Chapter 22 Notes
advertisement
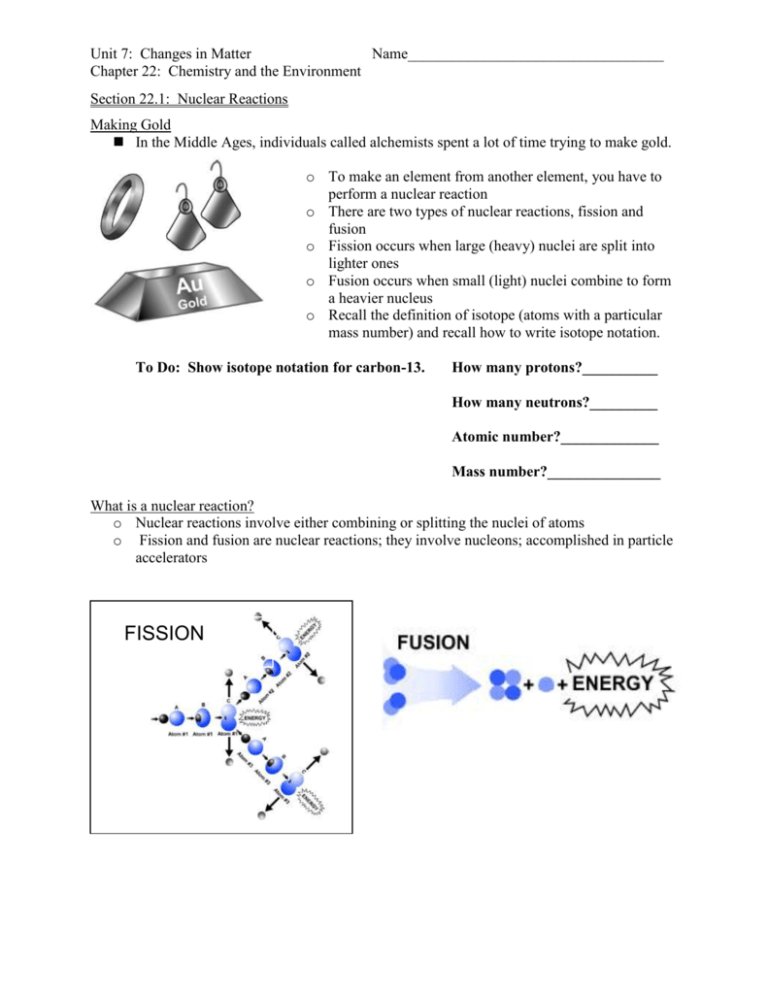
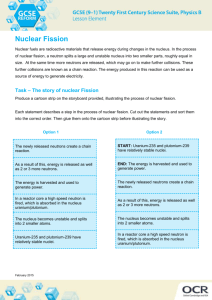
Unit 7: Changes in Matter Name__________________________________ Chapter 22: Chemistry and the Environment Section 22.1: Nuclear Reactions Making Gold In the Middle Ages, individuals called alchemists spent a lot of time trying to make gold. o To make an element from another element, you have to perform a nuclear reaction o There are two types of nuclear reactions, fission and fusion o Fission occurs when large (heavy) nuclei are split into lighter ones o Fusion occurs when small (light) nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus o Recall the definition of isotope (atoms with a particular mass number) and recall how to write isotope notation. To Do: Show isotope notation for carbon-13. How many protons?__________ How many neutrons?_________ Atomic number?_____________ Mass number?_______________ What is a nuclear reaction? o Nuclear reactions involve either combining or splitting the nuclei of atoms o Fission and fusion are nuclear reactions; they involve nucleons; accomplished in particle accelerators FISSION Unit 7: Changes in Matter Name__________________________________ Chapter 22: Chemistry and the Environment To Do: Use in-text context clues or glossary to define the following. nucleon— Unit 7: Changes in Matter Name__________________________________ Chapter 22: Chemistry and the Environment o Chemical reactions involve electrons; accomplished in chemistry labs Comparing Chemical and Nuclear Reactions What part of atom? How is it started? What is the outcome? How much energy? How much energy? Chemical Reactions Outermost electrons Atoms brought close together Chemical bonds form A small amount Burning, eating, cleaning, medicines Nuclear Reactions Protons and neutrons Atoms smashed together # of protons and neutrons change A huge amount The sun, nuclear power plants, x-rays Forces in the Nucleus o Recall the strong nuclear force which holds nuclei together o The strong nuclear forces causes every proton and neutron to be attracted to every other proton and neutron; it is stronger than the electromagnetic force that causes the protons to repel one another o For heavier atoms, more neutrons than protons are needed to hold the nucleus together; the neutrons add attractive force without increasing electromagnetic repulsion What is Radioactivity? o Radioactivity is any process where the nucleus emits particles and energy To Do: Explain the difference between radioactive and radioactive decay. Define each in your answer. Use the glossary or in-text context clues for help. What is a radioactive isotope? What is radiation? o An unstable nucleus will do this until it transforms itself into a stable nucleus o 3 common types of nuclear decay are alpha, beta, and gamma Alpha Decay-an alpha particle, a helium-4 nucleus is released from an unstable nucleus. In alpha decay the number of protons and neutrons both decrease by 2. Unit 7: Changes in Matter Name__________________________________ Chapter 22: Chemistry and the Environment Beta Decay-a neutron splits into a proton and electron; the proton stays behind, but the electron is emitted. In beta decay, the number of protons increases by one, and the number of neutrons decreases by one. Gamma Radiation-the release of high energy, electromagnetic radiation. When gamma radiation is emitted, the numbers of protons and neutrons do not change. To Do:How is an alpha particle depicted?__________________or______________________ How is a beta particle depicted?____________________or______________________ How is a gamma particle depicted?______________________________ To Do: Explain the difference between stable and unstable. Define each in your answer. Use the glossary or in-text context clues for help. Using nuclear reactions for our energy needs o The sun is a multi-step fusion reaction o Nuclear reactors in nuclear power plants use fission Unit 7: Changes in Matter Name__________________________________ Chapter 22: Chemistry and the Environment o Nuclear reactions often involve nuclear waste o Half-life is the length of time it takes for half of the radioactive material to decay to another form o Decay products can also be radioactive, so waste products need to be stored for long periods of time (Yucca Mountain) o U.S. gets about 20% of its energy from nuclear power plants o Fusion to produce energy is being researched Other Uses of Nuclear Reactions o Radioactive isotopes can be used to detect problems in organ systems. o The age of some fossils can be determined using radioisotopes such as carbon-14. o It is possible to figure out the age of objects made from plants or animals that are between 50,000 and a few thousand years old using carbon dating. o Medical tracers, food irradiation, weapons detection, radioactive dating all involve using a detecting nuclear reactions Section 22.2: Carbon Reactions in the Environment We all depend on the carbon reactions performed by plants o Plants convert the sun’s energy into products we use. o Basic Photosynthesis Reaction: Plants use chlorophyll to absorb energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water to glucose and oxygen. Plants use the glucose for energy and release the oxygen back to the environment. o We then make use of the energy and oxygen by-products of photosynthesis. Unit 7: Changes in Matter Name__________________________________ Chapter 22: Chemistry and the Environment We depend on carbon reactions for transportation. o Cars burn fossil fuels for energy. o Use of (the burning of) fossil fuels affects the environment by releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Increased levels of greenhouses gases (or global warming gases) have far-reaching detrimental effects on our environment. Greenhouse or global warming gases include CO2 (carbon dioxide), CH4 (methane), and N2O (nitrous oxide). To Do: A fossil fuel is defined as an organic substance found underground in deposits formed in a previous geologic period and used as a source of energy. Name as many fossil fuels as you can. Are fossil fuels considered to be a renewable energy resource? The Combustion Reaction in Cars o Incomplete combustion of fuel leads to air pollutants being released into our atmosphere. o In addition to CO2, CO (carbon monoxide) is produced, which is poisonous o Nitrous oxides are also produced which lead to acid rain formation. o Ozone and hydrocarbons are also released, which are both harmful to humans. o The catalytic converter, introduced in the 1970’s, reduces hydrocarbon and carbon monoxide emissions by converting these molecules to carbon dioxide and water. Unit 7: Changes in Matter Name__________________________________ Chapter 22: Chemistry and the Environment