artificial rearing, management practices- topping, fishing, ear notching, tattooing, castration, dehorning, branding, drenching, and record keeping. Dairy cattle management. Health management and housing of different stocks, feeding. APH 403 Aquaculture And Fish Farming 0-0-6 (2 units) Aim and type of aquaculture in Nigeria. Principles of aquatic, living and pond fertilities, food supply, growth rate and food conversion selection of culture e.t.c. APH 404 Livestock Disease and control 0-0-6 (2units) Routine health management procedures in cattle, sheep, goat, pig, rabbit and poultry, vaccination, deworming, debeaking, dehorning, hooftrimming, dipping, spraying, castration, etc. APH 406 Processing Techniques and Utilization of Animal and Fish Products 00-6 (2units) Methods of processing Animal and fish products and their utilization classification and utilization by man, fish transportation techniques, meat and fish quality control and new products development. Abbatior inspection for anti-mortem and post-mortem, Abbatoir and hatchery management. ANB 401 Poultry and Feed Mill Management 0-0-6 (2 Units) Design and types of incubators, collection and handling of hatchable eggs, hatchery operations; transport of chicks, management of day old- chicks species. Housings and equipment management. Procurement of feed ingredients; processing of feed ingredients; ration formulation, weighing, 30 grinding, mixing, handling and distribution of feed, processing and marketing of poultry products. Health management practices. ANB 402 Special Techniques in Mini-Livestock Production 0-0-6(2units) Management breeding, and nutrition production of mini-livestock including grass cutter, japanesse quail, snail and duicker. ANB 403 Livestock toxicology and Biochemistry 0-0-6 (2units) Systemic bacteriology, virology and mycology. Understanding immunology. Principles of detecting conditions caused by organic poisons, inorganic poisons, organophosphophatic compounds, chlorinated hydrocarbons and poisonous plants on animals. Venoms and palliative measures on livestock. ANB 404 Rabbit and Swine production 0-0-6 (2units) Selection of breeding stock, breeding and care of pregnant animals, kindling and care of fryers, construction of hutches, daily routine management practices, record keeping and dsease management. Selection of breeding stock; breeding and care of pregnant animals, farrowing and care of piglets, grower and fatteners. Occasional management practicesearnotching, castration, deworming, control of ecto paracites etc. Marketing of pork, disease control and management. Record keeping. Housing system for pigs. ARD 401 On-Farm Demonstration /Field Trips Extension 0-0-3 (1 unit) Definition and features of On –farm demonstration. Types of and steps in On-farm demonstration. Case studies /example(s) from each type. Data presentation of extension messages. Excursion /field trips. Organization of farmers’ field days. Participation in Agricultural Seminars / workshop and shows. Extension methods. Lectures, demonstrations, field trips, Panel discussion; group discussion. Questions / Answers. ARD 402 Report Writing and Record Keeping in Agriculture 0-0-6 (2 units) Types of report and their importance, technical reports, student’s project, report writing for Seminar/Conferences/Journals. Problems and prospect of record writing and record keeping in agriculture. ARD 403 Applications of Audio Visuals in Training Farmers 0-0-3 (1 unit) The role of audio-visual aids in training. The purpose and use of aids. Visual-aids. Audio aids, Preparation and use of teaching materials and audio visual aids in extension, various types of audio-visual aids. Important audio-visual aids and their use. Preparing audio-visual aids. CEP 401 Environment Monitoring Systems and Techniques 0-0-6 (2 units) Definition and general principles of environmental monitoring, organization of monitoring programmes for site and resources specific 31 strategies. Classification of monitoring techniques and use (physical, chemical biological radioactive) global sources sinks and transport (mass balance) of both man made and natural atmospheric trace components. Ocean - atmosphere interactions, reversible effect of human activities on the global environment e.g. greenhouse effect, climate change, depletion of stratosphere, ozone layer, acid rain. Air pollution meteorology, chemistry and biology. Atmosphere dispersion models. Elements of air pollution control sampling and air monitoring techniques. Mechanism of pollutant interaction with soil and vegetation. General principles of bio testing, aquatic toxicity, types, bio- assays, data analysis and interpretation. CEP 402 Experimental Pesticide Chemistry Residue Analysis. 0-0-6 (2 units) Sampling, planning the sampling programmes, sample containers, collection of various environmental samples – water solid sediments, regetation blood, milk, fish, invertebrates CEP 403 Principles and Practices of Crop Protection 0-0-6 (2 units) Identification of various insect pests, diseases, and weeds, in the field and at storage. Different methods of controlling pests and diseases, Chemical method of controlling pest and diseases Safety measures of pesticide usage. Types of pesticides formulation. Pesticides calculation and Application. Pesticide equipment and calibration. CEP 404 Mushroom Production Technology 0-0-6 (2 units) Importance of mushroom in human diets. Classification of mushroom fungi. Methods of culturing mushroom. Different media for culturing mushroom. Management of mushroom Growth chamber. Harvesting and storage of mushroom. Processing and packing of mushroom Marketing of mushroom. CEP 405 Apicultural Management 0-0-3 (1 unit) Beekeeping as a venture, Importance of Apiary, Factors to be considered in citing an Apiary Types of Hives, Apiary Equipment, Apiarist Responsibility, Harvesting of an apiary, Extraction of Honey from combs, Honey storage and processing, Honey bee wax processing CPS 401 Crop Production Techniques and Nursery Operations 0-0-6 (2 units) Land preparation methods, Nursery operations and field establishment of different crops. Planting techniques, Husbandry practices including fertilization, weed control and harvesting. Propagation methods, cultivation practices for cassava, yam, cocoyam, pest and disease control in cassava, yam, and cocoyam. Pest and disease control in legume crops – cowpea, soybean, etc. Nutrient bases in tissue culture. Environmental control in tissue culture, influence of pathogens on cultured propagates. 32 CPS 402 Processing and Storage of Agricultural Products 0-0-3 (1 unit) Crop handling, processing and utilization. Crop storage methods and storage structure. Storage pests and their control. Environmental factors that affect storage. Methods of crop preservations: their merits and demerits. Features of crop storage in the tropics. CPS 403 Soil Survey and Land Use Planning 0-0-3 (1 unit) Surveying of farmlands and the production of topographic maps of such lands. Local soil classification, land evaluation –land capability, classification and land suitability evaluation. CPS 404 Soil Testing, Fertilizer Application and Soil Conservation techniques 0-0-6 (2 units) Soil testing procedures; role of soil testing in land use planning; Soil testing and efficiency of fertilizer use. Soil testing services. CPS 405 Tillage, Mechanization and Workshop Practices 0-0-3 (1 unit) Selection, operation and maintenance of farm machineries including ploughs, harrows, planting equipment, etc. AEC 403 Market and Marketing of Agricultural Produce 0-0-3 (1 Unit) Visitation to market place, Identification of types of mark and channels, Evaluation of market prices of crop and animal produce. Trends in market prices, Influence of marketing functions on market prices, Identification of market Segmentation and branding, Advertisement and Sales promotion, Spatial equilibrium, Strategies in Agricultural marketing. Problems of agricultural marketing and Suggested Solution. 500 LEVEL APH 501 Poultry, Swine and Rabbit Production 3-0-0 (3 units) Breeds of poultry. Inheritance of qualitative and quantitative traits. Breeding for improvement. Parent and grandparent, production. Physiology of egg production. Incubation, and hatchery management. Care of day old chicks, growers and layers. Ration formulation production, systems. Rural poultry production. Building and equipment. Disease control. Breed of turkeys and guinea fowls. Generics of turkeys and guinea fowls. Rearing and management techniques development of the pig and rabbit industries in Nigeria. Breeds, breeding, feeding, management, building, equipment and health care of pigs and rabbits. Commercial and village level rabbit production in Nigeria and forage for rabbits, slaughter, preservation and marketing of pigs and rabbits. APH 502 Beef and Dairy Cattle Production 3-0-0 (3units) General definition of animal health ad diseases; general signs of ill-health and disease in animals. Some important diseases affecting production in cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, poultry and rabbits with emphasis on etiology, 33 epidemiology, diagnosis, management, control and prevention. Hygiene and its importance in disease prevention and control. Herd/flock record. Prophylaxis vaccines, vaccination, dipping and spraying, stress and animal welfare. APH 503 Small Ruminant Production and Management 3-0-0 (3units) Common breeds of sheep and goat in Nigeria. The management small ruminant animal including housing, feeding, routine management, disease control and marketing. APH 504 Animal Health and diseases 2-0-0 (2units) General definition of animal health ad diseases; general signs of ill-health and disease in animals. Some important diseases affecting production in cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, poultry and rabbits with emphasis on etiology, epidemiology, diagnosis, management, control and prevention. Hygiene and its importance in disease prevention and control. Herd/flock record. Prophylaxis vaccines, vaccination, dipping and spraying, stress and animal welfare. APH 505 Seminar, Animal Experimentation, Field Lots Operation and Research Techniques 3-0-0 (3units) Techniques and procedures in animal Experimentation. Basic statistical designs in animal science research problems Presentation and discussion of various topics in Animal Science, the student is also expected to prepare and participated in all seminars and present a seminar in the final year. Principles of field experimentation animal sciences. Research methodology; experimental layout, field survey; normal distribution and sampling: measurements and data results. APH 506 Special Topics In Domestication And Production of Other Small Animals 2-0-0 (2units) Animal biology of selected animals including glasscutter, snail, duckers Japanese quail etc with emphasis on population dynamics, their ecology and adaptation. General utritional characteristics and possible housing patterns. APH 507 Applied Animal Breeding and Genetics 2-0-0 (2units) Foundation stock in livestock production. Production traits of farm animals. Selection and breeding for improvement of various species of farm animals, performance tests, random sample, meat, and egg tests.. APH 508 Animal Products and Processing 3-0-0 (3 units) Animal products and by products. Classification and utilization by man. Milk quality, milking processing and preservation, egg quality and processing. Meat quality and processing techniques pathogenic and spoilage organism, food borne inspection, law enforcement agencies 34 sanitation, antemotem and postmortem inspection, marketing and labeling of animal products. APH 510 Range Management 3-0-0 (3units) Range productivity in Nigeria. Taxonomy and ecology of range plants. Environment effects of the soil-range plant – animal relationships. Range improvement, management and utilization. APH 598 Research Project ANB 501 Monogastric Animal Nutrition Principles of poultry and nutrient requirements for various classes and species of poultry. Rabbit nutrition and feeding of rabbits. Swine nutrition and nutrient requirements for the various classes of pigs. Elements of human nutrition, dietary allowance, food surveys, food balance sheet and feeding standards. Feed additives. Water in relation to nutrition. Water metabolic computation and ration formulation. Feed evaluation. Feed mixing and manufacturing on large scale. The feed industry. ANB 502 Ruminant Animal Nutrition 2-0-0 (2units) Microbiology of the rumen; physiology of rumen action, metabolic progresses and pathways; non-protein nitrogen utilization; determination of digestion coefficients, balance traits; systems of energy evaluation, scheme for protein values; water in relation to ruminant nutrition and water metabolism; requirement and their inter-relationship, in nutrition; feed additive, ration formulation, nutritional disorder in ruminant animals. ANB 503 Reproductive Physiology and Artificial Insemination 3-0-0 (3units) Anatomy and Histological aspects of reproductive system in male and female farm animals. Endocrinology and reproduction; pregnancy, pubertal development and parturition. Fertility and sterility. Techniques for enhancing reproductive efficiency. Definition of artificial insemination. Historical and role of artificial insemination in livestock improvement. Methods of semen collection, processing, storage and utilization. Environmental physiology and lactation 2-0-0 (2 units) Effects of climate on livestock production, acclimatization and adaptation, physiological basis of adaptation. Heat loss, heat stress and various physiological and behavioural responses to heat stress. Determination of heat stress indices. Modification of microclimate to enhance animal productivity. Management of exotic breeds in tropical environment. Comparative mammary gland anatomy of cattle, sheep, goat, pig and rabbit. Mammary gland development, mammary cytology and lactogenesis, hormonal influence on lactation. Galactopoiesis. Mastitis. ANB 506 0-0-12(4units) 35 ANB 510 Aquaculture 2-0-0 (2units) Principles of aquaculture. Water needs adequacy of drainage area protection. Pond capacity land evaluation and storm run off. Hydrologic estimates of and grouping of soils. Engineering survey. Embarkment and excavated ponds ponds sealing, maintenance and safety. Aquatic ecosystems. Fish pond design, construction and feeding. Basic strategies in effective management of aquatic renewable resources. Applied fielproblems, water quality measurement and use of fishery equipment. Commercial fish culture. AEC 505 Agricultural Development and Policy 2-0-0 (2units) Historical and analytical treatment of government agricultural policies and programmes in Nigeria and developing countries in general. Objectives of economic development: theories and models of economic development: agriculture’s contributions to economic development: appropriate technology in agriculture, economic institutions: population pressure: consumption, savings and capital formation, agricultural policy: case study in Agricultural problems and prospects of agricultural development: Imperatives for Agricultural Development. Interrelationship between agriculture and individual development; Sectoral Planning of Agriculture and its problems: Integrated rural development planning and project implementation. 36 NOW YOU MAY BE WELCOME BACK Wishing you a successful pursuance of post-graduate degree in this enviable department. You are welcome. 37 DEPARTMENT OF ANIMAL PRODUCTION AND HEALTH POSTGRADUATE PROGRAMMES 1. INTRODUCTION After a successful completion of your first degree, you may be welcome back to the department for your post-graduate studies (PGD, M. Tech, M.Phil or Ph.D). The department currently runs a very good post-graduate programme in the areas like: Monogastric Animal Nutrition and Management, Ruminant Animal Nutrition and Management, Animal Biochemistry and Biotechnology, Animal Breeding and Genetics, Animal Physiology, Pasture and Range Management, Animal Products and Processing, Dairy Science and Technology, Aquaculture, 2. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES The programmes of the Department aim at training suitable agricultural graduates in the theory and practice of animal production and health management with the objective of generating the high level and competent manpower needed to achieve self-sufficiency in animal protein supply in Nigeria. 3. DEGREES OFFERED M.Tech, M.Phil and Ph.D. 4. AREAS OF SPECIALISATION (a) Animal Nutrition (APH) (b) Animal Production and Management (APH) (c) Animal Biochemistry and Physiology (ANB) (d) Pasture Agronomy and Utilization (APH) (e) Animal Breeding and Genetics (APH) (f) Reproductive Physiology (ANB) (g) Animal Welfare (APH) (h) Animal Product and Processing (ANB) (i) Animal Biotechnology (ANB) 5. ADMISSION REQUIREMENT General requirements for admission are incorporated in the regulations of the School of Postgraduate Studies. In addition, the candidate must hold a first degree in Animal Science related courses. The candidate must also show evidence of having successfully completed B.Agric./B.Sc./B.Tech. programmes involving the following courses to be allowed to undertake the advanced work required for the M.Tech, M.Phil or Ph.D. degree: (a) Agricultural Biochemistry (b) Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals (c) Fundamentals of Animal Nutrition (d) Basic Soil Science, Plant Nutrition and Crop Physiology (e) Animal Breeding (f) Pasture Agronomy and Range Management (g) Animal Health 38 (h) 6(a) Agricultural Statistics COURSE REQUIREMENTS HOURS APH 601 APH 602 APH 603 APH 604 APH 605 APH 606 APH 607 APH 608 APH 609 APH 610 APH 611 APH 612 APH 613 APH 614 APH 615 APH 616 APH 617 APH 618 APH 619 APH 620 APH 621 6(b) Foodstuffs and Ration Formulation Practical Animal Nutrition Advanced Course on Carbohydrates and Lipids Advanced Course in Proteins, Nucleic acids, Minerals and Vitamins Pasture Agronomy Non-Ruminant Nutrition and Management Ruminant Nutrition and Management Biostatistics I Biostatistics II Quantitative and Population Genetics Reproductive Physiology and Artificial Insemination Genetics of Beef and Dairy Cattle Genetics of Poultry and Small Animals Special Techniques in Animal Breeding Research Animal Products and Processing Animal Behaviour and Environment Digestive Physiology Animal Health I Animal Health II Endocrinology and Immunology Seminar L 2 1 3 3 3 2 3 3 2 3 2 3 3 3 2 3 2 2 3 3 0 T 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ASSESSMENT OF COURSES i. The M. Tech student shall have completed a minimum of 24 units of course work before taking the final oral examination. ii. M.Phil: A student who scored less than 55% on the average at M.Sc/M.Tech level, shall be admitted to M.Phil. Such student shall be required to take and pass course work of not less than 24 units at lower levels as may be recommended by the department. iii. M.Phil/Ph.D.: A student who scored between 55 – 59.5% on the average or the equivalent at Masters level shall be admitted to M.Phil/Ph.D and shall be required to take course work of not less than 4 units at lower levels as may be found necessary by the department. Candidate will be required to sit for a conversion examination not later than one session or two sessions for part time students after registration. Candidate is expected to bating 60% in the examination. iv. Ph.D.: A student who obtains a weighted average mark of at least 60% and above at Masters level shall be admitted directly to Ph.D. Student who is deficient in any relevant course work shall be requested to register for 39 P 3 6 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 3 0 3 3 0 0 6 such as may be determined by the department. The Ph.D. student who has completed the minimum course work requirements and had his research project well under way shall be required to take a preliminary oral examination (Seminar). The preliminary oral examination shall be taken at least 12months before the final oral examination. 6(c) 7. THESIS (a) A Guidance Committee comprising two Staff (minimum) for the M.Tech. Student or three Staff for a M.Phil. or Ph.D. Student shall be set up and headed by the student’s supervisor. (b) For the M.Tech/M.Phil and Ph.D. programmes, the Board of Examiners shall comprise all the members of the Guidance Committee, the Head of Department who shall be the Chief Examiner and at least one External Examiner. (c) A thesis based on analysis of data of a research conducted in the Department (or approved library research) according to standards prescribed by the School of Postgraduate Studies shall be presented by the candidate for M.Tech. The thesis shall include a review of relevant literature, materials and methods, results and discussion of the research work or analysis of data carried out by the candidate. (d) A thesis based on results of original research and on title and research plan approved by the School of Postgraduate Studies shall be presented by the candidate for M.Phil. and Ph.D. The thesis shall be examined by an oral examination on the subject matter of the thesis and overall knowledge of the field of study. 8 RESEARCH The Department has a modest collection of equipment of effectively train students in the determination of the gross chemical composition of biological samples and materials. The University Research Laboratory is equipped with such items as Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer; Gas Chromatograph; High Performance Liquid Chromagraph; UV/Visible Spectrophotometer and IR Spectrophotometer all of which would be valuable in enhancing our teaching and research capabilities. Basic Livestock management facilities (poultry, rabbitry, piggery, fishery and ruminant) exist on the LAUTECH farm and would be available for use by students of the department. 9 COURSE DESCRIPTION APH 701 Feedstuffs and Ration Formulation (3 Units) Feed classification and description of feed nutritive value. Sources and techniques of processing Nigerian feedstuffs. Current methods employed in formulating rations for various classes of farm animals. Economic factors in ration formulation. 40 APH 702 Practical Animal Nutrition (3 Units) Review of the concept of proximate composition. Practicals involving the measurements of gross energy (GE), digestible energy (DE), metabolizable energy (ME), net energy (NE), protein efficiency ration (PER), net protein utilization (NPU), net protein value (NPV) and biological value (BV) in different livestock species using short experimental approaches. APH 703 Advanced Course in Carbohydrates and Lipids (3 Units) Study of the current concepts in carbohydrate and lipid utilization by farm animals. Mechanisms of cellular digestion and nutrients uptake. The estimation and prediction of energy value of feeds. Biosynthesis and transformation of carbohydrates and lipids. APH 704 Advanced Course in Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Minerals and Vitamins (3 Units) New outlook on protein and nucleic acid metabolism. Biosynthesis of amino acids, nucleic acids and their precursors. The role of nucleic acids in protein structure and function. The role of minerals and vitamins in intermediary metabolism. Mode of action and interrelationship of vitamins and minerals in mammalian systems. APH 705 Pasture Agronomy (3 Units) Distribution, classification, identification and utilisation of grasses, legumes, weeds and toxic plants in pastures and range lands. Physiological, developmental and management system in relation to growth, yield, nutritive value and persistence of pasture and rangeland plant species. APH 706 Non-Ruminant Nutrition and Management (3 Units) The life-cycle, nutrition and management of swine, poultry, rabbits, horses and donkeys. Current concepts concerning energy, protein, amino acids, vitamins and essential inorganic elements nutrition and their interrelationships. Scientific application of the concepts to the optimum feeding of poultry and swine. Study of gastro-intestinal manipulation of digesta and utilization of resultant nutrients in poultry and swine. Training of horses and donkeys for work and sports. APH 707 Ruminant Nutrition and Management (3 Units) Discussion on the common breed with emphasis on the adaptation, distribution and productive potential of tropical breeds of beef and dairy cattle, sheep and goats. In-depth study of the nutrition, breeding, management and marketing bases for a successful operation. Anatomy and physiology of the digestive tract and implications for the nutrition 41 requirement of ruminants. The current concepts of nutrition of energy, protein (including bypass protein), vitamins, minerals and their interrelationship for cattle, sheep and goats. Rumen microbiology and their roles in ruminant nutrition. Idiosyncratic feeding of the different classes of rumonants. APH 708 Biostatistics I (3 Units) Review of basic statistical terms, concepts and estimation. Basic requirements for planning, sampling and designs for animal experimentation, tests of hypotheses and inference. Discrete distributions, Chi-square tests, Paired comparisons. Analysis of data in one and two factor experiments, uses of completely randomized, randomisd complete block and Latin-square designs in animal experimentation. Simple regression and correlation analysis. APH 709 Biostatistics II (3 Units) Models of Analysis of Variance: Fixed, random and mixed models. Three factors analysis of variance. Analysis of data with unequal classes. Nested and factorial designs. Estimation and use of variance components; covariance analysis. Multiple regression and correlation analysis. Overview of the anatomy of microcomputers. Introduction to data structures, scalar data, structural data, array, record, files. Introduction to the use of statistical packages. APH 710 Quantitative and Population Genetics (3 Units Genetic properties of populations, changes in gene frequencies of effective population size. Continuous variation, population mean and variance, breeding value, heritability and repeatability estimates, selection methods and systems. Response to selection correlated response, genetics of all or none traits, in-breeding and cross-breeding. Change of population mean and variances; the utilization of heterosis in livestock improvement. APH 711 Reproductive Physiology and Artificial Insemination (3 Units) Comparative physiology of reproduction in higher animals: endocrine functions involved in fertility; research techniques used to enhance reproductive processes; genetic and environmental variations in fertility. Techniques for collection, examination and insemination of gametes and embryos. APH 712 Genetics of Beef and Dairy Cattle (3 Units) The definition of selection goals, estimation of breeding values and genetic change, heritability of dairy characters, dairy herd improvement plans, progeny tests, inheritance of beef characters, their measurement and selection. Performance testing programmes improvement of national herds. 42 APH 713 Genetics of Poultry and Small Animals (3 Units) The inheritance of body characters, the definition of selection goals for pigs, poultry, rabbits, sheep and goats. Selection practice and breeding systems, random sample eggs and meat production tests. Other performance testing programmes, improvements of the national flocks. APH 714 Special Techniques in Animal Breeding Research (3 Units) The utilization of the principles of genetics and breeding in farm animal improvement, experimental techniques in animal breeding research. Methods for estimating genetic and phenotypic parameters for use in animal breeding, models for genetic evaluation of livestock; mixed model methodology, estimation of genetic trend and general problems of analysing large, unbalanced data files. APH 715 Animal Products and Processing (3 Units) Manufacture of dairy products, nature of cleaning and product quality, processing and handling of dairy products in the tropics. Production and storage of egg products, meat and meat products, fish, crustaceans and molluscs; slaughtering, processing, storage and marketing techniques. APH 716 Animal Behaviour and Environment (3 Units) Basis of the behavioural ecology of finding resources; control of avian migration; play behaviour in animals. Environment and animal function and performance; adaptation to the environments; terms and concepts. Hamesthermy, heat balance and heat flow. Determinants and partition of heat exchange, insulation control and integration of thermoregulatory process, stress and animal welfare. APH 717 Digestive Physiology (3 Units) Basic histology; haematological and chemical methods of body fluid analysis, including function tests. Comparative physiology of the digestive systems of livestock species, food seeking, feeding, prehension, mastication, tongue and taste, the stomach, its gastric secretions and motility. The small intestine and dynamics of absorption, immunoglobulina and colostrum; hydrophobic hydrophilic concepts in lipid digestion, the liver, structure and function, the pancreas and enzymes synthesis, microbial fermentation and water electrolyte recovery in the large intestine. APH 718 Animal Health I (3 Units) Microbiology of the rumen, meat, dairy and fermented animal feeds. Classification of protozoan parasites; protozoan parasites of the digestive tract, cardiovascular system and reproductive tract, their economic importance and control. Fungal and bacterial origins of microbial toxins, micro-organisms and viruses in relation to animal diseases. 43 APH 719 Animal Health II (3 Units) Classification and control of helminth parasites, helminth infestations and animal productivity, insects and other arthropod vectors of diseases of man and livestock; those causing direct injury or annoyance to man and livestock. Control programmes, especially of tsetse fly and mosquito. APH 720 Endocrinology and Immunology (3 Units) Anatomy and physiology of the vertebrate endocrine system, properties and biochemical nature of hormones. Mechanisms of hormones action. New dimensions in the biology of immune responses and immunochemical methods. Study of immunological functions of retiouloendothelial tissues; cell-mediated immunity with models of mechanisms of immune specificity and infections. APH 721 Seminar (6 Units) Discussion of current literature; preparation and presentation of scientific report in a field of animal production and health. A MESSAGE TO ALL STUDENTS Beloved students of Animal Production and Health. Make sure you attend all your Lectures. Field and Laboratory Practical including Tutorials regularly, this is because your lecturers may decide to give you unannounced tests or quiz. In case of any problem, please consult with your lecturers, or level advisors or even the Head of department. Dear students, work hard, play hard, keep straight and, above all, fear God and make the best use of your time. Wishing you a successful stay in the department. Dr. I. O. Oladunjoye Ag, Head of Department. 44