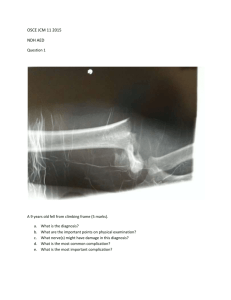
Work Program 1 - TMA Department Sites
advertisement

Ministry of Higher and Secondary Special Education MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE REPUBLIC OF UZBEKISTAN TASHKENT MEDICAL ACADEMY DEPARTMENT OF CHILDREN AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE "APPROVED" Vice Rector for Academic Affairs prof. .......................... Teshaev OR "_____" ____________ 2014 WORKER TRAINING PROGRAM Masters students For the Master's degree 5A510107 - Infectious Disease (Children's infectious diseases) DIRECTIONS ON THE BASIS OF UNDERGRADUATE 5720200 - pediatric case Total hours - 3238 Practical exercises - 1058 Seminars - 1688 Research and teaching activities - 240 Master's thesis - 252 Abbreviations and definitions PDMO - graduate medical education (Master's degree) The sponsoring institution - medical educational institution, or organization, which carries full responsibility for the success of the program PDMO. Participating institutions - medical educational institution, or organization that provides the acquisition of special knowledge, skills and practical skills in the program PDMO. Faculty - the institute, involved in the implementation of the program PDMO as moderators of training seminars or coaches individual rotations. The program - accredited educational complex, comprising a phased acquisition of knowledge and skills in the specialty within the requirements of certification and licensing. Graduate student - a person enrolled in an accredited program PDMO Senior graduate student - enrolled in the program of the closing year PDMO with a greater proportion of independent work and greater clinical responsibility. Program Director - Officer sponsoring institution, bearing full responsibility for the implementation of the program PDMO. Moderator - Officer sponsoring or participating institution responsible for implementing the thematic seminar. Supervisor - Officer sponsoring or participating institution responsible for implementing the thematic rotation. Rotation - thematic cycle, providing for the purchase by a resident of the necessary practical skills. ABBREVIATIONS HS - viral hepatitis HBV - hepatitis B. HAV - hepatitis A HBV, hepatitis B virus NVsAq - HBV surface antigen. NVeAq-intermediate HBV antigen. NVcAq - HBV core antigen. Anti-HBs antibodies k HBsAq PCR - polymerase chain reaction. SARS - acute respiratory viral infection. HBV - chronic viral hepatitis B. CPU - cirrhosis of the liver. ARF - acute liver failure. 2 INTRODUCTION Infectious diseases of childhood are the most important section of Pediatrics and is a serious medical and social problem for the child population. In modern conditions occur, many infectious diseases are more common in children. In this regard, the growing need for doctors - a pediatrician in infectious diseases, owing in full at the appropriate level skills combined treatment of infectious diseases in children, with different combinations and complications that adds value to professionals at this level. In addition, masters - pediatricians, infectious disease, being highly skilled professionals will be able to carry out not only curative and preventive work, but also the administrative and managerial, medical and social, organizational and methodological work in health care. In view of the above, the master - a pediatric infectious disease specialist may be in demand in today's conditions in full. According to the curriculum, a master's degree in "Children's infectious diseases" provides 3year full-time education. On the theoretical lessons given to them in 1606 from 1050 hours of classes and 556 hours of independent work on a master's practice - 3338 hours on the teaching and research work 378 hours to prepare their master's research project, 378 hours. Maximum load of classroom practice and master volume set at 54 hours per week. Classes are held at the Department of Infectious and pediatric infectious diseases at the basic institutions of the department, as well as medical research institutes and medical centers in the Republic of Uzbekistan. Theoretical training graduate students in the specialty is held in the form of seminars in all areas of pediatric infectious diseases and includes 15 thematic blocks. Part of those taken out of regular classes for self-study. Practical training (Master's practice) is carried out in specialized diagnostic and infectious wards of hospitals and hospital pediatric infectious diseases through self TashMI Supervision of patients and interpretation of the results of additional studies of medical diagnostic procedures, in accordance with the list of skills in each rotation. Control study carried out by checking the daily reports of work, with the proportion of self involve graduate students, as well as of the PC and IC. Practical training (Master's practice) is carried out under the guidance of supervisors in specialized infectious wards, as well as intensive care units and emergency assistance in the auxiliary diagnostic departments (offices) of a hospital, clinic consultation, with the implementation of the necessary therapeutic and diagnostic procedures and treatments, filling medical records, part of the practical skills mastered during duty. 1. The purpose of learning. The purpose of training: training of highly qualified specialists with the skills of diagnosis, treatment and prevention of infectious diseases in children, as well as their complications with the use of modern medical technology. 1.2. Learning objectives: • Develop up to date knowledge on the epidemiology, etiology, pathogenesis and clinical infectious diseases in children • To develop knowledge on the use of modern techniques in the diagnosis of infectious diseases in children. • develop skills of self-determination of the required volume and a set of diagnostic and treatment interventions for patients with infectious diseases of childhood; • learn to take appropriate and adequate therapeutic and diagnostic procedures and manipulation of children with infectious pathology in a hospital; • develop the ability to interpret the results of modern laboratory and instrumental studies to children with infectious pathology; 3 • develop the skills of high quality care to date in case of emergency in children with infectious pathology • develop skills in intensive care for children with infectious pathology in a hospital; • develop the knowledge to carry out the complex rehabilitation of convalescents of infectious diseases; • develop the ability to implement preventive measures to reduce the incidence of the most common infectious diseases in children and the prevention of its complications. 1.3. The requirements for knowledge, skills and experience on the subject matter. Master in "childhood infectious diseases" shall: have an idea - About contemporary issues and main directions of development of medicine; - New technologies in the diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases in children. Know and be able to use - Epidemiological information, the impact of etiologic factors and risk factors on the course and outcome of disease - The modern theory of the pathogenesis, classification, - Modern methods of diagnosis, including early - The treatment regimen at various stages, primary and secondary prevention of infectious diseases in children; - Orders and regulations of the health authorities of the Republic of Uzbekistan on the pediatric service. have the skills to: - Questioning highly infectious diseases of children from their parents and caregivers.; - Perform a perfect physical examination of children with infectious diseases; - Determine the amount of necessary treatment and diagnostic measures of children with infectious diseases; - Independent of some medical and diagnostic procedures for sick children with infectious pathology; - Interpretation of the results of additional research: laboratory (bacteriological, serological, Allergic, bakteroskopicheskoy), morphological, functional, endoscopic, radiological X-ray, immunological; - Conduct a comprehensive self-individualized treatment of children suffering from infectious diseases and certain complications in a clinic, the profile of infectious hospital, resuscitation and intensive care; - Holding some resuscitation and assistance in case of emergency at the clinic of infectious diseases; - Development and implementation of rehabilitation of convalescents of infectious diseases; - Advising patients non-infectious profile; - Maintenance of medical health records. 1.4. Requirements for seminars. - Note-taking-developed literature. - Banquet of the literature to prepare for seminars. - Preparation of reports on clinical conference on a separate issue (s) of classes. - Drafting tables, charts, algorithms on the key issues of seminars. - Decision of the complicated case studies on the topic of seminars. - Decision sophisticated test tasks on seminars. - Analysis of clinical cases on the subject of seminars. 1.5. Requirements for the Master's practice: • self-examination of infectious patients in the emergency department of the hospital and in the clinic • self-examination and supervision of patients in specialized departments of infectious • planning and implementation of a set of necessary medical, diagnostic and rehabilitation 4 activities with infectious diseases • participation in the clinical, pathological conferences, clinical analysis and diagnostic critically ill patients • analysis of the results of additional studies (laboratory analyzes, conclusions ultrasound, radiographs, etc.) • analysis of the "theme" of patients • participation in rounds held senior lecturers, professors and specialist consultants • Filling out-cards, medical records, statistics, coupons and other medical medical documentation • preparation of daily reports showing the proportion of self involve graduate students 1.6.Perechen academic disciplines and their partitions needed for the study of the academic discipline. Education master's degree in "childhood infectious diseases" is based on the knowledge and skills acquired on the therapeutic and clinical departments during training at the medical school training program for general practitioners and includes the following: 1. normal anatomy (structure of the internal organs of the child's body) 2. normal physiology (functional physiology of the internal organs of the body of child) 3. Pathological Anatomy and Histology (macro-and microscopic disease substrate for treatment of internal organs the child's body)). 4. Pathological physiology (mechanisms of the disease, the adaptive-compensatory reactions and patterns of homeostasis of the organism in infectious diseases). 5. Biochemistry (basic biochemical reactions that underlie the development of infectious diseases in complex adaptively compensatory mechanisms child's body). 6. Microbiology (microbiological and biochemical characteristics of etiological agents, methods for their identification and selection techniques optimal antimicrobial treatment of infectious diseases in children). 7. Propedeutics infectious diseases (medical questioning, physical examination methods, clinical syndromes, laboratory and instrumental methods of diagnosis). 8. Infectious diseases (etiology, pathogenesis, classification, clinical manifestations, complications, diagnosis). Differential diagnosis, comprehensive treatment, rehabilitation and prevention of their children. 9. Surgical diseases in children (complications of internal diseases requiring emergency or elective surgical treatment, clinical, laboratory and instrumental criteria for the most common surgical diseases). 10. Anesthesiology and Intensive Care emergencies in children (emergency care and resuscitation in diseases of childhood.) 11. Phthisiology (visceral tuberculosis in children, clinical, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic criteria). 12. Pediatric endocrinology (the diagnostic criteria and principles of treatment of the most common endocrine disease, damage internal organs with endocrine diseases). 13. Clinical Allergy (common clinical manifestations of allergic diseases and syndromes, diagnostic criteria damage internal organs in allergic diseases, emergency care). 14. Ophthalmology (pathology of vision in children with infectious diseases). 15. Dermatovenereology (loss of internal organs with skin diseases of childhood, the diagnostic criteria). 16. Hematology in children (diseases of the internal organs, accompanied by anemia, Leukemia diagnostic criteria, treatment guidelines). 17. Child Neurology (clinical manifestations, neurological symptoms and syndromes of infectious diseases, emergency conditions in neurology). 18. Children's Otolaryngology (ENT organs, accompanied by general symptoms, loss of upper respiratory tract infectious diseases). 19. Pediatric Dentistry (individual oral disease in the clinic of infectious diseases). 20. Clinical pharmacology (mechanism of action, pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, drug 5 interactions). 1.7. Checks 1. Monitoring of the discipline on classes in the form of an interview and test solutions, 2. interim control for the academic practice at the end of each rotation, 3. final inspection performed at the end of each semester in the form of a written test survey on ELT seminars and development of practical skills. 1.8. New training technologies - Decision to training and supervising of tests on all the theoretical part of the program and the master's practice using the computer. - Distributing information material (photocopies of articles and abstracts, manuals, data sheets, brochures medicinal drugs, guidelines and manuals). - Tables, slides. - Training videos and audio tapes. - Movies, computer training and monitoring programs - Role-playing - Work in the "Internet". 2. Implementation of the learning process 2.1.Obyazannosti director of the program: - Carry out all the organizational work related to the accreditation of the program, including the timely preparation of all necessary documents for the commission of Ministry of Health. - Is directly involved in the admission and selection of the most deserving candidates as graduate students. - Solves all the issues related to the organization of the educational process at a qualitative level consistent with recognized standards, including the logistics of the learning process, as well as the selection and arrangement of the most qualified and experienced staff of the Institute as a training staff. This should be created such conditions that the teaching and coaching activities was attractive for the specified personnel, both materially and in terms of a possible appointment to a higher post, which will allow for selection on a competitive basis. - Organizes the learning process and creates all the necessary conditions for a full study of residents: to master the theoretical knowledge and practical skills, including how to manipulate the diagnostic and therapeutic procedures and surgery techniques. - Together with the coaches defines and articulates a specific goal and objectives of each rotation, as well as the best ways to implement them. - Planning the learning process in such a way as to ensure the participation of residents in the continuity of the process of examination, treatment, follow-up care and rehabilitation of patients with ENT pathology and disease prevention, providing for a gradual increase in the proportion of their personal responsibility and participation in the final result. - Keeps all current and accounting documentation related to the educational process. - Carries out regular monitoring (current, monthly, intermediate, final, etc.) of graduate students, including the acquisition of theoretical knowledge and practical skills, academic work, learning a foreign language, etc. - Pays due attention to the creation of master's students a competitive atmosphere through regular assessment of their individual rankings with the reflection of these results in terms of publicity. At the same time, if possible, should be created financial incentives most academically and provides for certain penalties to achieving, up to their potential contributions. - Focuses on providing students graduate normal conditions for study and work (including their jobs, shape, etc.), as well as household, personal and other problems graduate students who may have an impact on the quality of the educational process. - Periodically evaluates and monitors the activities of the program and the faculty through selfassessment and an anonymous survey. 6 - In time to prepare documents for the planned assessment and monitoring of the program by the Commission on Accreditation of Health Ministry. 2.2. Duties of the moderator and coaches: - Are responsible for the daily implementation of the program at this institution under the general supervision of the Director of the program. In the future, all staff involved in the educational process must be certified and licensed as an infectious disease specialists or pediatricians or specialists in related disciplines (including the staff of participating institutions). After defining and articulating (together with the director of the program) objectives and goals of each workshop, the moderators of training workshops: - Make up lesson plan, - Determine the necessary list of literature - Prepare the slides and other demos, - Are questions for the workshop. - Make special programs for the subsequent test control (as an exception, at the organizational stage, you can provision be made in the form of test control of the written exam). All training materials are in the process of preparation are consistent with the program director and approved by him in the form of the final version. Test questions for each topic should be evaluated in accordance with international standards and discriminatory nature of the complexity of their subsequent correction. After defining and articulating (together with the director of the program) goals and objectives of each specific rotation and the list of required skills, the coaches of individual rotations: - Make plans for workshops with students graduate by providing a phased acquisition of practical skills, with a gradual increase in the proportion of their personal involvement in the implementation of manipulation, procedures, operations, etc. These plans are also approved by the director of the program. Monthly and at the end of the rotation the coaches evaluate the work of graduate students with the preparation of the final performance. In addition to the director of the program, there should be at one officer, whose activities will be fully dedicated to the program and monitor the quality of teaching graduate students. In general, the adequacy of teacher-mentors graduate students to implement the training program can be estimated level of participation of graduate students in the treatmentprocess under the supervision of coaches and the overall supervision of the program director. 2.3.Obyazannosti and law graduate students: Responsibilities: The primary responsibility of graduate students is a full mastery of theoretical knowledge and practical skills provided through the program. - Graduate students are required to keep a daily record, reflecting the work done by them (including the acquisition of practical skills in some rotations, duty and other practical activities) with the proportion of their personal involvement in% certified coaches rotations. - Monthly and at the end of the individual rotations provide students graduate program director and current reports with the final rating items signed by coaches. - All records, plans, reports, reports, specifications and other documentation to the estimates notes and observations from the program director to be collected in chronological order, in special files and documents stored until completion of master degree. They must be presented on demand for control by the higher authorities, and after the certification and licensing of master, such documents shall be deposited in the archives of the sponsoring institution for further storage. - Graduate students are required to take an active part in training seminars, as in addition to theoretical knowledge will be identified and their activity with setting a separate assessment to be added to the overall rating score. - Graduate students are required to pass current, interim and final test computer polls according 7 to the approved schedule. - Graduate students must be at least 1 time per week on duty at the clinic with a detailed written reflection of their work and the report on the morning of the conference. The share of their personal involvement in the% must be checked and certified by the responsible duty of his signature. - Graduate students must take an active part in the daily clinical conferences and walkthroughs, as well as in scientific congresses and conferences, participate in reports, presentations, testing and dissertations, as well as all other activities related cognitive, scientific and practical importance. - Graduate students must constantly improve their knowledge of a foreign language. Rights: - Graduate student is entitled to one day off per week. - Graduate student is entitled to 4 weeks of paid vacation during the school year. - Graduate student has the right to rest and sleep during the 24 hour day (while on duty). 2.4. Equipment training bases Education master's degree in "childhood infectious diseases" carried out at the Department of Infectious and Pediatric Infectious Diseases TMA, which is the main base, as well as UzNII EMIZ, CIB № 1,2,4, 5,6, RSSPMC Pediatrics, Institute of Virology, Research Institute Immunology. Number of classrooms at the main base - 3 (85 m2), equipped with furniture, there are a set of slides, one with a set of computer disks, video, TV, multi-media, a set of training tables, 4 video, cathedral library, complete with textbooks, monographs, guidelines for infectious diseases, reference books, medical journals. Bedspace clinic at the Department of Infectious and Pediatric Infectious Diseases is 50 beds. In TSKDL have ultrasound machines, ECG, endoscope, a clinical and biochemical and bacteriological laboratory also has TashMI MRI scans, X-ray department. In UzNII EMIZ, has the following offices: diagnostic, receiving, boxes, emergency department, intensive care, helminthological, protozoan, intestinal, viral hepatitis in total, calculated with 250 beds. In UzNII EMIZ graduate students are rotated by an acute intestinal infections and feverish, parasitology, helminthiasis, protoozam, intensive care unit patients with infectious diseases. The base is equipped with a clinical, bacteriological and biochemical laboratories, X-ray ultrasound and cabinets Republican gepatologichesky center has a clinic and a hospital, clinical, biochemical, immunological and bacteriological laboratory and ultrasound machines. Designed for 500 visits per day. In CIB number 1imeetsya reception, diagnostic, boxed, meningitis offices, a lecture hall and a study room. The base is equipped with a functional diagnostics, laboratory tank, rentgenkabinetom, physical therapy equipment. Clinical Hospital has 250 beds. Graduate students are thematic cycles of "feverish infections, meningococcal disease, meningitis, airborne infection. In UzNII Virology has a section of viral hepatitis in young children, OCI up to 3 months, the ICU, bacteriological, biochemical, morphological and immunological laboratory. Graduate students are rotated on viral hepatitis and acute intestinal infections in young children, resuscitation and intensive care of young children. Children's Hospital of Infectious number 4 has branches viral hepatitis, acute intestinal infections, is equipped laboratories designed for 120 beds. Children's Hospital of Infectious number 6 has 2 laringitnyh department, emergency room, intensive care unit. Thus, teaching graduate students is in the largest health care facilities that meet modern requirements for Master pediatricians - infectious diseases. 8 2.5. In blocks of hours specialty disciplines. № 1 2 3 4 5 name of the block Infectious diseases occurring in children with jaundice syndrome Air-respiratory infection in children with catarrhal syndrome Air-respiratory infection in children with the syndrome of angina Air-respiratory infection in children with the syndrome of exanthema Acute intestinal infection in children 6 Emergency conditions in infectious diseases 7 Infectious diseases occurring in children with febrile syndrome 8 parasitosis 9 Helminthosis 10 arboviral infections 11 Infection with lesions of the nervous system. 12 zoonoses 13 Particularly dangerous infection 14 questions vaccination 15 HIV / AIDS in children only Electives in total * approximate list of optional subjects: 1. pathophysiology 2.Klinicheskaya pharmacology 3. necropsy 4. immunology Number hours. labor content Audit and seminars self-study 210 210 126 150 100 50 120 90 30 150 100 50 210 210 80 100 60 40 150 100 50 60 100 30 100 40 60 30 60 20 40 74 100 80 80 1058 260 1866 40 60 60 60 34 40 20 20 12/156 1560 92 648 40 5. microbiology Academic load for the discipline specialty 2.3. Academic load for the discipline specialty labor The distribution of the teaching load by type of semester content employment (hours) self-study 9 I П III IV V VI in total Independent Independent Master Practice development of development of (thematic rotation) theoretical thematic knowledge rotations Total Practical and seminars 300 220 220 350 80 170 360 240 240 254 200 220 160 160 150 154 220 160 160 150 154 350 340 340 400 448 140 80 80 70 80 176 150 186 200 222 1606 1606 1050 3338 556 1112 The distribution of the teaching load per semester and week semesters Name of subjects (courses) and scientific activities I II III IV General methodological discipline 9 4 7 3 Discipline specialty - "childhood infectious 10 12 5 11 diseases" Scientific - practical activities 17 18 22 20 The Master practice 17 18 19 15 Scientific - pedagogical work 3 3 Preparation of Master's research project 2 Electives 2 2 2 Operation of modern medical techniques and technology in a clinical setting TOTAL 36 36 36 36 2.6. Topics of seminars. V VI 8 8 25 19 3 3 28 26 2 3 36 36 The clusters. 1 year of study 2.6.1. "Infectious diseases in children, occurring with damage to the liver and jaundice syndrome. 1. Viral hepatitis is a fecal-oral route of infection (HAV, HEV). 2. HBV viral hepatitis in children. 3. Viral hepatitis C in children 4. Viral hepatitis A in children. 5. HS outcomes in children (recovery, acute liver failure, carrier, prolonged hepatitis.) 6. Chronic viral hepatitis. 7. Congenital biliary tract disease in children and gepatozy. 8. Methods of diagnosis of diseases of the liver and biliary tract. 9. Epidemiology at HS (active and passive seroprevention. 10. Differential diagnosis with hemolytic jaundice in children. 11. Infectious diseases proceeding with jaundice syndrome (Leptospirosis, yersiniosis, yellow lihoradkamalyariya, cytomegalovirus infection, Ext. Mononucleosis, hydatid disease). 12. The basic principles of diet therapy and treatment. 10 2.6.2. Infectious diseases in children that are transmitted by airborne droplets occurring with catarrhal syndrome. 13.Koklyush, features of the pathogen, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinic, diagnostics. 14.Koklyush, the criteria of severity, complications, treatment. Features of motion in children the first 3 months. life. Differential diagnosis with parakoklyushem, prevention, indications and contraindications for vaccination. 15.Gripp. Features of the pathogen, epidemiology pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis. Criteria gravity complications Treatment 16. Other SARS - Adenovirus infection, parainfluenza, rhinovirus infection, RSV infection Features of pathogens, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical features of each type of diagnosis. The criteria of severity. 17.Oslozhneniya influenza and other viral respiratory infections (pneumonia, laryngitis, meningitis, etc.). The principles of treatment and prevention. 18.Meningokokkovaya infection, the properties of the causative agent, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical classification, clinical meningococcal nasopharyngitis, diff. diagnosis with other nasopharyngitis. 2.6.3. Infectious diseases in children, occurring with tonsillitis. 19. Diphtheria. Etiology, especially diphtheria bacilli, epidemiology, pathogenesis. Classification of diphtheria throat and other sites. 20. Diphtheria of the larynx, nose and rare localizations. 21. Complications and outcomes of diphtheria, their pathogenesis and treatment of diphtheria. DTP - vaccination, indications and contraindications, complications 22. Infectious mononucleosis - illness Filatov. 24. Bacterial and viral sore throats (Simanovskiy - Vincent, stafillo and strep, fungal). Angina secondary to other infectious diseases. The principles of treatment of sore throats and their complications. 2.6.4. Infectious diseases in children, occurring with the rash. 25.Kor. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention. 26.Krasnuha, etiology and pathogenesis, clinical picture, especially in pregnant women, congenital rubella, diff. Dagnostika with measles, 27. Scarlet fever, etiology and pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, classification, diagnosis, complications, early and late. Outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment at home and in hospital, prevention. 28.Psevdotuberkulez, etiology and pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis. Complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment 29.Meningokokktsemiya, clinical picture, differential. Diagnostics, medical tactic. 30.Enterovirusnye exanthema. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, early and late, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment at home and in hospital, prevention 31.Gerpeticheskaya infection: chickenpox, shingles, herpes simplex. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention. 32. Streptococcal and staphylococcal skin infection in children. 2 year training. 2.6.5. Infectious diseases in children, occurring with a fever. 11 34. Typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 35. Brucellosis. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 36. Malaria. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention, differential diagnosis with rickettsial diseases, septic conditions of an infectious nature, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention. 2.6.6. Infectious diseases in children that occur with diarrhea. 37. Salmonellosis in children. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 38.Dizenteriya in children. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, differential. Diagnosis of amoebic dysentery, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 39.Pischevye toxicoinfection. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 40.Virusnye diarrhea. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention. 41. Diarrhea caused by the UPF. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention. Dysbacterioses. 2.6.7. "Emergency conditions in children." 42. Cereals (laryngitis) in young children. 43.ITSH in children. 44.Otek brain. 45.Sudorozhny syndrome and hyperthermic syndrome with inf. Pathology 46. Acute adrenal ND. 47. Acute renal and hepatic acute ND. 2.6.8. Infectious diseases in children, occurring with damage to the nervous system. 48. Polio. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 49.Meningity, entsefality.Etiopatogenez, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 50.Stolbnyak in children. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 51.Beshenstvo in children. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, differential. Diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 52. Neurotoxicity in children. 53.Botulizm. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 3 year training 2.6.9. Helminth infections in children. (60ch.) 54. Enterobiasis in children. The special characteristics of the helminth, pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, treatment, prevention 55.Askaridroz in children. The special characteristics of the helminth, pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, treatment, prevention 56.Gimenolipedoz in children. The special characteristics of the helminth, pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, treatment, prevention 57.Teniarinhoz in children. The special characteristics of the helminth, pathogenesis, 12 epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, treatment, prevention 58.Tsestodozy in children. The special characteristics of the helminth, pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, treatment, prevention 2.6.10 Parasitic infections in children (40ch.) 59.Ehinokokkoz in children. The special characteristics of the helminth, pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, treatment, prevention 60.Hlamidiynaya infection in children. 61Toksoplazmoz in children. 62.Tsitomegalovirusnaya infection. 2.6.11. "Zoonoses in children." 63.Sibirskaya ulcer. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, . Complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 62.Yaschur. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, differential. Diagnstika with glanders, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 63.Leptospiroz etiology and pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 2.6.12. Particularly dangerous infections in children. 64. Hemorrhagic fever. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention. 65.Holera. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention. Hypovolemic shock 66.Ospa monkeys. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, treatment, prevention 67.Chuma. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, treatment, prevention 2.6.13. Arboviral infection in children 68. Tick-borne encephalitis. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis,. Complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 67.Zoornitozy children etiology and pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention 2.6.14 "Vaccination" 68.Raznovidnosti vaccines, their preparation technique, indications and complications противопоказания.Поствакцинальные. Provision of medical care. 3.15. HIV / AIDS in children. 69.vrozhdenny and acquired AIDS in children. The order of seminars. The seminars are held on the approved program and measured in accordance with the position of the ranking system of control of students' knowledge of the Judiciary. Preparation for seminars carried out in the form of a compilation of summaries, charts, tables, training materials worked monographs, theses, articles, training manuals, as well as the preparation of a report on the patient's medical history theme. Single issues of seminars on topical sections can be prepared by one or more students graduate in a report using the demo material. 2.7. Plans of seminars per semester 13 1semestr Infectious diseases in children, occurring with jaundice syndrome. plans of seminars number 1: "Viral hepatitis with fecal-oral contamination." 1.morfologiya liver (anatomy, physiology, pigment metabolism, liver biochemistry), especially in children. 2 .. the basic properties of the virus and HEV CAA. 3.osobennosti epidemiology of viral hepatitis A and E. 4. particular, clinics, current, HS outcomes with the fecal-oral contamination. 5.klinicheskaya classification of viral hepatitis. Plan number two seminars: "Viral hepatitis with parenteral mechanism of infection VS." 1.Osobennosti HBV virus, its structure and markers, their values at diagnosis. 2.Osobennosti virus and HCV markers. 3.Osobennosti epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, for HBV, and their outcomes. The value of carrier 4. Features of the epidemiology, clinical, course of HCV and its outcomes. 5 Features of HBV and HCV infection in young children. plans of seminars number 3: "Viral hepatitis with parenteral mechanism (VGD.)» 1 .. Features of the hepatitis delta virus. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical features. 2. Features of current IOP (co-infection and superinfection, chronic hepatitis D.) 3. Features of current IOP in young children plans of seminars number 4: "Based on the HS (acute liver failure, carrier, prolonged convalescence) 1.Vyzdorovlenie, clinical - biochemical characteristics. 2.Ostraya liver failure (hepatic coma), its characteristics in young children. 3.Nositelstvo HBV, its importance to the development of clinical HS. 4.Zatyanuvshayasya convalescence at HS. plans of seminars number 5: "Congenital biliary tract disease and gepatozy." 1. Congenital hepatitis. Features of the clinic. Diagnostics 2. Congenital malformations of the biliary tract, the differential diagnosis with congenital hepatitis. 3. Gilbert's syndrome, Crigler-Najjar, Dabina_-Johnson et al plans of seminars number 6. "Chronic hepatitis VS)." 1.Prichiny form of chronic viral hepatitis. 2.Klassifikatsiya chronic hepatitis, the clinical features in children, the criteria of severity. 3. Chronic hepatitis VT 4 degrees of activity, clinical and biochemical characteristics of. 4. Chronic hepatitis C. plans of seminars number 7: "Methods of diagnosis of diseases of the liver and biliary tract." 14 1.Biohimicheskie diagnostic methods (pigment protein, carbohydrate metabolism, cytolytic, cholestatic syndromes, etc.) 2.Serologicheskie diagnostic methods. 3.Instrumentalnye diagnostic methods. plans of seminars number 8: "Epidemiology at HS. (Active and passive seroprevention). " 1. Anti-epidemic measures in the hearth CAA. HEV .. 2.Protivoepidemicheskie events in HS with parenteral mechanism of infection. 3. Vaccination against HAV vaccine types, indications. 4.Vaktsinatsiya against HBV vaccine types, indications. plans of seminars number 9: "Differential diagnosis with hemolytic jaundice." 1.Gemoliticheskie jaundice in ABO and Rh - incompatibility. 2. Diseases of the blood of children, accompanied by jaundice syndrome. plans of seminars number 10: ". Infectious diseases proceeding with jaundice syndrome (leptospirosis, yersiniosis, yellow fever)." 1. Leptospirosis, etiology and pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features of the course of children, the nature of jaundice, diagnosis, treatment. 2. Yersiniosis: intestinal yersiniosis, pseudotuberculosis, etiology and pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features of the course of children, the nature of jaundice, diagnosis, treatment. 3. Yellow fever, etiology and pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features of the course of children, the nature of jaundice, diagnosis, treatment. plans of seminars number 11: "Infectious diseases proceeding with jaundice syndrome (malaria, cytomegalovirus, Ext. Mononucleosis, hydatid disease)." 1. Malaria, etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features of the course of children, the nature of jaundice, diagnosis, treatment. 2.Tsitomegaliya, etiology and pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features of the course of children, the nature of jaundice, diagnosis, treatment. 3.Infektsionny mononucleosis, etiology and pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features of the course of children, the nature of jaundice, diagnosis, treatment. 4.Ehinokokkoz, etiology and pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features of the course of children, the nature of jaundice, diagnosis, treatment. plans of seminars number 12: "Basic principles of diet therapy and treatment." 1. Diet number 5, its value and features, rough menu for the week 2. Protective regime, its value. 3. Detoxification therapy: oral and parenteral. 4. Bile products, their types (anticholinergics and holinoretiki). 5.Spazmolitiki, enzymes to improve the gastrointestinal tract. 6.Glyukokortikosteroidy, the indications for their intended purpose, principles and application of the scheme. 2.6.2. Infectious diseases in children that are transmitted by airborne droplets and proceeding with catarrhal syndrome. plans of seminars number 14. "Whooping cough". 1.Osobennosti pathogen, their types. 2.Epidemiologiya, (the source of infection, modes of transmission, the index of contagiousness, 15 age composition, immune status). 3. Pathogenesis, clinical (symptoms and syndromes). 4. Diagnostic value of bacteriological and serological diagnosis. plans of seminars number 15. "Whooping cough". 1.Kriterii severity, complications, treatment. 2.Osobennosti course in children during the first 3 months. life. 3.Differentsialnaya diagnostics in the prodromal period with bronchitis, pharyngitis, and other lesions of the respiratory tract, parakoklyushem. 4. General and specific prevention, indications and contraindications for vaccination. plans of seminars number 16. "Flu". 1.Anatomo and physiological characteristics of the respiratory system of children in the age aspect. 2.Osnovnye properties of the influenza virus (ABC), its variability. Features of influenza A virus 3.Epidemiologiya, an influenza pandemic. 4.Patogenez, clinical symptoms and complications of influenza 5.Klinicheskaya picture, the classification criteria of severity and complications. 6. Diagnosis (virological, serological) at this stage. plans of seminars number 17. "Influenza and other viral respiratory infections" 1 .. Adenovirus infection, the properties of the virus, especially epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations. 2.Paragripp, the properties of the virus, especially epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations. 3.Rinovirusnaya particular infection clinics, diff. diagnosis of the flu. 4. PC - Infection - especially clinics, diff. diagnosis of the flu. 5.Lechenie influenza and other viral respiratory infections. plans of seminars number 18: "Complications of influenza and other viral respiratory infections Principles of treatment and prevention." 1. Viral and bacterial pneumonia. 2.Meningity, secondary, serous. 3. Laryngitis and other upper respiratory tract infections. 4. Lesions of the paranasal sinuses and ear plans of seminars number 19: "Meningococcal disease" 1.Meningokokkovaya infection, the properties of the causative agent, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical classification, clinical meningococcal nasopharyngitis, diff. diagnosis with other nasopharyngitis. 2.Meningokokkovy meningitis, clinical indications for lumbar puncture, cerebrospinal fluid in purulent and serous meningitis, diff. diagnosis with the syndrome meningizma 3. Meningokokktsemiya, clinical syndrome Waterhouse-Fridreksena, diff. rash diagnosis, laboratory diagnosis,. 4.Oslozhneniya meningococcal disease - ITSH, brain edema, hydrocephalus, ependymitis, ventriculitis, etc. 5. The principles of treatment of meningococcal infection, depending on the clinical forms, vaccination 2.6.3. Infectious diseases in children, occurring with tonsillitis. plans of seminars number 20: "Diphtheria" 16 1.Osnovnye properties of diphtheria bacilli. 2.Epidemiologiya, meaning carriers of toxigenic strains. 3. Pathogenesis. 4. Classification of diphtheria throat and other sites. 5. The clinical picture of various forms of diphtheria throat. plans of seminars number 21: "Diphtheria of the larynx, nose and rare localization." 1.Difteriya larynx, its stages, features croupous, especially clinic. 2.Difteriya rare localization, their varieties, especially the clinic. 3. The differential diagnosis of false croup and diphtheria. 4. Diphtheria of the nose, clinical differentiation. diagnosis with other lesions of the nasal infectious nature. plans of seminars number 22: "Complications and outcomes of diphtheria, their pathogenesis and treatment of diphtheria." 1. Diphtheria myocarditis, their features, dif.diagnoz other myocarditis. 2. Nervous system lesions in diphtheria (paresis, paralysis). 3. Renal disease, and other organs in diphtheria. 4. Treatment of diphtheria and its complications. The value of diphtheria serum therapy. 5. DTP - vaccination, indications and contraindications, complications. plans of seminars number 23: "Infectious mononucleosis - Filatov's disease" 1. The basic properties of the virus Ebstein-Bar. 2. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical picture. 3. differential diagnosis of a toxic form of difteriyey throat, epid.parotitom, cervical lymphadenitis. 4. Serology, especially blood. 5. Treatment in the hospital and at home. plans of seminars number 24: "Bacterial Sore Throat: Simanovskiy - Vincent, stafillo and strep, fungal ".. 1. Etiology, epidemiology, pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of angina SimanovskiyVincent. 2. Staphylococcal sore throat, her features. 3. Streptococcal sore throat, her features. 4. Ludwig's Angina and its features. 5. Fungal angina. plans of seminars number 25: "Angina in other infectious and non-infectious diseases in children." 1.Anginy of scarlet fever. 2.Anginy for viral infections (adenovirus infection, enterovirus infection, flu, etc.). 3.Anginy in typhoid fever, 4. Angina at various blood diseases (leukemias, etc.) plans of seminars number 26: "The principles of treatment of sore throats and their complications." 1. The principles of purpose antibacterial drugs, their species and age dose. 2.Desensebilizirubschie drugs. 3. Topical preparations. 4. Prophylaxis of angina. Semester 2 2.6.4. Infectious diseases in children, occurring with the rash. 17 plans of seminars number 27: "Measles in children." 1. Etiology of measles virus features. 2. Epidemiology, particularly the spread of measles, the index of contagiousness, innate immunity in measles. 3. The pathogenesis of the pathological process in measles 4. The clinic, characteristic of periods of illness. 5. Dagnostika measles. plans of seminars number 28 "Measles in children." 1. Differential diagnosis of measles in different periods with other rash (measles, allergodermatity, Lyell's syndrome, Stevens-Johnson) 2. Complications, early and late (pneumonia, laryngitis, meningitis, etc.) 3.Iskhody, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention. plans of seminars number 29: "Rubella in children" 1. Etiopathogenesis, clinical picture. 2. Features of rubella in pregnant women. 3. congenital rubella, malformations of the fetus in congenital rubella. 4. Dif. dagnostika with deleted forms of measles. 5. Treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 30: "Scarlet fever in children" 1.Etiopatogenez, epidemiology, pathogenesis and its phases. 2. The clinic, classification, diagnosis and differentiation. diagnostics. 3. Complications: early and late. 4. Outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment at home and in hospital, prevention. plans of seminars number 31: "Psedotuberkulez in children" 1.Etiopatogenez, epidemiology, pathogenesis. 2.Klinika, classification, characteristics of different forms, diagnostics. 3.Differentsialnaya diagnosis. 4. Complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization and treatment. plans of seminars number 32: "Enterovirus exanthema in children." 1.Etiologiya, characteristic of enteroviruses, their versions. 2 Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis, 3.Oslozhneniya, early and late. 4.Iskhody, indications for hospitalization, treatment at home and in hospital, prevention. plans of seminars number 33: "Chickenpox, shingles, herpes infection in children." . 1 .. Chickenpox. The etiology, pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization, treatment, prevention. 2. Shingles. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization. Treatment, prevention. 3. Herpes infection. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization. Treatment, prevention. 4.Gemorragicheskie exanthema. Etiopathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, complications, outcomes, indications for hospitalization. 18 Treatment, prevention. 2.6.5. Infectious diseases in children, occurring with fever plans of seminars number 34: "Typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever in children" 1.Osnovnye property agent of typhoid fever, the types of antigens, their importance in the diagnosis. 2.Epidemiologiya, the value of the waterway in the spread of infection. Seasonality. Meaning bacteria carriers. 3.Patogenez symptoms of the disease, its stage, the types of temperature curves. 4.Patomorfologicheskie changes in the intestine and other organs. 5.Klinika, characteristic of periods of illness and pathognomonic symptoms. plans of seminars number 35: "Typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever in children." 1.Laboratornaya diagnosis (bacteriological, serological,) of their value in the diagnosis. 2. Specific and non-specific complications of typhoid fever. 3. Paratyphoid A and B, their features. 4.Differentsialnaya diagnosis of SMI in different periods of the disease to other febrile infections. 5.Lechenie and prevention. plans of seminars number 36: "Brucellosis in children." 1.Osnovnye property agents of brucellosis, their types. 2. Epidemiology, modes of transmission, the professional nature of the lesion. 3.Patogenez and pathological changes in the organs. 4.Klassifikatsiii N.I.Ragozy. 5.Klinika disease. Characterization of acute and chronic brucellosis. plans of seminars number 37: "Brucellosis in children." 1.Laboratornaya diagnosis. Seroreaktsy value in diagnosis. 2.Differentsialnaya diagnosis of acute brucellosis with other febrile infections. 3.Differentsialny diagnosis of chronic brucellosis with rheumatic rheumatic polirtritami. 4. Treatment. Prevention. plans of seminars number 38: "Malaria in Children." 1.Etiologiya malaria. Types of malaria parasites, their features. 2.Epidemiologiya, the value of endemic foci parazitonositelstva. 3. The pathogenesis of malaria process paroxysms. 4.Klinika, the classification of the current. Changes in the organs. 5. Complications of malaria. 6.Lechenie and prevention. plans of seminars number 39: "Rickettsial diseases in children." 1.Etiologiya Q fever. Types rikketssy, their features. 2.Epidemiologiya. 3. The pathogenesis of the pathological process, the paroxysms. 4.Klinika, the classification of the current. Changes in the organs. 5. Complications Ku fever .. 6.Lechenie and prevention plans of seminars number 40: "Hemorrhagic Fever (Arboviral infection) 19 in children. " 1.Etiologiya hemorrhagic fevers. Types of arboviruses, their features. 2.Epidemiologiya. Uzbek, Crimean-Congo, Omsk, Lassa, Ebola, Marburg fevers. 3. The pathogenesis of the pathological process, hemorrhagic exanthema .. 4.Klinika, the classification of the current. Changes in the organs. 5. Criteria of severity, complications, and outcomes. 6.Lechenie and prevention plans of seminars number 41: "Septic conditions infectious nature. " 1. The etiology of sepsis, their types. 2. Epidemiology, especially typhoid, and other Brucella species sepsis. 3. Staphylococcal sepsis in neonates and infants. 4. Features of treatment of sepsis in children. 2 year training. 2.6.6. Infectious diseases in children that occur with diarrhea. plans of seminars number 1: "Salmonellosis in children." 1. Anatomic - physiological characteristics of the gastrointestinal tract of newborns, infants and older children. 2. Etiology, Salmonella species, their distinctive features. 3. Epidemiology, the value of each of the transmission paths. Seasonality, immunity. 4. Pathogenesis and morbid anatomy. 5. The clinic, severity criteria. 6. Clinical classification. Plan number two seminars: "Salmonellosis in children." 1. Symptoms, Types and extent exsicoses. 2. Laboratory diagnosis. 3. Differential diagnosis with dr.OKI .. 4. Complications. 5. The principles of treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 3: "Dysentery in children" 1. Etiology, Shigella species, their distinctive features. 2.Epidemiologiya, the value of each of the ways of transmission. Seasonality, immunity. 3.Patogenez and pathological changes in the intestine during colitis and gastroenterological forms .. 5.Klinika, severity criteria. 6.Klinicheskaya classification. plans of seminars number 4: "Dysentery in children" 1.Laboratornaya diagnosis. 2.Differentsialnaya diagnosis of amoebic dysentery. 3.Oslozhneniya. 4.Printsipy treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 5: "Foodborne diseases in children" 1. Botulism, etiology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical features. 2. The etiology of food toksikoinfktsy (staphylococci, E. coli, salmonella, etc.). 3. The clinical picture. 20 4. Laboratory diagnosis. 5. Treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 6: "Viral diarrhea in children." 1. Etiology (enterovirus, adenovirus, rotavirus, etc.) and their distinctive features. 2.Epidemiologiya, seasonality, immunity. 3.Patogenez. 4.Klinika, severity criteria. 5.Klinicheskaya classification, laboratory diagnosis. 6.Printsipy treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 7: "Diarrhea caused by UPF in children." 1. Etiology (Proteus vulgaris, zither bacteria and others), their distinctive features. 2. Epidemiology, seasonality, immunity. 3.Patogenez. 4.Klinika, severity criteria. 5.Klinicheskaya classification, laboratory diagnosis. Treatment and prevention 6.Printsipy plans of seminars number 8: "Cholera in children." 1. The etiology of the basic properties of Vibrio cholerae, their types and features. 2. Epidemiology, the value of the water factor, seasonality, immunity. 3.Patogenez diarrhea. 4.Klinika exsicoses, severity criteria. 5.Klinicheskaya classification, laboratory diagnosis. 6.Printsipy treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 9: "Dysbacterioses in children." 1.Etiologicheskie factors dysbiosis, their types and features. 2. The value of immunity. 3.Patogenez pathological changes. 4.Klinika dysbiosis, severity criteria. 5.Klinicheskaya classification. 6.Laboratornaya diagnosis . 7 .. The principles of treatment and prevention 2.6.6. "Emergency conditions in children plans of seminars number 10: "Cereals (laryngitis) in young children." 1. The etiology of laryngitis in young children (influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus infection, enteroviruses). 2. Pathogenesis of laryngitis. 3. The clinical picture, the stage of development of the croup. 4. The differential diagnosis with diphtheria croup alien throat, polyposis, and others, complications 5. Standards of treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 11: "Infectious-toxic shock syndrome in children." 1.Etiologiya ITSH in young children (influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus infection, meningococcal infection). 2.Patogenez ITSH and its stages .. 21 3.Klinicheskaya picture. 4.Oslozhneniya. 5. Standards treatment and prevention plans of seminars number 12: "The convulsive syndrome in children with various infectious. pathologies " 1. The causes of seizures in children with infectious diseases. 2. The pathogenesis of seizures (swelling of the brain, neurotoxicosis, meningoencephalitis, spazmofiliey, etc.). 3. The clinical picture. 4. Complications. 5. Standards treatment and prevention of convulsions. plans of seminars number 13: "Hypovolemic shock in children." 6. 1. Causes of hypovolemic shock (such as cholera, salmonellosis, viral diarrhea) in children with infectious diseases. 7. The pathogenesis of hypovolemic shock (exsicosis, hypoxia, muscle atonia, etc.). 8. The clinical picture of hypovolemic shock .. 9. Complications. 10. Standards of treatment and prevention. Plans of seminars number 14: "Hyperthermia syndrome in children." 1.Prichiny hyperthermia syndrome in children with infectious Zab 2.Patogenez of hyperthermia syndrome. 3.Klinicheskaya picture. 4.Oslozhneniya. 5.Standarty treatment and prevention of hyperthermia syndrome .. plans of seminars number 15: "Acute adrenal insufficiency in children." 1. Causes of acute adrenal LP in children with infectious diseases. 2.Patogenez of acute adrenal ND .. 3.Klinicheskaya picture syndrome Waterhouse - Fridreksena. 4.Oslozhneniya. 5.Standarty treatment and prevention of acute adrenal ND. plans of seminars number 16: "Acute renal failure in children." . Causes of acute renal ND syndrome in children with infectious Zab 2.Patogenez of acute renal failure. 3.Klinicheskaya picture. 4.Oslozhneniya. 5.Standarty treatment and prevention of acute renal failure. plans of seminars number 17: "Acute hepatic encephalopathy in children." 1 .. The reasons for PEI in children with infectious diseases. 2.Patogenez of PEI (viral hepatitis and other liver diseases). 3.Klinicheskaya picture, the stage of development. 4.Oslozhneni, outcomes. 5.Standarty treatment and prevention of PEI. 2.6.8. Infectious diseases in children, occurring with damage to the nervous system. 22 plans of seminars number 18: Polio. 1 The etiology of the basic properties of the virus. 2.Epidemiologiya index of contagiousness, seasonality. 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 19: Meningitis and encephalitis in children. " 1, Etiology: viral and bacterial (basic properties of pathogens). 2.Epidemiologiya. 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention plans of seminars number 20: "Tetanus in children." 1 The etiology of the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention plans of seminars number 21: "Rabies in children." 1 The etiology of the basic properties of the virus. 2.Epidemiologiya index of contagiousness, seasonality. 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention plans of seminars number 22: "Mumps in children" 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. 2.6.9. Worm infestation in children. 23 plans of seminars number 23: "Nematodosis in children." 1. Enterobiasis, askaridroz, trichocephalosis, trichinosis in children. 2. Features of the structure and basic properties of these worms. 3. Epidemiological features of each species. 4. The pathogenesis of lesions of the internal organs and systems. 5. Methods for detection of these types of helminth infections. 6. methods of treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 24: "Cestodiasis in children." 1.Gimenolipedoz, teniasis, beef tapeworm infection. 2. Features of the structure and basic properties of these worms. 3. Epidemiological features of each species. 4. The pathogenesis of lesions of the internal organs and systems Features defeats digestive system, asthenia, and allergic syndromes. 5. Methods for detection of these types of helminths (koproovoskopiya) 6. Methods of treatment and prevention. The criteria for cure (to control parasitological studies). Rehabilitation therapy. Clinical examination. plans of seminars number 25: "Antitrematode in children." 1. Helminth infections, mainly affecting the organs Digestion: opistorhoz, fastsiollez. 2. Features of the structure and basic properties of these worms. 3. Epidemiological features of each species. 4. The pathogenesis of lesions of the internal organs and systems. 5. Methods for detection of these types of helminth infections. 6. methods of treatment and prevention. 2.6.10. Parasitic infections in children plans of seminars number 26: "Echinococcosis and alveococcosis in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 27: "Amebiasis in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention plans of seminars number 28: "Giardiasis in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 24 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention plans of seminars number 29: "Chlamydia infection in children." 1. Psittacosis, felinoz, respiratory chlamydia. The etiology of the basic properties of the pathogen. 2. Epidemiology, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention plans of seminars number 30: "Cytomegalovirus infection in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention plans of seminars number 31: "Toxoplasmosis in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 32: "Wound infections - mug in children" 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. 3 year training. 2.6.11. "Zoonoses in children" plans of seminars number 1: "Anthrax in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 25 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. Plan number two seminars: "Yashur in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. 2.6.12. Particularly dangerous infections in children. plans of seminars number 3: "Hemorrhagic fever in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 4: "Cholera in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 5: "Monkeypox in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 6: "Plague in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. 26 2.6.13. Arboviral infection in children plans of seminars number 7: "Tick-borne encephalitis in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. plans of seminars number 8: "Hospital-acquired infections." 1. Etiology: Antimicrobial resistant pathogens. 2.Epidemiologiya nosocomial infections. 3. Its importance in the development of the epidemic and the complications of the underlying disease 4. Precautions against the development. plans of seminars number 9: "HIV / AIDS in children." 1.Etiologiya, the basic properties of the pathogen. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention. 2.6.14 "Problems of vaccination in children" plans of seminars number 10: "Vaccines". 1. Calendar vaccinations received in the territory of the Republic of Uzbekistan, it differs from other vaccine schedules. 2.Raznovidnosti vaccine technology of their preparation. 3 .. Characteristics of vaccines. 4.Pokazaniya and contraindications for vaccination .. plans of seminars number 11: "Post-vaccination complications." 1.Postvaktsinalnye complications after vaccination with BCG vaccine (subcutaneous cold abscesses, lymphadenitis). 2.Postvaktsinalnye complications after vaccination with DTP vaccine - a vaccine (Hyperthermic reaction, allergic reaction, anaphylactic shock, damage to the nervous system.) 3.Postvaktsinalnye complications of measles vaccine - hyperthermic response, encephalitis. plans of seminars number 12: "Providing medical aid of vaccine complications and their prevention." 1. Treatment of post-vaccination complications. 2. Sparing methods of vaccination. 3. Methods of prevention of post-vaccination complications. 27 2.6.15. HIV / AIDS in children. plans of seminars number 13 The etiology of the basic properties of the pathogen HIV / AIDS. 2.Epidemiologiya, 3. The pathogenesis of the disease. 4.Klinicheskaya picture, the main symptoms and syndromes. 5.Diffrentsialnaya diagnosis. 6. Complications outcomes. 7 standards of treatment and prevention of congenital and acquired AIDS in children. The Master Practice Practical training (Master's practice) is held under the guidance of a coach in the offices of Infectious diseases, as well as resuscitation and intensive therapy, diagnostic departments (offices) of a hospital, with the implementation of the necessary therapeutic and diagnostic procedures and manipulations, filling medical records, some of the practical skills mastered in When on duty. In the first year, the joint duty with the coach or the duty doctor offices, and from the second year of study planned independent duty. 1 year of study I semester 2.8.1. Thematic rotation number 1: Department of viral hepatitis of childhood. The rotation is carried out in the children's department hepatic TashMI 3 clinics and in the emergency department of the same hospital. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents on their own (under the supervision of the trainer) highly skilled management of patients with viral hepatitis children with the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1) Identify the objective and subjective symptoms of viral hepatitis. 2) Formulation of a preliminary diagnosis. 3) Develop a plan for examination of patients using clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods. 4) Evaluation of the results of additional research methods. 5) Development of individualized diagnostic and treatment activities and diet, taking into account the results of other surveys. 6) The formulation of the clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications of viral hepatitis .. 7) Maintenance of medical records in accordance with modern requirements. 8) The definition of further tactics of convalescent viral hepatitis. 2.8.2. Thematic rotation number 2: City gepatologichesky center. The rotation is carried out in clinics and ultrasound-based office located at 5 City Hospital for Infectious Diseases. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents interpret conclusion ultrasonography ultrasound study of diseases of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas, as well as the management of sick children, convalescents HS with different outcomes. Required Skills for rotation: 1) The definition of indications for ultrasonography of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas. 2) Identification of ultrasound-related symptoms, normal ultrosonograficheskoy picture of the 28 liver, gallbladder and pancreas. 3) Identification of ultrasound criteria for liver and gall bladder. 4) Allocation of the results of an ultrasound study with clinical symptoms the patient. 5) Education tactics and treatment of convalescents HS with different outcomes. 2.8.3. Thematic rotation number 3: Immunological methods of diagnosis HS. The rotation is carried out in the laboratory of the Institute of Immunology. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to train resident immunological methods for diagnosis of HS, HS definition of markers and their interpretation. Required Skills for rotation: 1) Identification of markers HS various serological methods. 2) Their interpretation depending on the type HS, period, and disease severity. 3) Diagnosis of infectious diseases of various etiologies using serological diagnostic methods. 2.8.4. Thematic rotation number 4: Chronic hepatitis in children. The rotation is carried out in the Department of Chronic Viral Hepatitis Research Institute of Pediatrics of the RU. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents on their own (under the supervision of the trainer) highly skilled management of patients with chronic viral hepatitis children with the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1. Identification of objective and subjective symptoms of chronic viral hepatitis. 2.Formulirovanie preliminary diagnosis. 3.Development plan examination of the patient using clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods. 4.Otsenka results of additional research methods. 5 Develop individualized diagnostic and treatment activities and diet, taking into account the results of additional tests. 6. The formulation of the clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications of chronic viral hepatitis in children. Medical records in accordance with modern requirements. 2.8.5. Thematic rotation number 5: Viral hepatitis in children in the first year of life. The rotation is carried out in the department of viral hepatitis in children in the first year of life, Institute of Virology of the RU Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents on their own (under the supervision of the trainer) highly skilled management of patients with infants, viral hepatitis, with the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1. Identification of objective and subjective symptoms in infants, sick HS allowing for the flow. 2.Formulirovanie preliminary diagnosis. 3.Development plan examination of the patient using clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods. 4.Otsenka results of additional research methods. 6 Develop individualized diagnostic and treatment activities and diet, taking into account the results of additional tests. 7. The formulation of the clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications of viral hepatitis in children. 8. Medical records in accordance with modern requirements. A list of the minimum required skills under the section "Communicable diseases in children, occurring with jaundice syndrome." 29 1. Curation of patients - 110 2. interpretation of clinical analyzes: • Complete blood count - 110 • General analysis of feces - 30 • Tech determination of bile pigments in the urine-30. 3. Interpretation of biochemical tests: • Liver enzymes (AST, ALT), organ-specific enzymes, alkaline phosphatase - 100 • Total protein + protein fractions - 20 • Thymol test - 50 • A method of determination of bilirubin and its fractions - 100 4. Markers of hepatitis A, E, B, C, D and their interpretation - 10 5. Interpretation conclusion ultrasound of the liver, gall bladder, interpretation of the results of serological studies of blood - 5 6. Carrying on tubage Dem'yanov (blind intubation w / bubble 7. Duty - 10 2.8.6. Thematic rotation number 6: Whooping cough in children. The rotation is carried out in the Department of pertussis to infants children's infectious diseases clinic TashMI. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents on their own (under the supervision of the trainer) highly qualified case management of children with pertussis, the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1. Identification of objective and subjective symptoms and epidemiological data in children with whooping cough, taking into account characteristics of the course. 2.Formulirovanie preliminary diagnosis. 3.Development plan examination of the patient using clinical, laboratory: bacteriological and serological methods. 4.Otsenka results of additional research methods. 5.Development individualized diagnostic and treatment and preventive measures. 6.Formulirovanie clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications of pertussis. 7.Vedenie medical records in accordance with modern requirements. 2.8.7. Thematic rotation number 7: Influenza and other viral respiratory infections in children and their complications. The rotation is carried out in cubicles Department of Clinical Infectious Diseases Hospital laringitnom number 1 and 6 children's infectious diseases department of the hospital. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents on their own (under the supervision of the trainer) highly skilled management of children with influenza and other viral respiratory infections, with the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1. Identification of objective and subjective symptoms and epidemiological data in children with influenza and SARS, taking into account characteristics of the course. 2.Formulirovanie preliminary diagnosis. 3.Development plan examination of the patient using clinical, laboratory: virological and serological methods. 4.Otsenka results of additional research methods. 5. The development of individualized treatment and diagnostic and preventive measures. 6.Formulirovanie clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications of influenza and other viral respiratory infections. 7.Vedenie medical records in accordance with modern requirements. 30 2.8.8. Thematic rotation number 8: Meningococcal disease in children and their complications. The rotation is carried out in the Department of meningococcal infections Clinical Infectious Diseases Hospital number 1. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents on their own (under the supervision of the trainer) highly skilled management of children with meningococcal disease, with the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1. Identification of objective and subjective symptoms and epidemiological data in children with meningococcal disease, taking into account characteristics of the course. 2.Formulirovanie preliminary diagnosis. 3.Development plan examination of the patient using clinical, laboratory: bacteriological and serological studies of blood and cerebrospinal fluid. 4.Otsenka results of additional research methods. 5.Development individualized diagnostic and treatment and preventive measures. 6.Formulirovanie clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications of influenza and other viral respiratory infections. 7.Vedenie medical records in accordance with modern requirements. A list of the minimum required skills under the heading "Air - respiratory infection in children, occurring with catarrhal syndrome." 1. Examination of the patient and the clinical description of symptoms - 110 2. interpretation of clinical analyzes: Complete blood count - 110 General analysis of feces - 30 General analysis of urine urine-30. 3.Bakteriologichesky crop swab from the throat. 4.Okazanie aid to the patient at the time of the attack of whooping cough whooping cough .. 5. Helping the patient at the time of the attack of whooping cough apnea. 6. Helping the patient laryngitis. 7 .. right to take throat swab for bacteriological seeding method cough zadneglotochnyh plates or swabs. 8. Correctly produce bak.posev on Wednesday or Wednesday AMC Borde-Zhang. 9. Interpreting the results of blood tests on paired sera from influenza and SARS. 10.Tehnike taking nasopharyngeal swabs for virological examination - 100. 11. Duty - 10 2.8.9. Thematic rotation number 9: Infectious diseases in children, occurring with the syndrome of angina .. The rotation is carried out in cubicles Diagnostic Department of Clinical Infectious Diseases Hospital number 1. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents on their own (under the supervision of the trainer) highly skilled management of children with tonsillitis contagious nature, the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1. Identification of objective and subjective symptoms and epidemiological data in children with tonsillitis contagious nature, taking into account characteristics of the course. 2.Formulirovanie preliminary diagnosis. 3.Development plan examination of the patient using clinical, laboratory: bacteriological and serological blood tests. 4.Otsenka results of additional research methods. 31 5.Development individualized diagnostic and treatment and preventive measures. 6.Formulirovanie clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications of angina. 7.Vedenie medical records in accordance with modern requirements. A list of the minimum required skills under the heading "Infectious diseases in children, occurring with the syndrome of angina." 1.Osmotr throat and description - 120. 2.Opisanie nature of plaque in the throat. 3.Tehnika a swab from the throat to the bacteriological seeding in diphtheria throat 4.Mikroskopicheskoe (bacteriascopical) smear of diphtheria. 5. Helping about complications after the introduction of diphtheria syvorotki_. 6. Regulations to antitoxic diphtheria serum. 2.8.5. Thematic rotation number 5: Infectious Diseases in Children proceeding with rash. The rotation is carried out in cubicles Diagnostic Department of Clinical Infectious Diseases Hospital number 1 and measles pediatric infectious diseases clinic TashMI. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents on their own (under the supervision of the trainer) highly skilled management of children with a variety of rash infectious nature, the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1. Identification of objective and subjective symptoms and epidemiological data in children with various infectious rash nature, taking into account characteristics of the course. 2.Formulirovanie preliminary diagnosis. 3.Development plan examination of the patient using clinical, laboratory: bacteriological and serological blood tests .. 4.Otsenka results of additional research methods. 5.Development individualized diagnostic and treatment and preventive measures. 6.Formulirovanie clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications of measles, scarlet fever, etc. psedotuberkuleza. 7.Vedenie medical records in accordance with modern requirements. A list of the minimum required skills under the heading "Infectious diseases in children, occurring with exanthema syndrome." 1.Osmotr skin rashes and description - 120 2.Opisanie nature of the rash. 3.Osmotr throat and description. 4.Vzyatie blood for serological diagnosis of measles. 2.8.6. Thematic rotation number 6: Infectious Diseases in Children occurring with fever. The rotation is carried out in cubicles Diagnostic Department of Clinical Infectious Diseases Hospital number 1 and Division of Infectious Brucella TashMI clinics, as well as in the diagnostic department UzNIIMEIIZa .. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents on their own (under the supervision of the trainer) highly skilled management of children with infectious diseases proceeding with high and prolonged fever, with the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1. Identification of objective and subjective symptoms and epidemiological data in children with typhoid and paratyphoid, brucellosis, malaria, Q fever, etc., taking into account characteristics of the course. 2.Formulirovanie preliminary diagnosis. 3.Development plan examination of the patient using clinical, laboratory: bacteriological and serological blood tests. 4.Otsenka results of additional research methods. 5.Development individualized diagnostic and treatment and preventive measures. 32 6.Formulirovanie clinical diagnosis of these diseases in the context of existing classifications. 7.Vedenie medical records in accordance with modern requirements. A list of the minimum required skills under the heading "Infectious diseases in children, occurring with high and prolonged fever." 1.Osmotr patient and description of clinical symptoms - 120 2.Tehnika blood sampling for blood culture-bacteriological blood cultures at SMI. 3 Taking bak.posev material (feces, urine, bile, etc.) at SMI. 4.Vzyatie a thick drop of blood and smear for malaria and determination "Parasites." 5. Blood samples for serological testing (reaction Vidal, CFT, IHA). 6. Interpretation of serological data (Wright, Heddelsona, Vidal, etc.) .. 7. Data interpretation PCR and ELISA 8.Okazanie care for complications of SMI. 9.Dispanserizatsiya convalescents TPZ, malaria, etc. 2.6.7. Thematic rotation number 7: Separation of acute intestinal infections (infectious diseases in children, occurring with diarrhea syndrome). The rotation is carried out in the Department of acute intestinal infections in children's infectious diseases hospital number 4, the department of AEI for infants Institute of Virology, as well as in the department of AEI UzNIIMEIIZa. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents on their own (under the supervision of the trainer) highly qualified management, pediatric patients with acute intestinal breakdown for the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1) Identify the objective and subjective symptoms and epidemiological data AEI in children. 2) Formulation of a preliminary diagnosis. 3) Develop a plan for examination of patients using clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods. 4) Evaluation of the results of additional research methods. 5) Development of individualized diagnostic and treatment activities and diet, taking into account the results of other surveys. 6) The formulation of the clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications of salmonellosis, dysentery, ehsherihioza, viral diarrhea, etc. 7) Maintenance of medical records in accordance with modern requirements. 8) The definition of further tactics of convalescents these infections. A list of the minimum required skills under the heading "Infectious diseases in children, occurring with diarrhea syndrome." 1.Osmotr patient and description of clinical symptoms - 120 2. Examination of feces and description. 3. Assessment of the exsicoses and his kind. 4. Calculation of fluid for rehydration fluid therapy. 5. Calculation of fluid for rehydration. 6.Tehnika gastric lavage. 7.Vzyatie material from the patient (feces, urine, bile, etc.) and tank culture medium at inoculation. 8. Blood samples for serology (IHA, PHA). 9.Tehnika purification and formulation of high siphon enema. 10.Dispanserizatsiya convalescent dysentery, salmonellosis and so on. 11. Duty - 10 2.8.7. Thematic rotation number 7. The emergency and intensive care units (states of emergency 33 in children). The rotation is carried out in the emergency department and intensive care of children's infectious diseases hospital № 6, CIB number 1 in the ICU Institute of Virology, as well as in the department of ICU UzNIIMEIIZa Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents on their own (under the supervision of the trainer) highly qualified management, separation of children in the ICU with a variety of medical emergencies: PEI, laryngitis, ITSH, etc., the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment the present level. Required Skills for rotation: 1) Identify the objective and subjective symptoms. 2) Formulation of a preliminary diagnosis. 3) Develop a plan for examination of patients using clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods. 4) Evaluation of the results of additional research methods. 5) Development of individualized diagnostic and treatment activities and diet, taking into account the results of other surveys. 6) The formulation of the clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications 7) Maintenance of medical records in accordance with modern requirements. A list of the minimum required skills under the heading "The emergency and intensive care. 1.Osmotr patient and description of clinical symptoms - 120 2. Assessment of the severity of the patient. 3. Assessment of the exsicoses with hypovolemic shock. 4. Calculation of fluid for rehydration fluid therapy. 5. Catheterization technique of large vessels. 6.Tehnika gastric lavage. 7.Tehnika catheterization. 8. Tech productions cleaning and high siphon enema. 9. Intubation technique with laryngitis. 10.Tehnika spinal tap. 11. watch – 10. Thematic rotation number 8: Department of polio The rotation is carried out in four infectious diseases hospital for polio patients. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to educate residents on their own (under the supervision of the trainer) highly qualified management, children with polio to the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1) Identify the objective and subjective symptoms of polio. 2) Formulation of a preliminary diagnosis. 3) Develop a plan for examination of patients using clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods. 4) Evaluation of the results of additional research methods. 5) Development of individualized diagnostic and treatment activities and diet, taking into account the results of other surveys. 6) The formulation of the clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications 7) Maintenance of medical records in accordance with modern requirements. Thematic rotation number 8: Department of meningitis The rotation is carried out in the IRB number 1. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to train graduate students themselves (under the supervision of the trainer) highly qualified management, children with meningitis and encephalitis with the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. 34 Required Skills for rotation: 1) Identify the objective and subjective symptoms of meningitis and encephalitis. 2) Formulation of a preliminary diagnosis. 3) Develop a plan for examination of patients using clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods. 4) Evaluation of the results of additional research methods. 5) Development of individualized diagnostic and treatment activities and diet, taking into account the results of other surveys. 6) The formulation of the clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications 7) Maintenance of medical records in accordance with modern requirements. Thematic rotation number 9: Diagnostic Unit for patients with wound infections The rotation is carried out in the IRB number 1. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to train graduate students themselves (under the supervision of the trainer) highly qualified management, children with tetanus and rabies, anthrax. the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1) Identify the objective and subjective symptoms of tetanus, rabies, anthrax. 2) Formulation of a preliminary diagnosis. 3) Develop a plan for examination of patients using clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods. 4) Evaluation of the results of additional research methods. 5) Development of individualized diagnostic and treatment activities and diet, taking into account the results of other surveys. 6) The formulation of the clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications 7) Maintenance of medical records in accordance with modern requirements. 2.8.10. Thematic rotation number 10: helminthological department. The rotation is carried out in the department helminthological UzNIIMEIIZ. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to train graduate students themselves (under the supervision of the trainer) highly qualified management, children with helminthic infestation to the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1) Identify the objective and subjective symptoms of helminth infestations. 2) Formulation of a preliminary diagnosis. 3) Develop a plan for examination of patients using clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods. 4) Evaluation of the results of additional research methods. 5) Development of individualized diagnostic and treatment activities and diet, taking into account the results of other surveys. 6) The formulation of the clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications 7) Maintenance of medical records in accordance with modern requirements. A list of the minimum required skills under the heading "helminthological department. 1.Podrobny interrogation of the patient or his or her parents 2.Osmotr patient and description of clinical symptoms - 120 3. Koproovoskopiya, 4. Tech-taking perianal rectal scrapings. 5. Immunological methods: latex agglutination, indirect hemagglutination. 6. Flotation methods of diagnosing helminths. 35 2.8.11 .. Thematic rotation number 11. Department of Laboratory and protozoal infections (hydatid disease, amebiasis, giardiasis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus and chlamydial infection). The rotation is carried out in the laboratory and office protozoal UzNIIMEIIZ. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to train graduate students themselves (under the supervision of the trainer) highly qualified management, children with parasitic infections with the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1) Identify the objective and subjective symptoms and epidemiological evidence of parasitic infection. 2) Formulation of a preliminary diagnosis. 3) Develop a plan for examination of patients using clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods. 4) Evaluation of the results of additional research methods. 5) Development of individualized diagnostic and treatment activities and diet, taking into account the results of other surveys. 6) The formulation of the clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications 7) Maintenance of medical records in accordance with modern requirements. A list of the minimum required skills under the heading "Department of protozoal infections." 1.Podrobny interrogation of the patient or his or her parents 2.Osmotr patient and description of clinical symptoms - 120 3. Serodiagnosis of echinococcosis, 4. Parasitological method (detection of cysts in feces and other materials from the patient). 5. Immunological Methods: RCC, IHA, PHA. 6. The method of diagnosis of toxoplasmosis, skull radiography. 7. Management of patients with protozoal infections. 2.8.12. Thematic rotation number 12: Department of Diagnostic and Laboratory for dangerous infections (plague, cholera, hemorrhagic lihoralki, monkeypox). The rotation is carried out in the diagnostic department UzNIIMEIIZ, anti-plague station g Tashkent. Goals and objectives of the rotation: to train graduate students themselves (under the supervision of the trainer) highly qualified management, children with especially dangerous infections with the formulation and justification of the clinical diagnosis, the survey design and individualized comprehensive treatment to date. Required Skills for rotation: 1) Identify the objective and subjective symptoms and epidemiological data particularly dangerous infection. 2) Formulation of a preliminary diagnosis. 3) Develop a plan for examination of patients using clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods. 4) Evaluation of the results of additional research methods. 5) Development of individualized diagnostic and treatment activities and diet, taking into account the results of other surveys. 6) The formulation of the clinical diagnosis with regard to the existing classifications 7) Maintenance of medical records in accordance with modern requirements. 2.8.13. Thematic rotation number 13: Grafting business. The rotation is carried out in the vaccination clinics family offices urban and city diagnostic center of Tashkent. 36 Goals and objectives of the rotation: to train graduate students conducting immunization vaccination according to the calendar adopted in the Republic of Uzbekistan. Required Skills for rotation: 1) The definition of indications for vaccination of healthy children. 2) Identify contraindications for vaccination. 3). Determination of the quality and shelf life vaccines. 4). Warning complications possible during vaccination. 5). Population health improvement of children prior to vaccination. 2.8.22. Thematic rotation number 22: Department of admissions for infectious diseases. The rotation is carried out in the waiting room of infectious hospital TashMI Goals and objectives of the rotation: to train graduate students to assist patients to therapeutic profile. Required Skills for rotation: 1) The definition of the indications for emergency hospitalization in the profile department. 2) The ability to provide life-saving therapeutic care to patients in the waiting room, in accordance with the algorithms. 3) Determining the amount of medical and diagnostic facilities, including specialist advice to patients. 4) Implementation of the surgical patient consultations. 5) Fill the necessary medical documentation. 3.1.Teoretichesky section of the program in the specialty estimated as the TC and is conducted through oral questioning in seminars and IR in the form of a written test survey, which is conducted in a test center of the Institute. The criteria for evaluation of the level of the theoretical part of the program I to VI semester (maksimal. Score -100) levels of estimates CRITERIA points (%) The answer is original with a creative approach, using more information and high 96-100 quality, exceeding the requirements of the program. 86-100 76-85,9 65-75,9 91-95 Reply with details and highest quality that exceeds the requirements of the program. 86-90 Reply using the information in excess of the requirements of the program. 82-85 The answer of good quality, using the information above the requirements of the program in its entirety. 79-81 The answer of good quality, using the information above program requirements are not fully 76-78 The answer of good quality, consistent with the program 72-75 The answer is within the average, corresponds to the program. 69-71 The answer is within the average level, allows for inaccuracies. 37 65-68 The answer is within the average level, allows for inaccuracies, errors are marked individual. By the end of each semester IR - Grading criteria are similar to the current rating score. 3.3.Magisterskaya practice is evaluated in the form of TC, respectively, the criteria developed by the department at the end of the rotation and IR (as at the end of the interview II, IV and VI semester). Criteria for evaluation of master-level practice I to VI semester (maximum score - 100) levels of estimates CRITERIA (%) Practical skills are mastered in its entirety and held at a high level. Availability of 86-100% competent and fully furnished protocols daily work. 7685,9% 6575,9% Well mastered skills in full. The presence of a fully furnished protocols daily work. Learn how with flawed. Making daily reports are not in full. Scientific and methodological work is assessed on a monthly basis in the form of TC (III to V semester, the maximum score - 100) levels of estimates CRITERIA points % 96-100 86100% 91-95 86-90 82-85 76-85% 79-81 Prepare visual aids for practical classes (tables, charts, slides) at a high level. A solid plan for the development of practical training in the specialty and rating system knowledge resident in the department in its entirety. Frequent visits to the open lessons teachers. Prepare visual aids for practical classes (tables, charts, slides) at a high level. The development of the plan at the appropriate level of practical training in the specialty and rating system knowledge resident in the departments. Frequent visits to the open lessons teachers Preparing visual aids for practical classes (tables, charts, slides) at a high level. The development of the plan at a sufficient level of practical training in the specialty and rating system knowledge resident in the departments. Frequent visits to the open lessons teachers. Preparing visual aids for practical classes (tables, charts, slides) in compliance with the requirements of the department. The development of the plan of practical training in the specialty and rating system knowledge resident in the department at a good level. Visits open lessons teachers. Preparing visual aids for practical classes (tables, charts, slides) in compliance with the requirements of the department. The development of the plan of practical training in the specialty at the appropriate level rating system knowledge resident in the department. Visits open classes of teachers in sufficient volume. 38 Preparing visual aids for practical classes (tables, charts, slides) in compliance with the requirements of the department. The development of the plan of 76-78 practical training in the specialty and rating system knowledge resident in the department. Visits open lessons teachers are inadequate. Preparing visual aids for practical classes (tables, charts, slides) are not in full. The development of the plan of practical training in the specialty and rating 72-75 system knowledge resident in the department at the required level. Single visit to the open lessons teachers. Preparing visual aids for practical classes (tables, charts, slides) are not in full. The development of the plan of practical training in the specialty and rating 65-75% 69-71 system knowledge resident in the department below the required level. Single visit to the open lessons teachers. Preparing visual aids for practical classes (tables, charts, slides) are not in full. The weak development of the plan of practical training in the specialty and rating 65-68 system knowledge resident in the department. Single visit to the open lessons teachers IR at the end of this semester include: in the III semester - writing 100 tests and 25 case studies, max. -100 points. CRITERIA levels of estimates (%) points 96-100 86-100% 91-95 7685% 6575% Proper preparation (methodically and in the subject) with the creative approach of complicated tests with several correct answers. Methodically competent drawing on the subject of complicated tests with several correct answers. 86-90 Proper preparation on the subject of complicated tests. 82-85 Proper preparation (methodically and in the subject) with the creative approach of complicated tests with the correct multiple responses. 79-81 Methodically competent drawing up with a creative approach complicated tests with multiple correct answers, with only minor errors. 76-78 Proper preparation of tests with two correct answers, with only minor errors. 72-75 Compilation of simple tests with not enough answers. 69-71 Compilation of simple tests with not enough answers correctly. 65-68 Compilation of simple tests with not enough answers to serious errors. at the end of IV semester - making instructional recommendations to conduct workshops with students: max. -100 points. points CRITERIA (%) 39 96-100 86-100% 91-95 7685% 6575% Drafting of educational and methodical manuals at a high level in compliance with educational and methodical study of the Institute, with additional modern literature. Drafting of educational and methodical manuals on the level of compliance with the requirements in training and methodical study of the Institute, with additional modern literature. 86-90 Drafting of educational and methodical manuals on the proper level according to the requirements of educational and methodical study of the Institute, with additional modern literature. 82-85 Drafting of educational and methodical manuals in compliance with educational and methodical study of the Institute, with the use of textbooks published in the past 5 years and Activities. 79-81 Drafting of educational and methodical manuals in compliance with educational and methodical study of the Institute, with the use of textbooks, published more than 5 years and the method specified. 76-78 Drafting of educational and methodical manuals in compliance with educational and methodical study of the Institute, with the use of textbooks. 72-75 Drafting of educational and methodical manuals with the requirements of educational and methodical study of the institute., 69-71 Compilation of training and methodological benefits without regard for educational and methodical study of the institute. 65-68 Compilation of training and methodological benefits without regard for educational and methodical study of the Institute and with incomplete coverage of the material V at the end of the semester - holding an open lesson: max. -100 points. levels of estimates CRITERIA (%) points 96-100 86-100% 91-95 7685% Holding an open lesson with a creative approach to high methodological level, using modern technology training and monitoring the student's knowledge. Holding an open lesson with a creative approach at the appropriate methodological level, using modern technology training and monitoring the student's knowledge. 86-90 Holding an open lesson with the use of modern technology training and monitoring the student's knowledge. 82-85 Holding an open lesson with the correct methodological approach and the application of the rating control of students' knowledge. 40 6575% 79-81 Holding an open lesson with the correct methodological approach but with minor errors in the application of the rating control of students' knowledge. 76-78 Holding an open lesson with the correct methodological approach but with some errors in the use of the rating control of students' knowledge. 72-75 Holding an open lesson with methodological errors in the use of learning technologies and using knowledge control. 69-71 Weak holding an open lesson with methodological errors without the use of modern learning technologies and knowledge control. 65-68 Weak holding an open lesson with methodological errors without the use of modern technology and learning from serious errors in the application of knowledge control. A scientific project is evaluated on a monthly basis in the form of PC IV, V, VI semester. IV semester - collection and analysis of the literature on a particular issue of Medicine (in accordance with the theme of a research project) Levels of evaluation research project, max. -100 points. Отменить изменения levels of estimates (%) 86-100% 7685% 6575% CRITERIA points 96-100 Implemented a comprehensive collection of literature, including foreign, data, Internet, and its analysis covering the given scientific problem in this area is available is presented competent language 91-95 By collecting literature, including foreign, data, Internet, and its analysis covering the given scientific problem in this area is available is presented competent language 86-90 By collecting literature, including foreign and analysis covering the given scientific problem in this area is available is presented competent language 82-85 Implemented a comprehensive collection of Russian literature, new and underutilized foreign sources, given a competent scientific analysis of the scientific problem 79-81 Collection of literature is insufficient, under-utilized new and foreign sources have given an incomplete analysis of the scientific problems 76-78 Collection of literature is insufficient, under-utilized domestic and foreign sources have given an incomplete analysis of the scientific problems 72-75 Collection of literature is insufficient, do not use foreign sources have given incomplete analysis 69-71 Used primarily sources published over 5 years ago, made a cursory analysis Used mainly in older sources including textbooks, performed a cursory analysis 65-68 41 V semester - the results of their investigations and their interpretation CRITERIA levels of estimates (%) 86-100% 7685% 6575% points 96-100 These results of the research were statistically processed, the results correctly interpreted and discussed in comparison with results from other researchers at a high scientific level 91-95 These results of the research were statistically processed, given their interpretation is not complete, the results competently discussed in relation to the findings of other researchers on a good scientific level 86-90 These results of the research were statistically processed, given their interpretation is not complete, the results competently discussed. 82-85 These results of the research were statistically processed. Research results and their interpretation in comparison with the results of other researchers do not fully carried out 79-81 These results of the research were statistically processed, but not completely. Research results and their interpretation in comparison with the results of other researchers conducted entirely 76-78 These results of the research were statistically processed, but there are errors in the statistical analysis. Research results and their interpretation in comparison with the results of other researchers do not fully carried out 72-75 These results of the research were statistically processed. Interpretation of the results of our studies in comparison with the results of other researchers. 69-71 These results of the research are not subjected to statistical analysis. The interpretation of the results of our research in comparison with results from other researchers. 65-68 These results of the research are not subjected to statistical analysis. Interpretation of the results of our studies in comparison with the results of other researchers absent VI semester - the protection of a research project, max. -100 points. CRITERIA levels of estimates (%) points 96-100 86-100% 91-95 The scientific project is designed to fully when writing individual fragments was lagging behind the deadlines. Reported to competent language using modern visual aids. Practical recommendations are relevant and can be widely used in the practice of a physician. The scientific project is designed to fully when writing individual fragments was lagging behind the deadlines. Reported to the use of modern visual aids. Practical recommendations can be used in the practice of a physician. 42 76-85% 86-90 The scientific project is designed to fully when writing individual fragments were minor delays on the timing of the execution. Reported to competent language using modern visual aids. Practical recommendations can be used in the practice of a physician. 82-85 The scientific project is designed well, when writing individual fragments was lagging behind the deadlines. Visual tools do not fully cover the topic of a research project 79-81 The scientific project is designed well, when writing individual fragments was a backlog of deadlines. Visual tools do not fully cover the topic of a research project 76-78 The scientific project is decorated with minor comments in writing of individual fragments were lagging behind the deadlines. Visual tools do not fully cover the topic of a research project 72-75 The scientific project is decorated with errors when writing individual fragments had a significant backlog of deadlines. Reported to using visual aids 69-71 The scientific project is decorated with errors when writing individual fragments had a significant backlog of deadlines. Reported to without the use of visual aids 65-68 The scientific project is decorated with errors when writing all the tracks was a large backlog of deadlines. Reported to without the use of visual aids 65-75% The final control of the student graduate research project at the IV and V semesters conducted Certification Commission for semi-annual and annual performance appraisals resident with protocol prior discussion by the department. At the VI semester conducted, and a research project with the rating items. The maximum score - 100. Defence research project on the state assessment is carried out at the end of VI semester and evaluated by a special commission set up by order of the head of the institution on the following criteria. levels of estimates CRITERIA (%) 86-100% 7685% points 96-100 The quality of a research project reflects the excellent preparedness resident to research activities, the ability to analyze the information and the ability to generalize. The presented review has praised the scientific project. 91-95 The quality of a research project reflects good preparation for the resident to research activities, the ability to analyze the information and the ability to generalize. The presented review has praised the scientific project. 86-90 The quality of a research project reflects the excellent preparedness resident in research activities. The presented review has praised the scientific project. 82-85 The quality of a research project reflects good preparation for the resident to research activities, the ability to analyze the information and the ability to generalize. The presented review provides a good estimate of the scientific project. 43 6575% 79-81 The quality of a research project reflects good preparation for graduate student research. The presented review provides a good estimate of the scientific project 76-78 The quality of a research project reflects a sufficient qualification for resident research. The presented review contains a number of unimportant comments. 72-75 The project is designed to reflect a satisfactory resident preparedness for research activities, and the ability to analyze the information and the ability to generalize. review of the positive 69-71 The project is designed to reflect a satisfactory resident preparedness for research activities, and the ability to analyze the information and the ability to generalize. A review is positive, but there are observations. 65-68 The project is made banal and does not reflect the degree of preparedness of residents to the research activities, the ability to analyze the information and the ability to generalize. A review is positive, but there are substantive comments The order of evaluation and grading of students' knowledge of the Judiciary. The rating system is a modern and adequate method for monitoring learning styles of all sections of the curriculum of Magistrates, which allows a differentiated and objectively assess students' knowledge of students graduate. In assessing students' knowledge of Magistrates considered his attendance, active in class, participate in the manipulation, the degree of preparation for seminars, lecture notes the usefulness of including elaborated literature in a foreign language, participation in clinical conferences, conducting workshops, preparation of training materials, conducting research research. Graduate student assessment is carried out regularly during each semester in two phases in the following forms: Stage 1 - the current control (TC) Stage 2 - Final control (IR) - semi-annual or annual certification. Each of these phases is estimated B100 control points. Graduate student who receives the discipline throughout the semester for more than 65% of the maximum score is considered to be high performing. All the knowledge and practical skills gained by studying all program areas, including research and teaching activities, the preparation of a research project and the results are evaluated in the certification of the State of rating points and recorded separately in the rating booklet graduate student. Graduate students who receive less than 65% of the maximum score for the academic year are considered to be underachieving and deducted from the number of graduate students in the prescribed manner on the orders of the rector. Assessment criteria of rating points for graduate students have the following grades: Satisfactory - 65-75,9% maximum score of TC and IC. Okay - 76-85,9% maximum score of TC and EC. Excellent - 86-100% of maximum points of TC and IC. Conclusion. Points recruited graduate students for a semester as a committee or subcommittee shall be recorded in the academic journal in the department. To carry out the IR for each resident in the graduate dean's office presented: 1. Folder with daily protocols of graduate students. 2. Official results of TC or PC in the relevant disciplines and topics of the curriculum with an indication of points and their corresponding percent for the signature of the program director and 44 head of the department. 3. Certification graduate student sheet, which includes sections: A. The results of TC (PC) in the form of points of interest and appropriate assessment (preexposed in the department). B. The results of IR as a score, assessment and appropriate assessment (adjustable on the results of the semi-annual or annual certification). B. The final results in the form of points of interest and the corresponding estimate calculated by the sum of the two previous indicators 4. LITERATURE. MAIN REFERENCES 1.Virusnye hepatitis - S.N.Sorinson, 2-nd edition, St. Petersburg, 1999. 2. Guidance on infectious diseases in children - VF Uchaikin, ed. GEOTAR, medicine, 1998. 3. Chronic hepatitis in children - FI Inoyatov, Tashkent, ed. Abu - Ali Ibn Sino, 1997. 4. Diseases of the liver and biliary tract - Sheila Sherlock, 1999. 5. Viral hepatitis - Mayer ed. GEOTAR, 1997. 6. Guide to intestinal infections - Acad. I.K.Musabaev, Tashkent, Vol. Medicine, 1980. 7 Guidelines for airborne infections - Acad. I.K.Musabaev, Tashkent, Vol. Medicine, 1982. 8. Manual of hemorrhagic fever, typhus, encephalitis - Acad. I.K.Musabaev, Tashkent, Vol. Medicine, 1986. 9.Vozdushno-respiratory infection in children - YV. Chlamydia pneumoniae, VP. Mihonenko and others, St. Petersburg, 2000 10.Difteriya in children - VZ Ivanov, St. Petersburg, 2000. 11.Differentsialnaya diagnosis of infectious diseases - A.G.Kazantsev and others, Moscow, 1999. 12. Mumps in children. - O.S.Mahmudov etc. Tashkent, 1984. 13.Dizenteriya in children - O.S.Mahmudov, Tashkent, 1985. 14.Salmonellezy in children - O.S.Mahmudov, Tashkent, 1990. 15. Pseudotuberculosis in children - O.S.Mahmudov, Tashkent1986g. 16. Typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever in children - O.S.Mahmudov, Tashkent, 1980. 17. Ku - fever in children - O.S.Mahmudov, Tashkent, 1984. 18. Croup in children - NI. Nisevich, Moscow, 1971. 19. Brucellosis in children - K.D.Dzhalilov, Tashkent 1975. 20.Anginy in children - L.M.Kovaleva, O. Lakotkina, Moscow, 1981. 21.Ostrye viral encephalitis in children - E.V.Leshinskaya, IN Martynenko, Moscow, 1980. 22.Meningokokkovaya infection - Sh.H.Hodzhaev AND. A. Sokolova, Tashkent, 1986. 23.Kor - T.A.Daminov, NU Tadjiev, Tashkent, 2005. 24. Nosocomial infections in children T.A.Daminov, I.N.Nizametdinov, M.H.Sharapova, Tashkent, 2003. 25.Meditsinsky Journal of Uzbekistan. 26.Klinicheskaya medicine. Magazine. 27 Doctor. Magazine. 28 .. Pediatrics. Magazine. 29 .. Clinical Immunology and Allergology. Magazine. 30.Patologiya. Magazine. 31.Rotavirusnaya infection - Bukrinskaya AG and others, Moscow, 1989. 32. Fundamentals of vaccination - DA Askarova etc. Tashkent, 2003. 33.Gepatit and consequences of hepatitis - K.P.Mayer, a practical guide, translated from German, GEOTAR - honey. Moscow 2004. 34.Infektsionnye disease and epidemiology - Pokrovsky VI and co-authors textbook for high schools - GEOTAR honey, Moscow, 2003. 45 Further reading: 1.Virusnye hepatitis - a method. recommendations kaf.infektsionnyh disease Tashkent-2004. 2.Virusny hepatitis C in children metodich. recommendations Sh.T.Azimov Tashkent - 2002. 3 .. Early posindromnaya infektsionnh differential diagnosis of diseases with diarrhea syndrome - metod.posobie, kaf.infektsionnyh disease Tashkent-2004. 4.Tsitomegalovirusnaya infection - metod.rekomendatsii, Research A.G.Tashkent, 2003. 5.TORCH - infection and pregnancy-B.K.Saidkariev et al., Tashkent, 2005. 6.Antimikrobnaya therapy in pediatrics-DZh.D.Nelson.perevod from English. 1997. 7.Viral infections of infancy and childhood-The new York Academy of medicine, Harry.Rose MD 1996y. 8.Diseases of the Kidney-Maurice B, Strauss M.D. Boston 1991 9.Text book of pediatrics - Yictor C. Yauqhan 1985 10/Infections diseases - Paul D. Hoeprich, 1983. 11Rukovodstvo on pediatric emergency C-C Agzamhodzhaev, N.S.Agzamhodzhaeva, ER Ermanova-Tashkent-2005. 12.Immunomoduliruyuschaya therapy in pediatrics - metod.rekomendatsii, Tashkent, 2003. Table of Contents: 1.ABBREVIATURA AND DEFINITIONS 2. INTRODUCTION 3. IMPLEMENTATION OF EDUCATIONAL PROCESS 4. TEMS THE CLUSTERS. 5. PLANS OF SEMINARS 6. MASTER'S PRACTICE 7. MONITORING OF PROGRESS. 8. LITERATURE. 9. APPENDIX 46