Tolerogenic Effect of Graft-Derived Dendritic Cells in Facial Allograft
advertisement

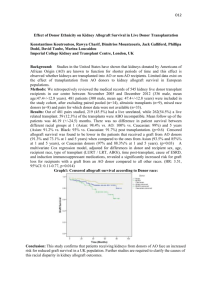
Tolerogenic Effect of Graft-Derived Dendritic Cells in Facial Allograft Model Aleksandra Klimczak, PhD, Galip Agaoglu, MD, Sakir Unal, MD, Maria Siemionow MD,PhD INTRODUCTION: Clinical application of composite tissue allograft transplants opened discussion on the restoration of facial deformities by allotransplantation. We have established an experimental full-face and hemiface allograft transplantation model in the rat (1-3). Hemifacial transplantation model in semi-allogeneic and fully-allogeneic transplants served as an experimental basis to study immunological aspects of this new composite tissue allograft. Recently we have reported operational tolerance in fully MHC mismatched rat hemifacial allograft model under low dose of cyclosporine-A (CsA) monotherapy (3-5). The potential of graftderived dendritic cells (DC) on chimerism induction was tested in hemiface allograft under CsA monotherapy across MHC barrier. MATERIAL AND METHODS: Twenty-four hemiface transplantations were performed in 4 groups (6 rats each). Rejection controls included semi-allogenic LBN(RT1l+n) (Group-1) and fully-allogenic ACI(RT1a) (Group-2) donors. Group-3 (LBN donors) and Group-4 (ACI donors) received tapered dose of CsA monotherapy started from 16 mg/kg/day, tapered to 2 mg/kg/day and maintained at this level thereafter. Surgical procedure. The composite hemi-facial flaps consisted of skin, subcutaneous fat tissue, facial muscles, parotid gland and external ear cartilage and were elevated, based on the jugular vein and common carotid artery. The facial skin of the recipient was removed as a full-thickness skin graft of the same dimensions including external ear but sparing the periorbital and perioral skin. Next, the common carotid artery and jugular vein of the allograft were anastomosed to the common carotid artery and jugular vein of the recipient in end-to-side fashion. Signs of graft rejection were evaluated on daily basis. At different time-point at days 7, 28, 63, 100 samples from lymphoid organs (spleen, lymph nodes, thymus) and blood were harvested. Flow cytometry monitored donor-specific chimerism for MHC class-I RT1n and RT1a antigens. Mechanism of allograft acceptance was assessed by the presence of donor dendritic cells (DDC) using monoclonal antibody for DC (clone OX-62) in combination with monoclonal antibodies specific for donor MHC class-I RT1n (clone MCA156)or RT1a (clone C3) antigens and double immunofluorescence technique. Apoptotic cells were detected by TUNEL technique. RESULTS: Face transplants under CsA monotherapy from LBN and ACI donors displayed presence of passenger leukocytes within lymphoid organs of recipients. At day 7 post-transplant DDC and donor leukocytes were detected within spleen and lymph nodes of recipients. During follow-up, the number of donor-origin DC significantly increased within spleen but only single cells were present within lymph nodes. DDC were not detected within thymus. Donor-specific chimerism in the peripheral blood of recipients at day 100 measured: LBN recipients at 1.4% for CD4/RT1n, 0.5% for CD8/RT1n and 2.6% for CD45RA/RT1n; for ACI recipients at 16.8% for CD4/RT1a, 3.7% for CD8/RT1a and 0.2% for CD45RA/RT1a. Apoptotic cells were detected at day 7 and during entire follow-up period (100 days) in the lymphoid organs of recipients. CONCLUSION: This study indicated that CsA monotherapy promoted T-cell tolerogenicity of DDC in hemifacial allograft transplants due to functional stabilization of DDC at the immature state. Migration and localization of graft-derived DDC into lymphoid organs of recipient confirmed immunomodulatory function of DDC for skin allograft acceptance in hemifacial allograft model. Anergy of T cells, demonstrated by the presence of apoptotic cells, contributed to longterm hemifacial skin allograft survival. a b c Figure 1. Immunofluorescene staining of the spleen of hemiface transplant recipient for the presence of a) dendritic cells (red staining); b) donor-origin cells RT1a positive (green staining) and c) combination of the staining for dendritic cells and RT1a cells proved that dendritic cells which are present within spleen of face transplant recipients are donor origin (yellow staining, arrow). REFERENCES 1.Siemionow M, Gozel-Ulusal B, Ulusal A, Ozmen S, Izycki D, Zins JE. Functional tolerance following face transplantation in the rat. Transplantation 75:1607-1609, 2003. 2.Gozel-Ulusal B, Ulusal AE, Ozmen S, Zins JE, Siemionow M. A new composite facial and scalp transplantation model in the rat. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:1302-1311, 2003. 3. Demir Y, Ozmen S, Klimczak A, Mukherjee AL, Siemionow M. Tolerance Induction in Composite Facial Allograft Transplantation in the Rat Model, Plast Reconst Surg 114: 1790-801, 2004. 4. Siemionow MZ, Demir Y, Sari A, Klimczak A. Facial Tissue Allograft Transplantation, Transplant Proc 37: 201-204, 2005. 5. Siemionow M, Demir Y, Mukherjee AL, Klimczak A. Development and maintenance of donor-specific chimerism in semi-allogenic and fully major histocompatibility complex mismatched facial allograft transplants. Transplantation 79:558-67, 2005.