Notes The Physiographic Provinces of Virginia
advertisement

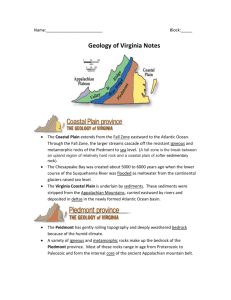
The Physiographic Provinces of Virginia Virginia has had a long, complex geologic history, over ___________years Events that have led to the formation of a rich diversity of rocks, and events that have___________, _____________ and rearranged those rocks in complex patterns. A physiographic province is a________________region, areas divided according to similar terrain that has been shaped by a common geologic history. Geographers recognize more than 20 physiographic provinces in North America; __________of these are in the state of _____________- Piedmont Each province is characterized overall by its elevation, relief, ___________, and geologic structure. Because of the region’s history of rock formation, deformation, and _______________, specific types of landforms or other geologic features may be associated with a given _______________ Coastal Plain The Coastal Plain is a ________________area underlain by young, unconsolidated sediments. Includes all of Virginia ___________of the________________ ____________. The Fall Line is where Rivers cross from the hard igneous and metamorphic rocks of the _____________onto the soft roundest rocks in Virginia. Deposits of________________, silt and clay including marine fossils deposited by rivers. Layers of sediment were produced by erosion of the _____________________Mountains and then deposited on the Coastal Plain. The ___________ is an area of rolling hills underlain by mostly ancient _______________ and ____________________ rocks. Igneous rocks are the roots of volcanoes formed during an ancient episode of ________________that occurred before the formation of the Appalachian Mountains. Largest physiographic province. Bounded on the east by the _____________- __________and on the west by the mountains of the Blue Ridge. Rolling ________________y, deeply weathered bedrock and rocks are strongly weathered. Rocks are generally buried under a thick (2-20m) blanket of _______________Topography is more rugged closer to the Blue Ridge. Blue Ridge The __________ _____________is a high ridge of crystalline rock separating the ______________-from the Valley and Ridge Province. The ___________--- _________old igneous and metamorphic rocks of the Blue Ridge are the oldest in the state. The ___________ _________province experienced mountain building during the Paleozoic era (750-700Ma). In central and northern Virginia, the 570 million year old _______________ are over ____________________ rock. Some metamorphism of these rocks occurred during the formation of the __________________ _____________ Valley and Ridge Long parallel ridges and valleys of _________________rock which were folded and faulted, and eroded differently. _____________million years old sandstones are overlain by carbonates that make up a region of __________________and dolomite. The folding and faulting of the sedimentary rocks occurred during a collision between ______________and North America. The collision, which occurred in the late _______________produced the Appalachian Mountains. Carbonates were deposited in a shallow _______________ocean along the southeast edge of North America. Carbonates in the Shenandoah Valley create the correct environment for caves and sinkholes (_________________ _________________) Appalachian Plateau The _________________ _______________has rugged irregular topography and is underlain by ancient, flat-lying __________________ rocks. Large folds of rock found in the Valley and Ridge become smaller folds and flat-lying rocks in the______________. Some parts of the Plateau are relatively flat, and some are hilly and rugged. The area is actually a series of plateaus separated by faults. The upper layers of the Plateau are rich in mineral resources like ________________, _________________ and _________________