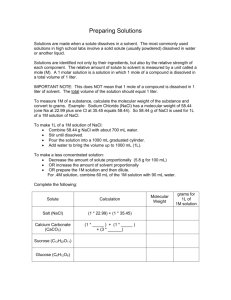
solvent particles
advertisement

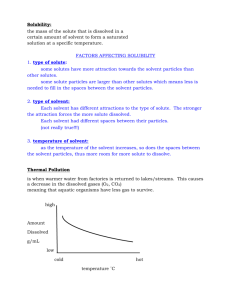
Chapter 15 Solutions Worksheet 1 Broz Fill In The Blank 1. _____________ is a uniform mixture that may contain solids, liquids, or gases. 2. The substance that dissolves a solute to form a solution is a ______________. 3. A substance that dissolves in a solvent is _______________ in that solvent. 4. A substance that does not dissolve in a solvent is ________________ in that solvent. 5. Two liquids that are soluble in each other are __________________. 6 __________________ is the process of surrounding solute particles with solvent particles to form a solution 7. Hydration is __________________ in water. 8. ____________________________________ is the general rule used to determine whether solvation will occur in a specific solvent. 9. There are 3 ways to increase the rate at which the solute dissolves: 1) ______________ 2) increase the ______________ 3) increase the ________________ 10. __________________ refers to the maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specified temperature and pressure. 11. A/An ________________ solution contains the maximum amount of dissolved solute for a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature and pressure. 12. A/An ________________ solution contains less dissolved solute for a given temperature and pressure. 13. ___________________ only affects the solubility of gaseous solutes and gaseous solutions. 14. ___________________ affects the solubility of all substances. 15. A/An _______________________ solution contains more dissolved solute than a saturated solution at the same temperature. 16. The __________________ of a gas in any solvent increases as its external pressure increases. 17. ______________________ states that at a given temperature, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas above the liquid. 18. The formula for percent by mass = __________________________________________. 19. The formula for percent by volume = ________________________________________. 20. The formula for Molarity (M) = ____________________________________________. 21. Pre-made concentrated solutions are called _________________ solutions. 22. The formula for molality (m) = _____________________________________________. 23. _______________________ properties are physical properties of solutions that are affected by the number of particles. 24. Colligative properties include freezing point ___________ and boiling point ____________. 25. Ionic compounds are called electrolytes because they ________________ in water to form a solution that conducts an electric current. 26. 1 mole of NaCl will produce __________________ mole/s of particles. 27. 1 mole of sucrose (C12H22O11) will produce _______________mole/s of particles. 28. 1 mole of BaCl2 will produce ___________________ mole/s of particles. 29. 1 mole of C6H12O6 (glucose) will produce _______________ mole/s of particles. 30. 1 mole of Na2SO4 will produce __________________ mole/s of particles. 31. 1 mole of AlCl3 will produce __________________ mole/s of particles. 32. Boiling point elevation is due to the number of ___________________ particles in the solution. 33. The freezing point of a solution is always ________________ than that of the pure solvent. Chapter 15 Solutions Worksheet 2 Broz Problems 1. You have 1500.0g of a bleach solution. The percent by mass of the solute sodium hypochlorite, NaClO, is 3.62%. How many grams of NaOCl are in the solution? 2. Calculate the percent by mass of 3.55g NaCl dissolved in 88g water. 3. Calculate the percent by mass of benzene in a solution containing 14.2g of benzene in 28.0g of carbon tetrachloride. 4. If you have 100.0mL of a 30.0% aqueous solution of ethanol, what volumes of ethanol and water are in the solution? 5. What is the percent by volume of ethanol in a solution that contains 35mL of ethanol dissolved in 115mL water? 6. A saline solution contains 0.90g of NaCl per 100.0mL of solution. What is its molarity? 7. Calculate the molarity of 0.060mol of NaHCO3 in 1500mL of solution. 8. You need 250mL of 0.20M NaCl; the stock solution on hand is 1.0M NaCl. How do you prepare the required solution? 9. You need 500.0mL of 0.50M NaCl; the stock solution on hand is 2.0M NaCl. How do you prepare the required solution? 10. How many kg of water must be added to 9.0g of oxalic acid, H2C2O4, to prepare a 0.025m solution? 11. Calculate the molality of a solution prepared by dissolving 10.0g of NaCl in 600.0g of water. Chapter 15 Solutions Worksheet 3 Broz 12. How many g of potassium iodide must be dissolved in 500.0g of water to produce a 0.060 molal KI solution? 13. What is the boiling point of a solution that contains 1.20mol of NaCl in 800.0g of water? Kb of water is 0.512ºC/m. 14. What is the boiling point of a solution that contains 1.25mol of CaCl2 in 1400g of water? Kb of water is 0.512ºC/m. 15. What is the freezing point of 1.40mol of Na2SO4 in 1750g of H20? Kf of water is 1.86ºC/m. 16. What is the freezing point of a 0.40m solution of sucrose in ethanol? Kf of ethanol is 1.99ºC/m. The freezing point of ethanol is -114.6ºC. Solubility / TAKS 1. How many grams of NaNO3 will dissolve in 100grams of water at 40ºC? 2. How many grams of Na2SO4 are needed to make a saturated solution at 20ºC? 3. Is 100grams of water at 55ºC saturated if 40grams of NH4Cl is added? 4. How many grams of NaCl will dissolve in 100grams of water at 50ºC? 5. How many grams of KBr will dissolve in 250grams of water at 10ºC? 6. If 60grams of KNO3 in 100grams of water is saturated, what is the temperature? 7. Using the chart above, 80grams of a compound is saturated at 10ºC, what is the compound? Chapter 15 Solutions Worksheet 4 Broz