Name: Date: ______ Per: ______ Pedigree Analysis Pedigrees
advertisement

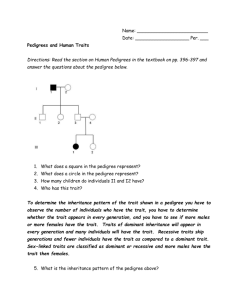
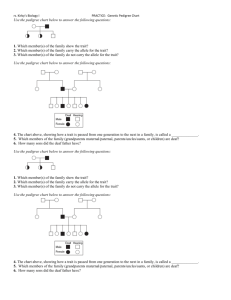
Name: ________________________________________________________ Date: _________ Per: ___________ Pedigree Analysis Pedigrees show INHERITED traits: traits that can be passed on from generation to generation. For instance, a pedigree would never be used to illustrate which members of a family have a cold or the chicken pox because this is not an inherited trait. Match the following terms with the appropriate symbol: Affected with trait, mating, male, deceased (dead), siblings, female, carrier for trait. Symbols: 1. How many generations are in this pedigree? __________ 2. How many males are in this family? II ____________ 3. How many females are in this pedigree? _________ 4. Which individuals are carriers of the trait? ____________ 5. Which of the following traits would not be shown in this pedigree? a. Influenza (flu) b. Dwarfism c. Sickle cell disease 6. Explain your answer to #5. _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Some traits are lethal, which means they kill an individual. Is this trait lethal or non-lethal? _________________________Explain your choice. ______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. What is the relationship between individual I-1 and II-2. (ex: mother-daughter? Grandmagranddaughter?) _________________________________________ 9. What is the relationship between individual I-2 and III-12? _________________________________ HINTS: If the trait is RECESSIVE, two copies of the allele must be present for it to be expressed. Only an individual with a genotype like rr would have the trait. Individuals that are RR or Rr would not have the trait. Parents are generally unaffected. Approximately 25% of children are affected if both parents are carriers. Two affected parents will always have an affected child. Recessive traits often result from consanguineous How do you recognize it? Ask yourself: Is there a situation in which the kids have the trait but the parents do not? If YES Recessive If the trait is DOMINANT, only one copy has to be present for it to be expressed. An individual with a GG and a Gg, for instance, would both have the trait. An individual that is gg would not have the trait. Trait occurs every generation. When one parent is affected, approximately 50% of children will be affected. Affected individuals are usually heterozygous. Unaffected parents do not produce affected children. Two affected parents can have unaffected children. How do you recognize it? Ask yourself: Is there a situation in which both parents DO have the trait, but the kids DON’T? If YES dominant If the trait is SEX-LINKED Affected males always pass the condition to daughters and affected females are homozygous recessive Children of an affected male (father) will not be affected. However, 100% of the female offspring will be carriers of the disease. An unaffected carrier female (heterozygous mother) will have approximately 50% affected male offspring and no affected female offspring (although approximately 50% of the female offspring will be carriers). How do you recognize it? Ask yourself: Is there a situation in which a MOTHER with the trait has only SONS with the trait? Is there a situation where an affected dad produces all carrier girls? If YES sex-linked Now, let’s try this out together: 1. How many generations are shown in this pedigree? _______________ 2. How many females are in this pedigree?______ 3. Number the individuals. 4. List the individuals that DO NOT have the trait. ______________________________ 5. What type of inheritance does this trait have? a. Sex-linked b. Dominant c. Recessive 6. Which individuals are carriers in this pedigree? _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Now on your own: 7. How many generations are shown in this pedigree? _______________ 8. How many males are in this pedigree?__________ 9. Number the individuals. 10. List the females that DO have the trait. ______________________________ 11. What type of inheritance does this trait have? a. Sex-linked b. Dominant c. Recessive 12. Which individuals are carriers in this pedigree? 13. Shade in the individuals that are carriers. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. How many generations are shown in this pedigree? _______________ 15. How many females are in this pedigree? _____________ 16. What type of inheritance does this trait have? a. Sex-linked b. Dominant c. Recessive 17. Shade in carriers in this pedigree? 18. Write in the genotype of as many individuals that you can. If you cannot determine both alleles, just leave it as a blank (ex: E__) Homework: Create a pedigree for Part A and fill in the chart for Part B using the “HINT” section of this packet. Part A: Pedigree Brown eyes are a dominant eye-color allele and blue eyes are recessive. A brown-eyed woman whose father had blue eyes and whose mother had brown eyes marries a brown-eyed man whose parents are also brown-eyed. They have a son who is blue-eyed. Please draw a pedigree showing all four grandparents, the two parents, and the son. Shade the whole individual if they express the trait and shade half the individual if they carry the trait. Write in the genotype of as many individuals that you can. If you cannot determine both alleles, just leave it as a blank (ex: B__) Part B: Cheat sheet for pedigree analysis: Type of inheritance Question to ask: (Use review sheet) How can you identify it? (Draw a piece of a pedigree) Recessive Dominant Sex-linked