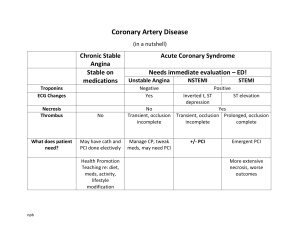
impact of risk factors on vascular complications
advertisement

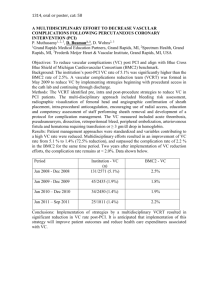
1550, either, cat. 58 IMPACT OF RISK FACTORS ON VASCULAR COMPLICATIONS AFTER PRECUTANEOUS CORONARY INTERVENTIONS IN SHAHEED RAJAEE HEART CENTER A.A. Yusefi1, H. Farshidi2, M. Madani1, F. Shakeryan1, H.R. Sanati1, A. Firoozi1, N. Salehi1 1 Iran University, Tehran, 2Hormozgan University, Bandar Abbass, Hormozgan, Iran, Introduction: Vascular complications (VC) are of the most common complications seen in patients undergone cardiac interventional procedures. Incidence of VC in PCIs have been reported from 2.6% to 6.6%. This study was designed to determine correlations of important risk factors with VC. Method: Demographic data, CAD risk factors, sheath size, serum creatinine level, LV function and VC were recorded. Hemostasis was maintained with manual compression. Radial access (RA) was used as an alternative route. for statistical analysis SPSS 18 were used and P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results: Of 2097 cases 553 were female Average age was 57 years, mean systolic BP 132 mmHg, mean weight 75kg and mean BMI was 26.7. A total of 21 VC were seen in 19 patients (1%). Most common complication was hematoma (0.5%) and the second common complication was pseudoaneurysma (0.2%). Retroperitoneal bleeding, blood transfusion A-V Fistula were seen in 0.1%. In 56 patients (2.7%) PCI was done via radial access (RA) without any VC. No correlation was seen between VC and sheath size, creatinine level, LV function, number of involved coronary arteries and presentation of the patient. Gender, weight, use of GP IIb/IIIa and hypertension were significantly correlated with VC. Conclusion: Predicting the risk of VC is feasible post PCI. Prominent risk factors of VC were female sex, lower weight, GP IIb/IIIa use and hypertension. RA for PCI seems to be a safe alternative method.