GeneticsReview
advertisement
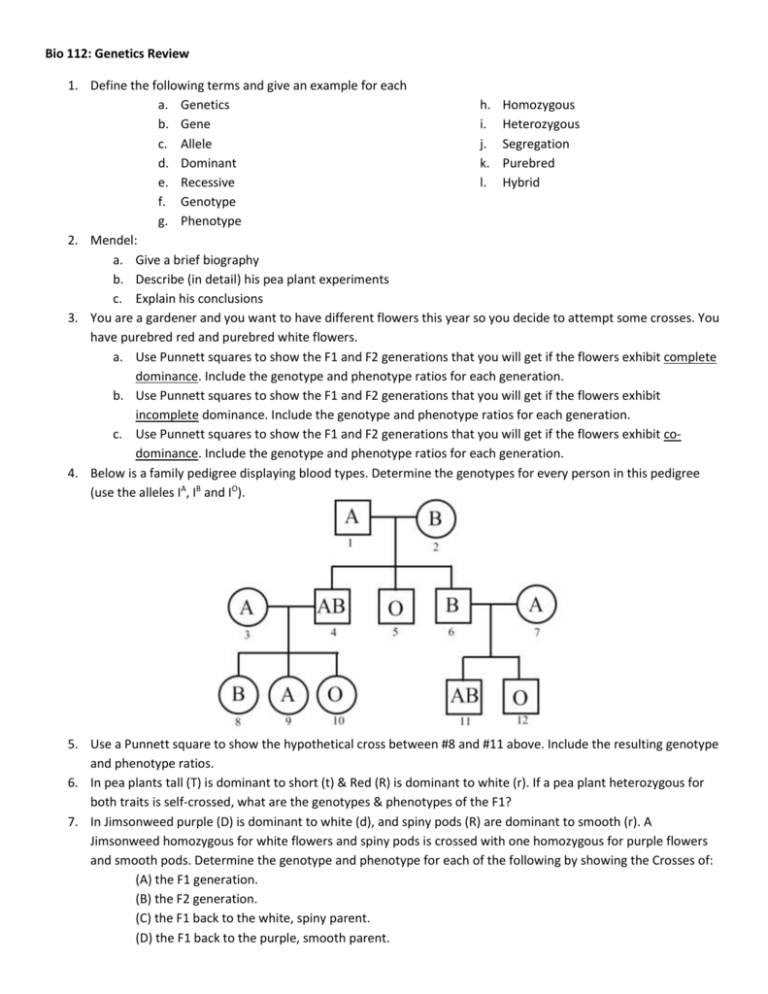
Bio 112: Genetics Review 1. Define the following terms and give an example for each a. Genetics h. Homozygous b. Gene i. Heterozygous c. Allele j. Segregation d. Dominant k. Purebred e. Recessive l. Hybrid f. Genotype g. Phenotype 2. Mendel: a. Give a brief biography b. Describe (in detail) his pea plant experiments c. Explain his conclusions 3. You are a gardener and you want to have different flowers this year so you decide to attempt some crosses. You have purebred red and purebred white flowers. a. Use Punnett squares to show the F1 and F2 generations that you will get if the flowers exhibit complete dominance. Include the genotype and phenotype ratios for each generation. b. Use Punnett squares to show the F1 and F2 generations that you will get if the flowers exhibit incomplete dominance. Include the genotype and phenotype ratios for each generation. c. Use Punnett squares to show the F1 and F2 generations that you will get if the flowers exhibit codominance. Include the genotype and phenotype ratios for each generation. 4. Below is a family pedigree displaying blood types. Determine the genotypes for every person in this pedigree (use the alleles IA, IB and IO). 5. Use a Punnett square to show the hypothetical cross between #8 and #11 above. Include the resulting genotype and phenotype ratios. 6. In pea plants tall (T) is dominant to short (t) & Red (R) is dominant to white (r). If a pea plant heterozygous for both traits is self-crossed, what are the genotypes & phenotypes of the F1? 7. In Jimsonweed purple (D) is dominant to white (d), and spiny pods (R) are dominant to smooth (r). A Jimsonweed homozygous for white flowers and spiny pods is crossed with one homozygous for purple flowers and smooth pods. Determine the genotype and phenotype for each of the following by showing the Crosses of: (A) the F1 generation. (B) the F2 generation. (C) the F1 back to the white, spiny parent. (D) the F1 back to the purple, smooth parent.











