Heat Exchanger Quiz Solution - ME 375
advertisement

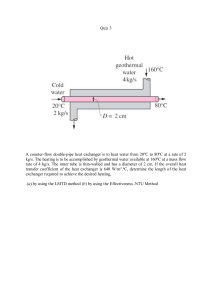
College of Engineering and Computer Science Mechanical Engineering Department Mechanical Engineering 375 Heat Transfer Spring 2007 Number 17629 Instructor: Larry Caretto Solution to Quiz Ten – Heat Exchangers A thin-walled double-pipe parallel-flow heat exchanger is used to heat a chemical whose specific heat is 1800 J/kgoC with hot water (cp = 4180 J/kgoC). The chemical enters at 20oC at a rate of 3 kg/s, while the water enters at 110oC at a rate of 2 kg/s. The heat transfer surface area of the heat exchanger is 7 m2 and the overall heat transfer coefficient is 1200 W/m2oC. Determine the outlet temperatures of the chemical and the water. We compute the maximum heat transfer by first computing the products of mass flow rate times heat capacity and finding which is the smaller. Cc m c c p ,c 3 kg 1800 J 1 W s 5400 W o s kg o C J C C h m h c p ,h 2 kg 4180 J 1 W s 8360 W o s kg o C kJ C So Cmin = Cc = 5400 W/oC. We use this to compute the maximum heat transfer. 5400 W Q max C min Th ,in Tc ,in o 110 o C 20 o C 486,000 W C In order to find the heat transfer we have to find the heat exchanger effectiveness. We do this by computing the NTU and using the charts that give the effectiveness as a function of NTU and the ratio of Cmin/Cmax. 1200 W 7 m2 2 o UAs NTU m C 1.556 5400 W C min o C 5400 W o C min C 0.646 c C max 8360 W o C For this parallel-flow heat exchanger we can find the effectiveness from the first equation in Table 11.4 on page 636 of the text.. 1 e NTU 1c 1 e 1.55610.646 0.56 1 c 1 0.646 The actual heat transfer is the product of the maximum heat transfer and the heat exchanger effectiveness. Q Q max 0.56 4.86 x10 5 W = 2.72x104 W We find the outlet temperatures from the first law energy balance for each stream. Jacaranda (Engineering) 3333 E-mail: lcaretto@csun.edu Mail Code 8348 Phone: 818.677.6448 Fax: 818.677.7062 Quiz ten solutions ME 375, L. S. Caretto, Spring 2007 Tc ,out Tc ,in Th ,out Th ,in Q Cc 20 o C 2.72 x10 4 W 70.4 o C 5400 kW o C Q 2.72 x10 4 W 110 o C 77.4 o C 8360 W Cc o C Page 2