Topic 4: Marine Ecosystems – Coral Reefs
advertisement

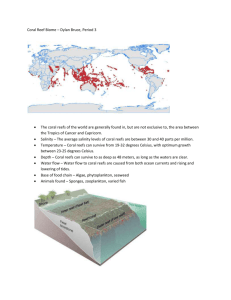
Marine Ecosystems – Coral Reefs I. Coral Reefs: all life in this habitat depends on each other to maintain a balance. a. Phylum: Cnidaria – multicellular animals characterized by two cell layers, saclike digestive tract, tentacles, radial symmetry & a nerve net b. Nematocycts – specialized cells used to sting & capture prey c. Polyp – a cnidarian attached to a Substrate II. Hard Corals: a. Secrete a skeleton of calcium carbonate (limestone), called a calyx (a cup-shaped stony structure that houses the coral polyp), which remains after the polyp has died b. The calyxes support the reef inhabitants. Examples: antler, brain, elkhorn, plate, saucer & staghorn Brain Coral Antler Coral Plate Coral III. Soft Corals: a. Secrete a skeleton of keratin (a protein similar to that of fingernails) b. Soft corals will decompose once dead Examples: sea fans, sea pens, sea whips, organpipe coral, umbrella coral, sea pansies & blue and red corals Sea Fan Organ pipe Coral Umbrella Coral IV. 3 Types of Coral Reefs: a. Fringing reef: grow in the shallows of continents & islands b. Barrier reef: serve as protective breakwaters to coastal areas i. example: Great Barrier Reef – the longest in the world, 1250 miles long, located off the coast of Australia c. Atoll: a coral island; the reef itself nearly or completely encloses a lagoon V. Commensalism: a symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits while the other species is not affected by the relationship a. Zooxanthellae: a single celled green algae; lives within the tissues of corals i. assists hard corals in manufacturing calcium carbonate ii. gives surrounding animals food & oxygen through photosynthesis VI. Coral Habitat: a. narrow temp. range: 70-84°F, with the greatest variety occurring between 77-84°F b. shallow, calm waters where light can penetrate c. tropical waters at approximately 30° north/south of the equator (lifeless sea, oasis to life) i. low in dissolved oxygen ii. low in nutrients iii. low in plankton VII. Some coral inhabitants: a. Shrimp, crabs, butterfly fish, lion fish, parrot fish, moray eels, trigger fish Butterfly Fish Lion Fish Moray Eel VIII. Some soft coral predators: a. Nudibranchs – shell-less members of the phylum Mollusca, feed on soft corals; cowries, flamingo-tongue snails, sundial snails Nudibranchs Cowries Flamingo-tongue snail IX. Some hard coral predators: a. Crown-of-thorns sea star – up to 2 feet of corals destroyed per day; Crown-of-thorns