Learning Assistance Department
advertisement
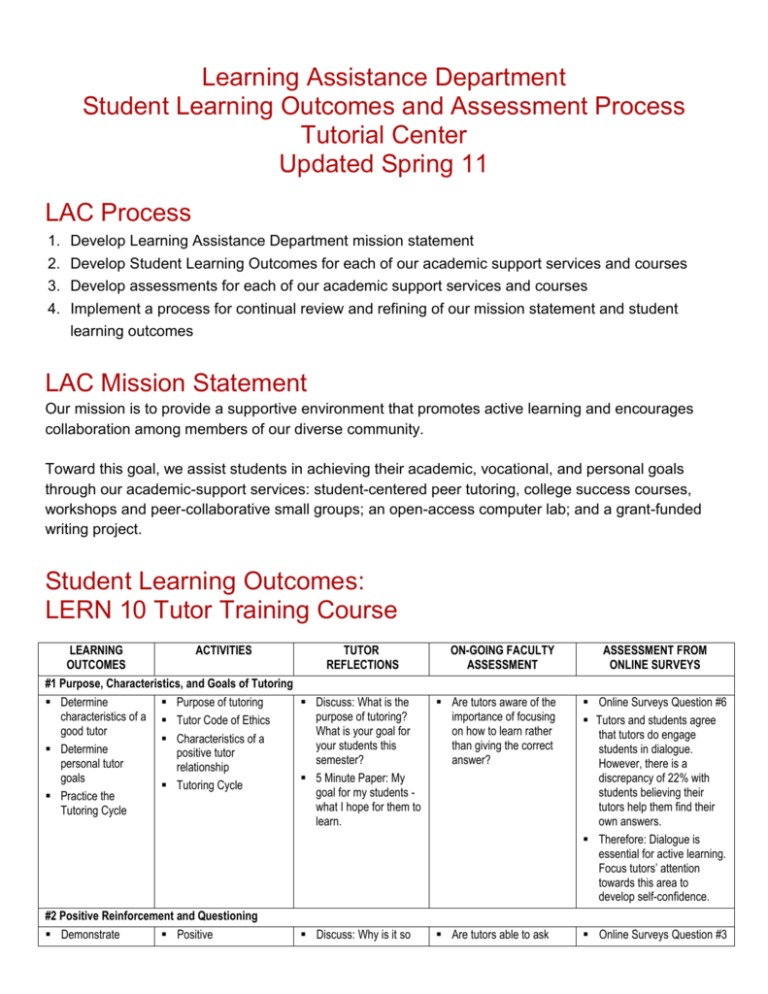
Learning Assistance Department Student Learning Outcomes and Assessment Process Tutorial Center Updated Spring 11 LAC Process 1. 2. 3. 4. Develop Learning Assistance Department mission statement Develop Student Learning Outcomes for each of our academic support services and courses Develop assessments for each of our academic support services and courses Implement a process for continual review and refining of our mission statement and student learning outcomes LAC Mission Statement Our mission is to provide a supportive environment that promotes active learning and encourages collaboration among members of our diverse community. Toward this goal, we assist students in achieving their academic, vocational, and personal goals through our academic-support services: student-centered peer tutoring, college success courses, workshops and peer-collaborative small groups; an open-access computer lab; and a grant-funded writing project. Student Learning Outcomes: LERN 10 Tutor Training Course LEARNING OUTCOMES ACTIVITIES TUTOR REFLECTIONS #1 Purpose, Characteristics, and Goals of Tutoring Determine Purpose of tutoring Discuss: What is the characteristics of a Tutor Code of Ethics purpose of tutoring? good tutor What is your goal for Characteristics of a your students this Determine positive tutor semester? personal tutor relationship goals 5 Minute Paper: My Tutoring Cycle goal for my students Practice the what I hope for them to Tutoring Cycle learn. ON-GOING FACULTY ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT FROM ONLINE SURVEYS Are tutors aware of the importance of focusing on how to learn rather than giving the correct answer? Online Surveys Question #6 Tutors and students agree that tutors do engage students in dialogue. However, there is a discrepancy of 22% with students believing their tutors help them find their own answers. Therefore: Dialogue is essential for active learning. Focus tutors’ attention towards this area to develop self-confidence. Are tutors able to ask Online Surveys Question #3 #2 Positive Reinforcement and Questioning Demonstrate Positive Discuss: Why is it so benefits & elements of positive reinforcement Demonstrate effective questioning techniques Define effective study techniques reinforcement/praise Questioning skills Open-ended questions Blooms Taxonomy for questioning Direct study techniques difficult to ask good questions? What makes a question good? 5 Minute Paper: How I will incorporate questioning and positive reinforcement techniques in my own tutoring. open-ended questions? Are the tutors able to give positive reinforcement and praise in appropriate ways? Students believe their tutors ask questions that make them think more often than tutors think they do. There was a 19% difference in student and tutor perceptions of tutors’ abilities to ask probing questions. Therefore: Provide additional time in tutor training for tutors to gain self-confidence in their questioning abilities. Discuss: Listen actively to others while they tell a bit about a class problem they’ve encountered. You do the same. Tell how it felt to listen, be listened to. 5 Minute Paper: How I will incorporate active listening and promoting independent learning into my tutoring. Are tutors able to listen actively and with focused attention to their students? Online Surveys Question #4 One of the three most-used and highly-rated tutoring strategies by both tutors and students. Tutors consistently rate this section of training as most interesting. Therefore: Continue to emphasize this area. Discuss culture and diversity in small groups. 5 Minute Paper: One area I hope to change in my tutoring sessions as reflected in my discussions on diversity and multicultural differences. Are tutors able to listen actively to, and ask questions of, others when they speak about their cultures? Online Surveys Question #10 One of the least used tutoring strategies despite training in this area. Therefore: Infuse tutor training with time to determine how to integrate knowledge of cultural influences into tutoring. Discuss: Learning is making connections, left and right brain learning styles, and how to study smarter using metacognitive techniques 5 Minute Paper: My personal learning style and how I intend to adopt my style to that of students I tutor. 5 Minute Paper: How I will incorporate metacognitive techs Are tutors able to articulate their personal learning style and address how to adapt their style to the style of their students? Are tutors able to incorporate metacognitive activities into their tutoring sessions? Online Surveys Question #9 One of the least used tutoring strategies despite training in this area. Therefore: Infuse tutor training with time to determine how to integrate knowledge of learning style differences into tutoring. #3 Active Listening and Independent Learning Describe significance of verbal and nonverbal techniques that promote active listening Demonstrate use of active listening techniques in tutoring sessions. Verbal and nonverbal active Listening Independent learning skills Personal Checklist of Listening Skills #4 Multicultural Awareness Define “culture” Definitions of Culture and “diversity” and and Diversity “cultural diversity” Cultural groups and Share personal characteristics: beliefs, cultural influences values, traditions, with others and relationships, behaviors listen actively to Assumptions cultural influences of others #5 Learning Styles and Strategies Define “Learning” as making connections Determine personal learning style as right/left brain dominant Describe use of pre and post tutoring activities using metacognition techniques “Learning” is making connections, connecting what you already know to something new that creates learning.” Left brain / right brain learning styles Studying smarter is using background knowledge, metacognition, and elaboration skills for pre, during, and post tutoring activities. Assessment: Tutors and Tutees LERN 10 and LERN 1000: Comparing Tutor outcomes with Student outcomes OVERVIEW The Learning Assistance Center developed SLO’s specific to our tutor training course during Fall 2007. First, the faculty developed outcomes, activities, tutor reflections and faculty assessments. Then during Fall 08 we addressed the problem of evaluating the faculty assessments. The Learning Assistance Department developed two complimentary online surveys to assess the student learning outcomes in the tutor training course. LERN 10. We wanted to understand how the SLO’s covered in the tutor training course were used in tutoring by tutors who completed the tutor training course. We also wanted to understand if students who are tutored by those tutors believe they are recipients of the same outcomes. We have used these two surveys for eight semesters now and have learned which tutoring strategies are most used, least used, most valued, and requires changes. Indeed, the assessment has pointed the way to a number of changes in the course curriculum. YEARLY UPDATES Fall 06: Fall 07: Sp 08: Fall 08: Sp 09: Fall 10: Sp 11: Revised course outlines Developed SLOs for LERN 10 Tutor Training Developed SLO for LERN 1000 – Supervised Tutoring Assessed SLO’s from both surveys Spring 10: Assessed and analyzed data from both assessments Developed a new online surveys using Survey Monkey Assessed data from both surveys and developed specific action plans MOST RECENT ASSESSMENT: SPRING 11 When comparing results of LERN 10 with LERN 1000: Areas of high agreement and high ratings: knowledge of subject, friendliness, explaining well Areas of lowest ratings by both: Incorporate study strategies, cultural awareness Areas of differing ratings: No significant differences. CHANGES MADE AS A RESULT OF MOST RECENT ASSESSMENT Improved tutor training course to provide additional information on how to explain using students own words. Final papers from tutors following the Fall 11 LERN 10 course show a very strong interest in developing listening skills. LAC Tutors Survey Spring 11 LAC Students Survey Spring 11





