introduction
advertisement

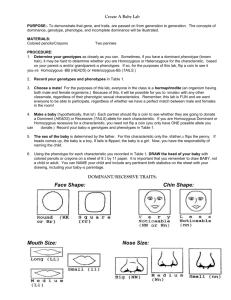
D11-Ugly Baby INVESTIGATING INHERITED TRAITS OF AN UGLY BABY INTRODUCTION Heredity is the passing on of traits, or characteristics, from parent to offspring. The units of heredity are called genes. Genes are found on the chromosome in the cell. The combination of genes for each trait occurs by chance. When one gene is stronger than the other gene, the trait of the second gene is masked or hidden. The stronger gene is the dominant gene. The gene that is hidden is the recessive gene. Dominate genes are written as capital letters and recessive genes are written as lower case letters. If both genes are the same, that is either both capital or both lower case, the trait is said to be pure. Some other terms for this are purebred, homozygous, and homeogenus. If the genes are not the same, that is one is capital and one is lower case, the trait is said to be hybrid, heterozygous, or heterogeneous-most of the time. Some traits can blend instead of one gene being stronger than the other. This is called incomplete dominance. The genetic makeup of an individual is their genotype. What the trait looks like is the phenotype. In humans, the sex of an individual is determined by the male gene. Individuals with the genotype XX are females and XY are males. PURPOSE In this investigation students will observe how the results of different gene combinations produce different phenotypes. The students will be exposed to inheritance patterns that are governed by Mendel’s Principles. Each pair of students will assume the role of mother and father. SAFETY Caution students about throwing coins. MATERIALS 1 coin of type per group of 2 students Copies of worksheets PROCEDURES 1. If the gender of both individuals in your group is the same, flip the coin to see who will assume the opposite role. 2. Who ever is the father flip the coin to determine the gender of the baby. If the coin lands head up, the baby is female. If it lands tails up, it is a boy. There is no need for the mother to flip since she can only offer an X chromosome. Write the gender (boy or girl) in the phenotype box on your lab sheet. In the Genotype box, write XX or XY, which ever is the case. 3. Each member of the group will flip the coin once to determine the genotype of their half of the gene pair (allele). Two alleles together make a gene pair. HEADS IS ALWAYS CAPITAL(DOMINANT) AND TAILS IS ALWAYS LOWERCASE (RECESSIVE) 4. Note which letter you are to use with each trait and notice that the letter changes with each trait. Revised 11/07 ASIM Biology: Genetics Page 1 of 11 D11-Ugly Baby 5. As you go through the traits, be sure to write both the phenotype and genotype on your lab sheet. Phenotype will always be a word and genotype will always be letters. 6. When you come to a double letter such as hair and eye color each person will flip the coin two times. These are examples of traits that are made of more than one gene pair. 7. When you have completely filled out your lab sheet. Look at the second trait, shape of face to see which face shape your baby has. When you have determined this, ask your teacher for the correct shape. 8. Draw your baby using the phenotypes on your lab sheet. Another words, if your baby is HH for curly hair, then your drawing should have curly hair. You can look at the pictures for help. Notice which traits are truly dominant and recessive and which ones blend, like hair texture. 9. Some traits are controlled by more than one pair of genes. We call these polygenic traits. Examples of polygenic traits are skin color, eye color, and hair color. Use the following instructions for determining these traits: Dark is dominant over light, to determine the genotype flip the coins for two complete sets then look the phenotype up on the chart below. SKIN COLOR AABB AABb AAbb AaBB AaBb Aabb aaBB aaBb aabb very dark brown dark brown light brown dark tan EYE COLOR medium tan light tan AABB beige AABb light beige AAbb ivory AaBB AaBb Aabb HAIR COLOR aaBB aaBb AABB black aabb AABb black AAbb red AaBB dark brown AaBb brown Aabb strawberry blonde aaBB light brown aaBb blonde aabb light blonde Revised 11/07 ASIM Biology: Genetics nearly black dark brown brown green with brown flecks green hazel (brownish or grayish green) grayish blue blue light blue Page 2 of 11 D11-Ugly Baby DATA SHEET Student Name___________________________ Partner Name___________________________ Class Period____________Date____________ TRAIT GENOTYPE PHENOTYPE Gender Shape of face Cleft in chin Hair type Widow’s Peak Spacing of eyes Shape of eyes Position of eyes Size of eyes Length of eyelashes Shape of eyebrow Position of eyebrow Size of nose Shape of lips Size of ears Size of mouth Freckles Dimples Skin color Hair color Eye color Revised 11/07 ASIM Biology: Genetics Page 3 of 11 D11-Ugly Baby Revised 11/07 ASIM Biology: Genetics Page 4 of 11 D11-Ugly Baby Revised 11/07 ASIM Biology: Genetics Page 5 of 11 D11-Ugly Baby Revised 11/07 ASIM Biology: Genetics Page 6 of 11 D11-Ugly Baby Revised 11/07 ASIM Biology: Genetics Page 7 of 11 D11-Ugly Baby Questions: 1. Would you expect the other pairs of students in your class to have an offspring similar to yours? Explain.________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ 2. If a man who has long eyelashes (LL) marries a lady who has long eyelashes (Ll), what are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of their children? Genotypes_________________ Phenotypes________________ 3. What are the possible genotypes of the parents of a child who has wavy hair (Hh)? ________________ 4. Which traits in the investigation showed blending of genes? ______________ ________________________________________________. This is called _________ dominance. 5. Can the actual traits of the offspring be determined by knowing the traits of the parents? Expalin.__________________________________________ 6 . A woman received the genes aBcD from her mother and AbCd from her father. Which of the following gene combinations could be present in her gametes: ABCD, abcd, ABCDD, aBccD, ABcd, AaBb. Circle the correct answer(s). Revised 11/07 ASIM Biology: Genetics Page 8 of 11 D11-Ugly Baby TEACHER ANSWER SHEET 1. Would you expect the other pairs of students in your class to have an offspring similar to yours? Explain. The chances are not good that another group would flip for the same phenotypes for all of the characteristics. 2. If a man who has long eyelashes (LL) marries a lady who has long eyelashes (Ll), what are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of their children? Genotypes LL, L1 Phenotypes: only long 3. What are the possible genotypes of the parents of a child who has wavy hair (Hh)? HH and Hh, or HH and hh or Hh and Hh or Hh and hh 4. Which traits in the investigation showed blending of genes? Hair, spacing of eyes, size of eyes, size of nose, shape of lips, size of ears, hair color and eye color This is called incomplete dominance. 5. Can the actual traits of the offspring be determined by knowing the traits of the parents? Explain. No, you would have to know the genotypes to determine for sure. 6 . A woman received the genes aBcD from her mother and AbCd from her father. Which of the following gene combinations could be present in her gametes: ABCD, abcd, ABcd, AaBb. Circle the correct answer(s). Revised 11/07 ASIM Biology: Genetics Page 9 of 11