Reading Study Guide for Unit II: Northern Africa
advertisement

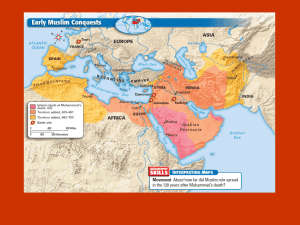
History 331 - African History Dr. C. Weber 8F Reading/Study Guide for Unit II: Northern Africa and the Impact of Islam Gordon and Gordon (GG), pp. 31b-36a What is the significance of the term Bantu? What attributes made these people distinct? Explain the Bantu migration. (30) Why is the term “prehistoric” inappropriate for many early African civilizations that lack written records? (31) In the absence of states, how was African society delineated, organized, and maintained? How did such systems impede European colonization? Compare and contrast stateless and state societies. How did each keep law and order? (31-33) Explain the importance of kinship in historical and contemporary Africa. (32-33) Explain the ways in which state societies formed in Africa. What characterized the state of the Nile valley, Ethiopian highlands and savannas? (33-36) GG, pp. 109-111 What were the earliest economies in Africa and where do they continue to exist today? What happened as societies became more sedentary? What was the role of trade? What were Africa’s links to international trade and what products were involved? What was the impact of the slave trade? What role did “legitimate” trade play? GG, pp. 317-328a Why is it impossible to overemphasize the importance of religion in understanding African social, economic, and political life? (317) What particular characteristics make African Traditional Religions harder to understand and define than religions such as Christianity and Islam? (318) What aspects tend to be common to most African Traditional Religions? (319) What is the traditional understanding of God or a Supreme Being in African religions? How do such Supreme Beings relate to Creation? (319) Since African thought is not given to speculation, how are religious ideas and conceptions formulated and expressed? (320) What similarities do some African Traditional Religions have with Christian doctrines—the Trinity, identity of God, etc? (320-321) Identify and explain the attributes and significance of orisha and bosom. (321) Explain the significance of ancestor spirits. What are some common misconceptions about these spirits? What roles do ancestors have in traditional African culture? (321-23) What are the different categories of ancestor spirits? (323) How is death perceived? How do these beliefs affect the idea of an afterlife? (323-24) What are the different types of religious leaders in African Traditional Religion? (324-25) What additional roles do spiritual leaders play in African life? (324-25) What religious significance do kings and chiefs possess? (325) Explain the significance, purpose, and location of religious shrines. (325) What are the roles of witches and sorcerers in African societies and religions? (326) What are the two aspects of magic in African Traditional Religions? How has Christianity changed in Africa since the 1800s? In what ways has it grown and changed? (327) Give a basic account of the origin and growth of Christianity in Africa. What were some significant locations and figures in early African Christianity? What were some early indigenous expressions of Christianity? (327-28) GG, pp. 337-347 Where in Africa is Islam most prevalent? (337) How was Islam introduced to Africa? How did is spread throughout the continent? (337-38) Who are the basic figures and what are the basic tenets of Islam? (337) What are some basic differences between Islam and Christianity? (337) When did Islam first enter Africa and how was it received? (337-38) Define and explain the significance of dhimmi and jizya. How were Christians treated? (337-38) What kind of conflict did Christianity and Islam experience? (338-39) How did the spread of Islam in Northern and Southern Africa differ? (339) How compatible/incompatible was Islam with African Traditional Religions and practices? Why was Islam attractive to elites? (339-40) In what ways did Islam spread throughout East Africa? (339-40) What was the second wave of the spread of Islam? What made it distinctive and especially effective? How did it specifically change the religious, social, cultural, and political environment in different parts of Africa? What role did militant movements and Sufi religious orders and marabouts play? Who were the Mahdi? (340-41) What relationship did colonialism and Christianity develop with Islam during this time? (341) How has Islam changed due to Western influences? (341-42) How has Western influence been complimentary and antagonistic to Islam in Africa? (341-42) Give some examples of the ways in which Islam and African Traditional Religions have been combined. (342-43) What is Hamallism and Ahmadiyya? (343) How have U.S.- African relations changed after September 11th? How would you describe the nature of Muslims in Africa? How has the war on terror effected Muslim-Christian relations in Africa? (344346) What is a “meaningful religion” in modern Africa? (346-47) GG, pp. 352-358a How is the oral tradition of a non-literate society different from that of a literate society? (352-53) What are some different ways in which the constants of African oral tradition are transmitted? What are the functions of a griot or bard? (352-53) How and why might a bard change his telling of a historical event, story, or myth? (353-54) How does the pluralistic nature of African civilization affect the preservation and perpetuation of oral history? (354) Explain the style, significance, and purpose of prose tales, myths, and the varieties of poetry in African oral tradition. (354-58) What are some additional genres of oral literature and their purpose in African life and culture? (357-58) Shaw, pp. 11-59 What are the wrestling matches that he identifies? What is his purpose in the book? What three traits does he use to define the kingdom of God? How does this relate to his wrestling theme and to his overall thesis? How was Egypt prepared for Christ’s coming? What is the importance of Egypt’s divine kingship to the rest of Africa? What is ma’at? What is St. Mark’s role? What were the three characteristics of early Jewish Christianity (in the first stage)? What is Gnosticism and how and why did it emerge? Why did it seem conducive to Egypt? Why was the church persecuted in north Africa and what were the results? Who were the key figures of the school at Alexandria and why is it important? Who were Antony and Pachomius and what did they accomplish? What characterized the two churches in Egypt? What did Athanasius believe and what doctrines did he develop? What impact did Justinian and Theodora have on the church? [See page on web site for this unit with explanations of Gnosticism, Monophysite and Montanism.] What characterized the church in Carthage? What brought about its growth? What did Tertullian and Cyprian contribute? What was Donatism and what resulted from it? Who were the Circumcellions? What were the contributions of Augustine? How did he compare to other African Christian leaders? What happened in the sixth century? How does all this fit into Shaw’s theme of the kingdom? Shaw, pp. 61-90 (NOTE: MAP on p. 299) Shaw, pp. 61-90 (NOTE: MAP on p. 299) Why is Nubia considered a “bridge,” “gateway” and “link”? What did the kingdom of Axum achieve culturally and in terms of Christianity? What did Frumentius accomplish? What did King Ezana accomplish? What did the Nine Saints accomplish? Why does Orthodoxy seem to have dominated in Nubia? What were Nubia’s connections to Byzantium? What is meant by theocracy and what are its consequences for the practice of Christianity? What are the four myths? What were the origins of Islam and how and when did it enter Africa? Who were the Kharijites? Who did they get support from? What stimulated Muslim missions? What was the effect of trade and of slaves? What did the Fatimids and Almoravids accomplish? Describe the “syncretistic tendency of Islam” and its manifestation in West Africa? How did Islam in West Africa compare to East Africa? How did African Christianity fare under Islam? What did the Ottomans achieve? What impact did theocracy and sacred kingship have? Note the traits of Ghana, Mali and Songhay and their major rulers. What characterizes Shirazi culture, Great Zimbabwe and Zulu kingdoms? What was the priestly role of the king and what was his divine character? How did the “longing for the kingdom of God” manifest itself?