1. MOISTURE in the air
advertisement

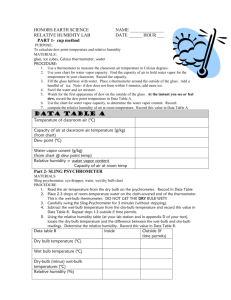
Meteorology Moisture in the Atmosphere Humidity Humidity – amount of WATER VAPOR in the air. When an object (including air) is heated, it EXPANDS. The expansion is creating “empty” space that can be filled with water vapor. Water holding capacity AIR TEMPERATURE Relative Humidity Relative Humidity – a comparison of the actual amount of WATER VAPOR in the air to the amount it can HOLD at a given temperature. Expressed as a PERCENTAGE Effect of Temperature on Relative Humidity Relationship: as air temperature INCREASES, and the amount of moisture remains the same, Relative Humidity relative humidity will DECREASE. AIR TEMPERATURE Warm Air & Relative Humidity Air warms and expands Warmer air has a HIGHER water vapor holding capacity As air temperature DECREASES, its ability to hold more water DECREEASES, and its relative humidity INCREASES. Effect of Time of Day on Relative Humidity If relative humidity decreases as air temperature increases then: o The highest relative humidity will occur at the COOLEST time of day 5:00am o The lowest relative humidity will occur at the WARMEST time of day. 2:00pm Dew Point Temperature Dew Point Temperature – The temperature to which air must be COOLED to reach SATURATION. o If the air temperature and dew point temperature are EQUAL, the relative humidity is 100%. o If the air temperature falls BELOW the dew point temperature, CONDENSATION begins. Sling Psychrometer Consists of two thermometers. One is the dry thermometer (dry-bulb) and the other has a wet cloth on the end (wet-bulb). The sling psychrometer is swung around and the wet cloth dries (evaporation) if the air is NOT saturated. Evaporation absorbs heat and is a COOLING process so the wet-bulb temperature should always be EQUAL TO or LOWER than the dry-bulb. Relationships The drier the air, the MORE evaporation will occur resulting in GREATER cooling. In turn, the difference in temperature between the dry-bulb and wet-bulb will be GREATER. The more humid the air, the LESS evaporation will occur resulting in LESS cooling of the wet-bulb thermometer. In turn, the difference in temperature between the dry-bulb and wet-bulb will be SMALLER. At saturation, the temperature difference between the dry-bulb and wet-bulb would be ZERO. Cloud Formation Clouds - Tiny droplets of liquid water or tiny ice crystals suspended in air. Conditions needed for cloud formation: 1. MOISTURE in the air 2. COOLING air temperature 3. Condensation Nuclei – AEROSOLS or DUST particles in the atmosphere which provide a SURFACE for water molecules to condense on Cooling in the Atmosphere As air RISES, the atmospheric pressure surrounding the parcel of air decreases. Therefore, the parcel of air EXPANDS in volume. As it expands, it becomes COOLER. When the temperature of the air falls BELOW the dew point temperature, the water vapor will CONDENSE and a cloud will form. Examples of Condensation – Dew Dew is MOISTURE that CONDENSES at the GROUND level. The layer of air within about a meter above the ground experiences rapid changes in TEMPERATURE from day to night. Therefore the temperature may be COOLER on the ground than the air above. Consequently, the air temperature close to the ground may cool to BELOW the dew point temperature for CONDENSATION to form. Moisture, therefore, is observed on grass and on the surface of some objects such as with metal surf Condensation – Frost Frost is observed as ICE crystals mostly on grass. It forms when dew FREEZES because the air temperature falls BELOW the level necessary for freezing (from liquid to solid form of moisture). Frost may also form under the process of DEPOSITION when water vapor is cooled so rapidly it forms ice (from gas to solid form of moisture). Condensation – Fog Fog can be described as a CLOUD forming very close to or at ground level. It requires air with sufficient MOISTURE to cool or to be cooled to a temperature to achieve CONDENSATION. Fog is more common in VALLEYS and near CREEKS or STREAMS. It also most commonly occurs overnight and during the morning.