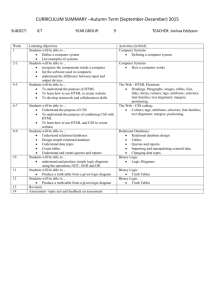
Web Design Notes (01)
advertisement

HKCEE CIT (Mod D)
Web Design
Web Design (10)
More about CSS
Soft copies of this handout and related demo web pages can be found at:
http://www.clsmss.edu.hk/~whlau/10CIT/#webdesign
Opacity
1. Opacity determines the degree of transparency of an element. The value of opacity ranges
from 0.0 (transparent) to 1.0 (opaque). Opacity can be applied to different elements.
Example:
div.photos img { opacity: 0.5 }
div.photos img:hover { opacity: 1.0 }
Ref: http://www.w3.org/TR/css3-color/#transparency
2.
Note:
a) Opacity is defined in CSS3. Some browsers do not support CSS3 and use proprietary
property for opacity. For example, IE uses filter:alpha(opacity=50) (IE
version 7 or below). To avoid writing non-standard CSS, use library ie7-js.
Ref: http://code.google.com/p/ie7-js/
b) Opacity is inherited, i.e., all elements in an element are set to the same opacity unless
otherwise specified.
Table with CSS
3.
CSS properties for table:
Property
border-collapse
border-spacing
caption-side
empty-cells
Values
separate or collapse (ignoring spacing between borders)
Length (in px, em, etc.)
top or bottom
show or hide
Ref: http://www.w3schools.com/css/css_table.asp
4.
It is possible to use CSS properties to replace or override HTML attributes:
<table border="2" cellspacing="5" cellpadding="4"> ...
a)
CSS property border (for table) border attribute of table
b) CSS property border (for td or th) border attribute of table
c) CSS property border-spacing (for table) cellspacing attribute of table
d) CSS property padding (for td or th) cellpadding attribute of table
table.score { border: 2px inset red; border-spacing: 5px }
table.score th { border: 1px solid #f33; padding: 4px }
table.score td { border: 1px solid #f66; padding: 4px }
...
<table class="score"> ...
Supplementary Notes – Web Design (10)
P.1/2
HKCEE CIT (Mod D)
Web Design
Inline VS Block
5. Recall:
a)
A block element is an element that takes up the full width available, and has a line break
before and after it. E.g. p, h1, div, etc.
b) An inline element only takes up as much width as necessary, and does not force line
breaks. E.g. b, strong, span, etc.
6.
To change the behavior of an element, we can change the display property.
a)
We can also hide an element (By using client-side script, such as JavaScript, it is possible
to change the CSS property so that an element can be “turned on/off” later).
b) If display property is set to none, the element is not shown and not taking up any space.
If visibility property is set to hidden, the element still takes up space.
Property
display
visibility
Values
none or inline or block or …
visible or hidden
Ref: http://www.w3schools.com/css/css_display_visibility.asp
Overflow Control by CSS
7. If the content occupies an area larger than the size (as restricted by height and width) of a
box (block element), we can use overflow property to change the overflow behavior:
Property
overflow
Values
visible (overflow content will be displayed outside of the box) or
hidden (overflow content will be hidden) or
scroll (scrollbars are added to the box) or
auto (scrollbars are added to the box only when overflow occurs)
Overflow content
is visible.
Overflow content
is hidden.
Both scrollbars appear,
but the horizontal one
is inactive.
Scrollbar only
appear when
necessary.
Useful Links
CSS Tutorial at W3C School
http://www.w3schools.com/css/
CSS Reference at W3C School
http://www.w3schools.com/CSS/CSS_reference.asp
CSS 2.1 Specfication
http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS21/
Next Topic: Layout by CSS, Table, and/or Frame!
Supplementary Notes – Web Design (10)
P.2/2