LECTURE 3 CH 4 VARIATIONS IN THE PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENT
advertisement

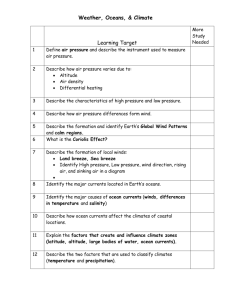
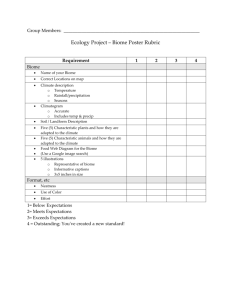
LECTURE 3 CH 4 VARIATIONS IN THE PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENT pg. 73-81; 87-88; 95 MAJOR CONCEPTS 1) Global patterns in temperature and precipitation are established by energy of sun. 2) Uneven heating of the earth’s round surface and the tilt of earth on its axis combine to produce predictable latitudinal variation in climate. 3) Uneven temperatures create winds; winds drive ocean currents that redistribute heat and moisture. 4) Proximity to water and topographic/geologic features cause local variation in climate. 5) Biome existence and location have shifted through time. Distribution of biomes is caused by variation in climate Proximate causes of global variation in climate *Overall model Solar radiation temperature wind and ocean currents precipitation Features of earth contributing to climate variation Temperature variation and its seasonality Angle of solar radiation affects heat input Latitudinal variation in temperature; hot at equator; cold at poles Greater temperature range in N than S; land temp changes more easily than water Seasonal change in location of solar equator seasonal variation in temperature Variation in temperature creates winds and winds affect ocean currents + direction Wind precipitation patterns Hadley cells variation in rain at 0 and 30 N and Spredictable locations of tropical forests and deserts ITCZ moves seasonality in rainfall; brings dry seasons to tropics Coreolis effect changes wind directionality from N and S to NE-SW and SE-NW Ocean currents variation in temperature and precipitation N = clockwise; S = counterclockwise affect whether bring warm or cold water Cause upwellings and affect productivity in ocean Cause shifts in biome location (deserts on W side of continents; temperate forests rather than boreal forest in N. Europe) Local effects on climate Proximity to water; continental vs. maritine climates Topography Mountains air cools as rises; cool air holds less moisture; it rains. Change in biome with change in altitude Changes in altitude parallel changes in latitude Wind brings moisture from a certain direction;(from W in temperate latitudes) Rain dumped on windward site rainshadow on leeward side Biome differs on different sides of mountain Orientation of mountain range (N- and S-facing slopes different sun and microclimate (temp and soil moisture) different vegetation on different slopes Causes of long-term temporal changes in biome distributions Continental drift; continents at different latitudes Mountain building rainshadows arise Milankovitch cycles bring changes in earth’s orbit, tilt, and wobble Past climate change Present climate change Human alteration in land cover; forest recycle water locally