Cell Structures and Functions
advertisement

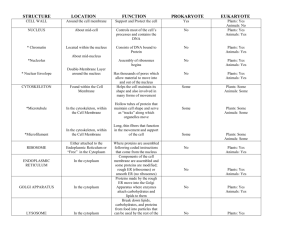
Nucleus -double membrane -disappears during cell division - contains DNA (genetic code to produce another cell) and RNA (production, nucleoplasm, nucleolus) - directs cell activity by expressing genes from DNA Nucleoplasm -thick, jelly like liquid - stains darker than cytoplasm - nuclear envelope contains nucleoplasm - contains amino acids, ribose sugars and nitrogenous bases to produce RNA and to copy DNA -contains chromatin Nucleolus - dark stained spherical structure within nucleoplasm - involved in making RNA (r-RNA is ribosomal RNA used in forming ribosomes) Cytoplasm -fluid inside cell membrane and outside nucleus -colourless -cell activities take place here - absorbed nutrients and wastes are transported and stored - provides constant environment for cells Mitochondria -oval (bean) shaped -smooth outerlining - inner membrane made of finger like projections called cristae -more in active cells - has its own DNA -produce energy through cellular respiration which is stored as ATP (adenosine triphosphate) (glucose and oxygen required for energy production) Lysosome -bound by single membrane -formed by Golgi Apparatus -only in animals -variety of enzymes that breakdown large molecules and cell parts in cytoplasm -breakdown food molecules brought into cell -WBC –engulf bacteria –enzymes destroy it -can destroy cell (apoptosis) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) -series of canals/parallel membranes found throughout cell -many ribosomes are present -transport materials throughout the cytoplasm (proteins, lipids, glycoproteins) *prevalent in cells specializing in secreting proteins Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) -series of canals/parallel membranes found throughout cell -NO ribosomes are present -fats (lipids) are synthesized here -*prevalent in cells developing seeds and animal cells that secrete steroid hormones Ribosome -made up of RNA and protein - 20 nm in length -among smallest organelles -protein synthesis - organizes and sequences amino acids to form functional and structural proteins -instructions from RNA tell which proteins to produce Vacuole -clear, fluid – filled membrane bound sac (most prominent in plant cells) -storage areas for water, food, minerals and wastes -contents exert pressure to keep plant cell walls rigid (turgor pressure) Golgi Apparatus -like a stack of flattened balloons – membranous sac piled on top of each other -stores, modifies and packages proteins from RER with fats -membrane-bound structures pinch off at end to produce small protein-filled sacs called vesicles which are used for transport (eg. hormones, neurotransmitters) Plastids -membrane-bound organelle *found in plants only -chemical factories and storehouses for food and colour pigment Chloroplasts -plastid which contains chlorophyll Has its own DNA and ribosomes *found in plants only -photosynthesis occurs here (carbon dioxide + water sugar and oxygen) Cell Wall -made of cellulose *found in plants only -protection, support -primary (single cell wall) -secondary (double cell wall) – extra protection and support Cell Membrane -protein, double layer of lipid -receptor site -holds content of cell in place -regulates movement in and out of cell -entry of materials affect cell activity -SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE *more info to follow Liposomes -double layered spheres -size of a cell -made of lipids -like cell membrane, fuse with cell membrane and deliver contents to cell’s interior -used for drug delivery (eg. cancer fighting drugs to target tumours) Nuclear Membrane -membrane found around the nucleus -controls what enters and exits the nucleus ie. RNA, copies of DNA -dissolves during mitosis and meiosis (cell division) Flagella (singular: flagellum) -whip like protein -may have one or many -found in animal cells -eg. sperm cells -help cell move – uses contractile proteins to spin in a corkscrew motion (propeller from boat) Cilia (singular: cilium) -short, hair like structures -uses contractile proteins for movement in a “coordinated” fashion -used for –locomotion -to create fluid currents to move materials (eg. lung cells) Microfilaments -threadlike (pipelike) structures -made of protein -found in cytoplasm -provide shape and movement for cells (muscle contraction, gliding, cytokinesis) Microtubules -tubelike structures -made or proteins -found in spindle fibres, cilia and flagella -transport materials throughout cytoplasm Chromatin -DNA molecules and associated proteins (chromosomes are long and thin) -unravelled DNA available to be copied into RNA Centromere -found between sister chromatids -structure that holds chromatids together Sister chromatids -a chromosome and its duplicate attached to one another by a centromere -remain attached until separated during mitosis Centrioles -formed by a bundle of nine microtubules -occur in pairs at right angles to one another -found only in animal cells -active during cell division -help to redistribute chromosomes (use spindle fibres)