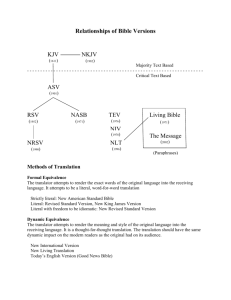
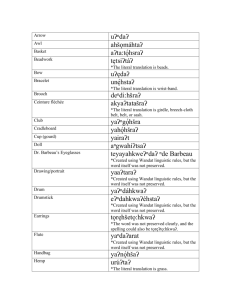
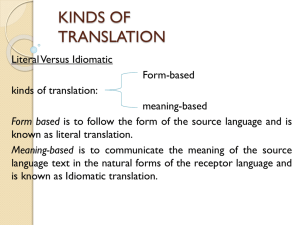
Activity 1 - Literal sense translations
advertisement

Using literal and sense translation to create Knowledge About Language part of the project Knowledge about Language (KAL) and Language Learning Strategies (LLS) as a source of next practice: A case study of Mandarin Chinese This resource provides teaching tips and a form the children complete as part of the activity. You will need a piece of work in the target language that produces different sense and literal translations. In this case a Tang Poem was used. Comments from children: ’I like the literal translation a bit better. The reason behind this is because it paints a image in my head.’ ‘I like the literal translation because it is strange. I chose this one because I love strange things.’ ‘I like the literal translation. You can see what the Chinese say in English.’ ‘I like the literal translation best because it helps me learn Mandarin.’ ‘I like the sense translation because it translates into English and I am English.’ ‘I like the sense translation because it is how we say it.’ ‘The literal translation is the proper one because it is how people from China talk but in English.’ © Crown copyright 2010, Department for Education These materials have been designed to be reproduced for internal circulation, research and teaching or training purposes. They can be reproduced for free provided that this material is acknowledged as Crown copyright, reproduced accurately and not used in a misleading context. Topic: ___________________________________ Question Choice Name: __________________________________ Reason for Choice Which do you like best? What is different between the two? Which translation do you understand best? Which tells you most about China? (Replace with appropriate country /culture) Which do you think is the ‘proper’ translation? © Crown copyright 2010, Department for Education Teaching Notes Choose a piece to translate. Pieces might include a poem, a newspaper article, a few sentences from a book, or a sentence that is constructed in a very different way to the language being learnt Provide the children with both a literal (word for word) and sense translation Read out both to the children and provide them with both written versions and the original Ask them to complete the attached table Produce graphs of numbers of children (or % if appropriate) who like which best, understand which most, tells more about the country of origin and its people and culture, is the proper translation…. Discuss the graphs and the reasons behind the choices the children made as recorded on their sheets. As them whether they liked the activity and why as well as what they learnt from it. © Crown copyright 2010, Department for Education