Number Name Honors Section 4-1
advertisement

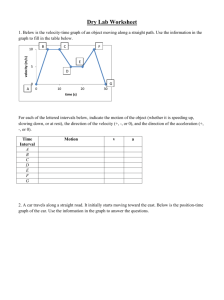
Number _________________ Name _____________________________________PHYSICS Honors Section 4-1 1. A car is traveling on an interstate highway in a positive direction could it have a positive velocity and a negative acceleration at the same time without changing direction? Yes. A car's velocity is positive with respect to its direction of motion from some point of reference. While moving in a positive direction if it was slowing down its acceleration would be negative. 2. You push a cart up the incline, after you release the cart, can the cart change the direction of its velocity when traveling with a constant acceleration? As the cart moved up the incline it will eventually change the direction of its velocity while maintaining a constant acceleration. If we define the direction of motion up as positive, its velocity decrease, then after it stops, it comes back down the incline. Throughout each change in the magnitude or direction of its velocity, the cart is undergoing uniform negative acceleration. 3. Can the velocity of an object change when its acceleration is constant? If you answer yes, give an example. If you answer no, explain why not. Yes. Drop a book. 4. What does the slope of the tangent to a velocity-time graph measure? The slope of the tangent to a velocity-time graph indicates acceleration. (Instantaneous) 5. If a velocity-time curve is a straight line parallel to the x-axis, what can be deduced about the acceleration? When the velocity-time graph is a line parallel to the x-axis, the acceleration is zero. 6. If you are given a table of velocities of an object at various times, how could you find out if the acceleration of the object is constant? Draw a velocity-time graph and see if the curve is a straight line. 7. Figure 4-4 shows the velocity-time graph for an accelerating car. The three "notches" in the curve occur where the driver shifts gears. a. Describe the changes in velocity and acceleration of the car while it is in first gear. Velocity increases rapidly at first, then more slowly. Acceleration is greatest at the beginning, but is reduced as' velocity increases. Eventually it is necessary for the driver to shift into second gear. b. Is the acceleration just before a gear change larger or smaller than the acceleration just after the gear change? Explain your answer. The acceleration is smaller just before the gear change because the slope is less at that point on the graph. Once the driver shifts and the gears engage, acceleration and the slope of the curve increase 8. Study Figure 4-4. During what time interval is the acceleration the largest? 0 to 1 sec , the smallest 24 to 25 sec? 9. Solve the equation vf = vi + at for acceleration. What is the equation you get? at = vf – vi a = vf – vi / t a = v / t 10. Look at Figure 4-17, which is a position-time graph of uniform acceleration. a. What type of curve does this graph represent? Parabola b. What does the slope of a tangent line taken at any point represent? Instantaneous velocity C. How would slopes taken at higher points on the line differ from those taken at lower points? Slopes at higher points would be larger indicating higher velocities.