File - Yr 12 Biology
advertisement

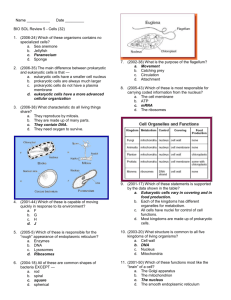
CELLS AND CELL STRUCTURES Question 1 A typical prokaryotic cell has: a) Nucleic acid b) Chloroplasts c) A small nucleus d) Membrane bound organelles Question 2 A defining characteristic of a prokaryote is the: a) Presence of a cell wall b) Presence of a nucleus c) Absence of ribosomes d) Absence of membrane bound organelles Question 3 A plant cell can be distinguished from an animal cell because of the presence of: a) Cytosol b) A cell wall c) A nucleus d) Chloroplasts Question 4 Observe the internal structures of the following cell. It is most likely to: a) Be a cheek epithelial cell b) Be a mature red blood cell c) Require high levels of oxygen d) Produce high levels of sugars Question 5 A prokaryotic cell contains a) A nucleus b) A vacuole c) Ribosomes d) Endoplasmic reticulum Question 6 Which of the following features found in a eukaryotic cell is also found in prokaryotic cells? a) Golgi apparatus b) Nucleus c) Linear chromosomes d) Endoplasmic reticulum e) Ribosomes Question 7 A human cell which contains a large amount of rough ER, many Golgi bodies and a prominent nucleus is most likely a: a) Muscle cell b) Secretory cell c) Epithelial cell d) Nerve cell e) Red blood cell Question 8 Which of the following organelles in a eukaryotic cell are correctly matched with their function? a) Nucleolus: assembly of nucleus b) Mitochondria: nucleotide degradation c) Lysosomes: synthesis of lipids d) Smooth ER: ATP synthesis e) Rough ER: protein synthesis Question 9 Which of the following is found in eukaryotic cells but not in prokaryotic cells? a) RNA b) Mitochondria c) Chlorophyll d) Lipids e) Ribosomes Question 10 Compared to human cells that secrete few proteins, human cells that secrete a large number of proteins are most likely to have: a) An extensive Golgi apparatus b) A thicker cell membrane c) Additional copies of the genes that code for the proteins d) Larger chromosomes e) Two or three rather than 1 ribosome Question 11 Which of the following (I to III) can contain functional ribosomes I Cytoplasm II Membrane of the ER III Mitochondria a) b) c) d) e) I only II only I and II only I and III only I, II and III Question 12 Which of the following structures can be found in all cells? a) Nucleus b) Golgi body c) Vacuole d) Ribosomes e) Centrioles Question 13 Which of the following cell types would you expect to be abundant in ER and Golgi bodies? a) Plasma B cells (which produce antibodies) b) Adipose cells (which store fats) c) Islets of Langerhans cells (secrete insulin) d) Red blood cells (transport oxygen) SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Question 1 (4 marks) The following table contains images of a number of structures seen in cells. Name each structure and identify a function of each. Question 2 (1 mark) Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic or eukaryotic. To which group do bacterial cells belong? __________________________________________________________________________________ Question 3 (3 marks) The table below contains the names of 6 cellular structures found in a plant cell. In the list below the table a number of functions of cellular structures are given. Complete the table by matching the letter of a function to the appropriate cellular structure in the plant cell. Cellular structure Golgi apparatus Mitochondria Chloroplast Lysosome Vacuole Cell membrane A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Matching function (A-H) Site where ATP is generated Digestion of macromolecules Site of protein synthesis Proteins modified and packaged for transport Selective barrier that limits movement in or out of the cell Solar energy is converted to chemical energy Contains DNA Storage of wastes and other materials