Understanding Presentations
advertisement

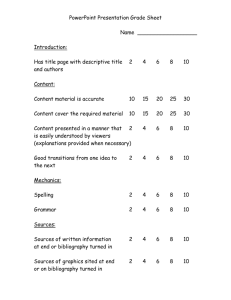
Understanding Presentations Everything you say, do and show effects understanding. 1. Why use presentation software? 2. How does the way I use the show impact the audience? 3. What can I do to make a slide show effective for the audience? First function, then form Effective Order of Verbal Content Give the epitome example (initial synthesis principle) Zoom in to a part of the epitome, then return to epitome, then back to another detail Instruction moves from general to detail, and from simple to complex At the beginning of each elaboration, relate it familiar through analogy Teach the most important thing first Keep the elaboration short enough to be recognized and synthesized (less than 5 ideas), but long enough to give detail (at least 3) Every so often, summarize before moving on Graphics Processing graphics uses Perception (sense understanding) Cognition (mental work) Benefits of Good Graphics Improves concept retention Shows visual and spatial relationships Organizes well, makes easier to remember Promotes usability Motivates learners or promotes trust Problems with Graphics People don’t understand abstract or complex visuals Cognitive effort required to get complex visual Can distract or mislead learners Not appropriate for every purpose Stages of Processing Graphics 1. Preattention o When we look at graphics, we perceive before we pay direct attention (preattentive perception) o Preattentive perception determines what is figure (girl) and what is ground (background) o We look horizontally and vertically (not front to back or diagonal) o We make images into meaningful hierarchies 2. Attentive perception o Directed by organization we made preattentively o Draws on cognitive resources o Is limited and selective (we choose what to pay attention to) o May be influenced by forming or chunking o Is reduced by too much or too little to look at Discontinuity = Less Understanding 3. Cognition o People form partial interpretation almost immediately, then keep amending o Use all information available to interpret (irrelevancies become “noisy”) o Is text-driven – cues come from prose and graphics (put picture with words) o Is knowledge driven (beliefs and preknowledge effect perception) So I should. . . Concept Create Pre-attention Create Attention (first impression) Support Motivation Support Cognition Practical Application o chunking o grouping o sequencing o appropriate dominance relationships o emotional response (affective) o establish visual relevance as close to audience experience as possible o chunking o grouping o sequencing o level of detail o word and image combinations o layout (rule of thirds, use of occlusion, white space) o consistency of document