Lesson 1 - Mrs. Parsiola`s Homepage
advertisement

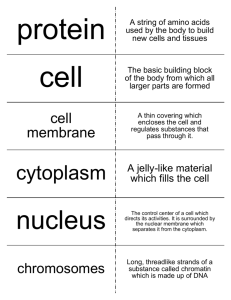
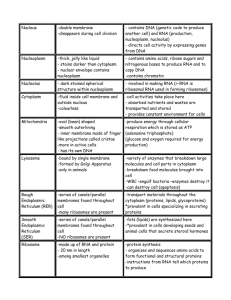
Life Science ____ Period Name: Date: Study quick vocabulary for lessons 1 & 2 Study Lesson Outlines for Lesson 1 & 2 I. Lesson 1: Cells and Life 1. How did scientists’ understanding of cells develop? by using better microscopes and looking for cells in many different places a. Cell Theory i. All living things are made of one or more cells. ii. The cell is the smallest unit of life. iii. All new cells come from preexisting cells. b. Robert Hooke – English scientist who built a microscope, observed a cork oak tree’s bark, and called the honeycomb openings he observed “cells” after the small rooms where monks lived. c. Matthias Schleiden –German scientist who used newer microscopes to observe plant cells d. Theodor Schwann – German scientist who used newer microscopes to observe animal cells e. Schleiden and Schwann realized plant and animal cells had similar features. f. Rudolf Virchow – German doctor who proposed that all cells come from preexisting cells 2. What basic substances make up a cell? a. Main ingredient (70% of cells’ volume) – Water i. fills and surrounds cells and helps maintain homeostasis ii. has a positive and negative end iii. ideal liquid for dissolving my substances iv. positive end attracts negative ions; negative end attracts positive ions b. Macromolecules – substances that forms by joining many small molecules i. Nucleic Acids – long chains of nucleotides together examples: DNA, RNA contains genetic information DNA makes RNA RNA makes proteins ii. Proteins – long chains of amino acids necessary for nearly everything cells do Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Function - Lesson 1&2 (pp. 40-59) Life Science ____ Period Name: Date: helps communication between cells transport substances around inside cell chemical breakdown of substances structural support examples: amylase, keratin iii. Lipids – macromolecules that don’t dissolve in water energy storage protective membrane/barrier communication examples: cholesterol, phospholipids, vitamin A iv. Carbohydrates – one sugar, two sugars, or long chain of sugar molecules energy storage structural support communication examples: starches (bread, pasta), sugar (fruits), cellulose (cell walls of plants for support) II. Lesson 2: The Cell 3. How are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells similar and how are they different? PROKARYOTES genetic material not surrounded by membrane don’t have many cell parts are bacteria EUKARYOTES have a cell membrane some have a cell wall have cytoplasm have a cytoskeleton genetic material surrounded by membrane contain membranesurrounded organelles make up plants, animals, fungi, and protists Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Function - Lesson 1&2 (pp. 40-59) Life Science ____ Period Name: Date: 4. What do the structures in a cell do? a. Cell membrane – flexible structure that protects the inside of the cell from the environment outside the cell (animal cell #2, plant cell #9) b. Cell wall – stiff structure that protects a cell from attack by harmful organisms (plant cell #2) c. Cell appendages – often used for movement, ex. cilia (small hairlike structures) and flagellum (long whiplike tail) d. Cytoplasm – fluid inside the cell that contains salts and other molecules (animal cell #8, plant cell #10) e. Cytoskeleton – threadlike proteins that form a framework inside the cell f. Nucleus – part of a eukaryotic cell that directs all cell activity and contains genetic material (animal cell #6, plant cell #8) g. Ribosomes – organelles that are involved in the production of proteins h. Endoplasmic reticulum – folded membranes that spread from the nucleus throughout the cytoplasm (animal cell #3, plant cell #3) i. rough ER – ribosomes are on the surface of the ER and site for protein production ii. smooth ER – doesn’t have ribosomes on the surface and makes lipids; helps remove harmful substance from a cell i. Mitochondria – the site of energy processing (animal cell #1, plant cell #5) j. Chloroplasts – process light energy, water and carbon dioxide to make glucose and release oxygen (plant cell #4) Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Function - Lesson 1&2 (pp. 40-59) Life Science ____ Period Name: Date: k. Golgi apparatus – prepares proteins for specific jobs (animal cell #4, plant cell #7) l. Vesicles – transport substances to other areas of a cell (animal cell #5, plant cell #6) m. Vacuoles – store food, water, and waste material (animal cell #7, plant cell #1) 6. 8. 8 9 4. Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Function - Lesson 1&2 (pp. 40-59) 10