Course Outline Template
advertisement

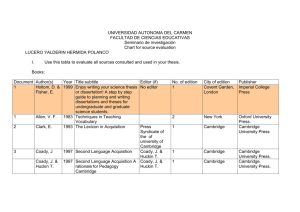
THE HONG KONG INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION Course Outline Part I Programme Title : Bachelor of Education (Honours) (English Language) (Five-year Full-time) Primary Bachelor of Education (Honours) (English Language) (Five-year Full-time) Secondary Course Title : Psycholinguistics and Second Language Acquisition Course code : ENG 3251 Department : Linguistics and Modern Language Studies Credit Points :3 Contact Hours : 39 Pre-requisite(s) : Nil Medium of Instruction: English Level :3 For Second Major (English Language): Core Course For Minor (English Language): Available _____________________________________________________________________ Part II 1. Synopsis: This course provides opportunities for students to develop their understanding of how language is learnt and how it is related to thinking. It introduces students to theories of second language learning and explores how second language development is affected by individual learner factors and social contextual factors. 2. Course Intended Learning Outcomes (CILOs) Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to: CILO1 demonstrate a clear understanding of how people comprehend and produce language; [PILO1 (SK1)] CILO2 identify the major theories that seek to explain second language acquisition; [PILO5 (SPK2)] CILO3 use relevant theoretical concepts to analyze how individual learner factors and social contextual factors affect second language acquisition; [PILO5 (SPK2)] 1 3. Course Intended Language Learning Outcomes (CILLOs) Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to: CILLO1 Write logical and coherent academic texts [PILO3 (SK3)] 4. Content, CILOs and Teaching & Learning Activities Course Content CILOs/CILLOs Suggested Teaching & Learning Activities How language develops in the first language CILO1 CILLO1 Key explanatory theories of second language acquisition: Behaviourism, Innatism, CILO1,2 CILLO1 Interactionism Stages and processes of second language acquisition: CILO1,2 CILLO1 learner language developmental sequences the processes of transfer, generalization, simplification and imitation Learner factors which affect second language CILO3 acquisition including: CILLO1 Lecture, Seminar, Group work, Students’ PPT presentation, Online learning activities language aptitude personality motivation learning styles and strategies Contextual factors that affect second language CILO3 acquisition: language and identity CILLO1 Structure a logical and coherent academic text CILLO1 Lecture, seminar, group work 5. Assessment Assessment Tasks Weighting (%) CILOs/CILLOs 2 a. Oral Presentation: Students work in groups to 40 CILO1, 2,3 60 CILO1,2,3 CILLO1 analyze their language learning experiences across group members, using relevant theoretical concepts to explain the similarities and differences of second language learning outcomes. b. Individual written essay: An essay in which each individual student analyzes his/her own language learning experiences in terms of theories associated with the processes of second language learning and / or with the effects of learner factors on second language learning. 6. Required Text(s) Nil 7. Recommended Reading Baker, C. & Prys Jones, S. (1998). Bilingualism and second language acquisition. In C. Baker & S. Prys Jones, Encyclopedia of bilingualism and bilingual education (pp. 635-64). Clevedon, UK: Multilingual Matters. th Brown, H.D. (2000). Principles of language learning and teaching (4 edition). White Plains, NY: Addison Wesley Longman. rd Cook, V.J. (2001). Second language learning and teaching (3 edition). London: Arnold. Dornyei, Z. (2001). Teaching and researching motivation. London: Longman. Dörnyei, Z. (2005). The psychology of the language learner: individual differences in second language acquisition. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum. Ellis, R. (1997). Second language acquisition. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Ellis, R. (2004). Individual differences in second language learning. In A. Davies & C. Elder (eds.) Handbook of applied linguistics (pp. 525-551). Oxford: Blackwell. Emmitt, M. & Pollock, J. (1997). Language and learning. Melbourne: Oxford University Press. Goh, C., & Silver, R. (2004). Language Acquisition and Development. Singapore: National Institute of Education. Johnson, K. (2001). An introduction to foreign language learning and teaching. Harlow: Longman. Lamb, M. (2009). Situating the L2 self: Two Indonesian school learners of English. In Z. D Dörnyei & E. Ushioda (Eds.), Motivation, language identity and the L2 self (pp.229-247). Bristol: Multilingual Matters. Lam, W. Y.K. (2005). Is Strategic Competence Teachable? The Journal of Asia TEFL, 2, 3 4, pp. 87-112. Leaver, B.L., Ehrman, M. & Shekhtman, B. (2005). Achieving success in second language acquisition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Littlewood, W. (2000). Foreign and second language learning. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press and Beijing: Foreign Language Teaching Press / People's Education Press. (Available for purchase only in the PRC.) Littlewood, W. (2004). Second language learning. In A. Davis & C. Elder (eds.) Handbook of applied linguistics (pp. 501-524). Oxford: Blackwell. Mackey, A. (2006). Second language acquisition. In R. Fasold & J. Connor-Linton (ed.) An introduction to language and linguistics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. McDonough, S. (2002). Applied linguistics in language education. London: Arnold. rd Peregoy, S.F. & Boyle, O.F. (2001). Reading, writing and learning in ESL (3 edition). New York: Addison Wesley Longman. Saville-Troike, M. (2005). Introducing second language acquisition. Cambridge University Press. Scovel, T. (1998). Psycholinguistics. Oxford: Oxford University Press. VanPatten, B. (2003) From input to output: a teacher's guide to second language acquisition. USA: McGraw Hill. Whitney, P. (1998). The Psychology of language. Boston, MA: Houghton Miffin. Williams, M. & Burden, R. (1997). Psychology for language teachers. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 8. Related Web Resources http://www.sk.com.br/sk-vygot.html This site gives information about language acquisition and the relation between language and cognitive development. 9. Related Journals Nil 4