File
advertisement

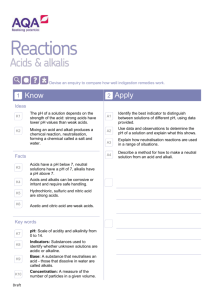
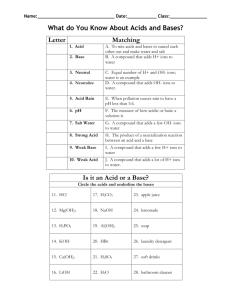
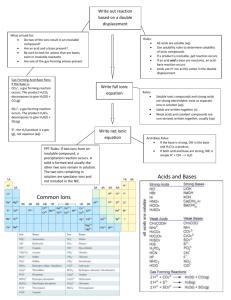
Standard Grade Chemistry Summary Notes Topic 8 : Acids And Alkalis General Learning Outcomes 1. Metal oxides are basic. 2. Most basic oxides are insoluble in water, but some dissolve to give alkalis. 3. Non-metal oxides are acidic. 4. Acidic oxides dissolve in water to give acids. 5. Sulphur dioxide in water leads to acid rain. 6. Acid rain is harmful to plants and animals. It can damage certain buildings, especially those made from marble and limestone. It can also speed up the corrosion of metals. 7. Acids turn indicator solution red or orange and have pH numbers in the range 0-6. 8. Alkalis turn indicator solution blue or purple and have pH numbers in the range 8-14. 9. Water and other neutral solutions turn indicator solution lime green and have a pH number equal to 7. 10. Examples of acids in the lab ; sulphuric, hydrochloric and nitric acids. 11. Examples of acids in the home ; ethanoic (in vinegar) and citric (in fruit) 12. Examples of alkalis in the lab ; sodium, potassium and calcium hydroxides. 13. Examples of alkalis in the home ; ammonia (household cleaners) and milk of magnesia (for indigestion). 14. Pure water is a covalent liquid but contains a small number of ions. 15. Acid solutions contain hydrogen ions – H+ (aq) 16. Alkalis contain hydroxide ions – OH-(aq) 17. When acids are diluted, the concentration of H+ (aq) decreases and the pH rises towards 7. 18. When alkalis are diluted, the concentration of OH-(aq) decreases and the pH decreases towards 7. Credit Learning Outcomes 1. Water is neutral because it contains an equal number of H+ (aq) and OH-(aq) ions. 2. Water and all aqueous solutions contain H+ (aq) and OH-(aq) ions. 3. Acid solutions contain an excess of H+ (aq) ions. 4. Alkali solutions contain an excess of OH-(aq) ions. In addition, you should be able to do the calculations involving : (i) the gram formula mass of substances (ii) the number of moles from the mass and vice versa (iii) moles, volume and concentration using : moles volume (l) conc (mol/l) How Acid And Alkali Solutions Can be Made (General) Non-metal elements can react with oxygen to form compounds called non-metal oxides. Example : sulphur + oxygen sulphur dioxide S (s) O2(g) SO2(g) Non-metal oxides which dissolve in water produce acid solutions. Example : sulphur dioxide + water SO2(g) + H2O(l) sulphurous acid H2SO3(aq) Alkaline solutions are made when soluble metal oxides or hydroxides dissolve in water. Check the solubility table in your data book to see which oxides dissolve Example : sodium oxide + water sodium hydroxide solution Na2O(s) + H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) The pH Scale (General) The pH scale is a continuous range of numbers which indicate the acidity or alkalinity of solutions. acids have a pH of less than 7 alkalis have a pH of more than 7 pure water and neutral solutions have a pH equal to 7 The chart below shows the pH of some common substances. lemon juice pH 1 2 3 4 vinegar salt solution 5 6 7 8 water 9 ammonia solution 10 11 12 13 14 milk of magnesia The Ions Present In Acid And Alkali Solutions An acid solution is one which contains hydrogen ions – H+ (aq) An alkaline solution is one which contains hydroxide ions – OH- (aq) The concentration of ions in pure water is small. (General) (Credit) In water and in neutral solutions the concentration of H (aq) and OH (aq) is the same. That is why water is neutral. An acidic solution contains more H+ (aq) ions than does pure water. An alkali solution contains more OH- (aq) ions than does pure water. + - What Happens When An Acid And An Alkali Are Diluted? (General) Diluting an acid by adding more water increases the pH of the solution towards 7, making it less acidic. Diluting an alkali by adding more water decreases the pH of the solution towards 7, making it less alkaline. Diluting an acidic solution decreases the concentration of H causes the pH to increase towards 7. + (aq) (Credit) ions. This Diluting an alkali solution decreases the concentration of OH- (aq) ions. This causes the pH to decrease towards 7.