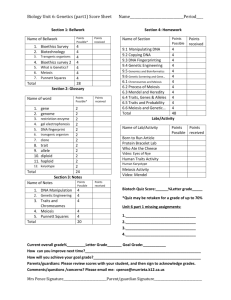
SOCIAL STUDIES: Skokie DISTRICT 68
advertisement

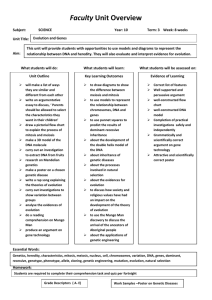
SCIENCE: Forest Ridge School District 142 Heredity, Variation, & Biodiversity Unit: Eighth Grade Unifying Theme: Evidence & Explanation Essential Question: How can we support our explanations (claims) with supporting evidence gathered through scientific investigation and technological design? Guiding Questions: How are characteristics of one generation of organisms passed to the next? What are the consequences regarding inheritance and variation across generations? How are the characteristics of one generation of organisms related to the next generation? Why do individuals of the same species vary in how they look and function? What are the costs/benefits of genetic engineering and testing? Big Ideas Reproduction is a characteristic of all living systems; some organisms reproduce sexually while others reproduce asexually. Power Standards Compare and contrast sexual and asexual reproduction. Hereditary information is contained in genes located in the chromosomes of each cell. One or many genes can determine an inherited trait of an individual. Examine DNA evidence to infer patterns of change. Evidence of change over time can be inferred by examining DNA sequences There are risks/benefits associated with genetic engineering and genetic testing. Determine the relationship of genes and chromosomes to inherited traits. Analyze risks/benefits and develop claims supported by evidence. Descriptors: Based on National & State Documents Justify why DNA is referred to as the blue print of life. Predict visible effects and variations amongst physical features and cellular functions of organisms based upon genetic combinations. Analyze patterns of inheritance and probability of genes and traits being passed on using Punnett squares and pedigrees. Analyze the transmission of genetic traits, diseases and defects. Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis. Compare and contrast characteristics of organisms produced from a single parent with those of organisms produced by two parents. Analyze the risks/benefits of genetic testing and engineering. ASSESSMENT Summative: Support with evidence the pro and/or diseases based upon an transmission of genetic traits, Formative: Compare and contras Diagram meiosis and Compare characterist parent (asexual) with parents (sexual). Create a Punnett Squ Analyze a Punnett Sq Explain why DNA is re Summative: Formulate a position on genet claim with evidence. Formative: Create a cost/benefit personal cost, person a decision of genetic Distinguish claim from Summative Assessment Write to a person who had a m with evidence why they should State what experiences they m Formative Assessment Use formative assessm Baby Mice - Adaptatio Journal Entry Graph Data/Conduct An Calculations Scientific Inquiry Scientific inquiry is a dynamic process that is not limited to one scientific method. Propose scientific questions and engage in active inquiry gathering and prioritizing evidence, formulating explanations, making connections to scientific knowledge and communicating and justifying explanations. Prioritize evidence Develop an explanation based upon evidence/data Develop a vaccine based upon analysis of generated data from coin toss. (DNA Sequence) Formative: Collect and represent Analyze data (DNA Se Use analysis to devel Generate, represent and analyze data Generate data Organize data Represent data Analyze data Formative: Collect and represent Analyze data (DNA Se Use analysis to devel Justify explanations Formative: Create a cost/benefit personal cost, person a decision of genetic Distinguish claim from Inquiry engages learners in asking scientifically oriented questions, gathering and prioritizing evidence, formulating explanations, making connections to scientific knowledge and communicating and justifying explanations. The Nature of Science Science is an imaginative endeavor that is subject to modification as new information challenges current theories. It involves the collection of data, the use of logical reasoning, argumentation and the devising of hypotheses and explanations informed by evidence. Habits of Mind Scientists keep honest/unbiased, clear and accurate records, value hypotheses and understand that more than one explanation can be given for the same evidence. Summative: Formulate a position on genet claim with evidence. Scientists value the role of computation and estimation in their work. Scientists use a variety of tools to inform their observations. Scientists organize information using tables, graphs, diagrams and symbols. Scientists question claims based on vague attributions and are skeptical of arguments based on small data samples. Scientists embrace unexpected results. Vocabulary Tier Two: evidence, claim, support, argue, defend, analyze, justify, generation Tier Three: DNA, Punnett Square, nucleotides, sexual, asexual, meiosis, mitosis, genetic engineering, cloning, genetic testing, dominant, recessive, alleles, chromosomes, inheritance, variation