Practice Exam #1
advertisement

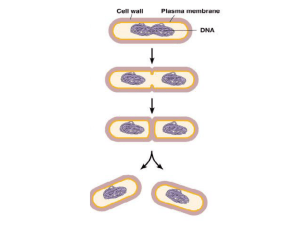
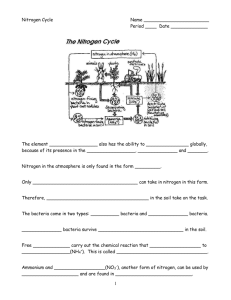
Bio 211 Practice Exam I – A (Wilsey) 1. Banded iron formations in marine sediments provide evidence of: a. The 1st prokaryotes around3.5 billion years ago b. Oxidized iron layers in terrestrial rocks c. The accumulation of oxygen in the seas from photosynthesis of cyanobacteria d. The evolution of photosynthetic archea near deep-sea vents e. The crashing of meteorites onto Earth, possibly transporting abiotically produced organic molecules from space 2. Why is the diversity of life now organized into three domains? a. The domains of Bacteria and Archea reflect the early evolutionary divergence within the prokaryotes b. Molecular evidence indicates that the protests really include three separate lineage c. The eukaryotes are more alike than are the prokaryotes and thus belong in one big group d. The division into plants, animals, & bacteria is more intuitive and accessible to most people e. The origin of life involved three distinct stages – protobiont, prokaryote, and eukaryote – and each domain represent one of those stages 3. Gram-positive bacteria a. Have peptidoglycan in their cell walls, whereas gram-negative bacteria do not b. Have an outer membrane around their cell walls c. Have lipopolysaccarides in their cell walls and thus may be more pathogenic than gram-negative d. Are members of domain Archea e. Have simpler, thicker peptidoglycan cell walls 4. Chemoautotrophs a. Are photosynthetic b. Use organic molecules for an energy source and a carbon source c. Oxidize inorganic substances for energy and use CO2 as a carbon source d. Use light to generate ATP but need organic molecules for a carbon source e. Use light energy to extract electrons from H2S 5. Some cyanobacteria are capable of nitrogen fixation. This process: a. Oxidizes nitrogen-containing compounds to produce ATP b. Allows these bacteria to live in anaerobic environments c. Removes soil nitrite or nitrate and returns N2 gas to the atmosphere d. Converts N2 to ammonium, making nitrogen available to plants for incorporation into proteins and nucleic acids e. Is an essential part of the nitrogen cycle that reduces nitrogen trapped in mineral deposits and makes them available to organisms for their nitrogen metabolism 6. Which of the following groupings are mismatched? a. Proteobacteria – diverse gram-negative bacteria including pathogens such as rikettsias, Salmonella, Halicobacter pylori b. Chlamydias – intracellular parasites, including a species that causes blindness c. Spirochetes – helical heterotrophs, including pathogens causing syphilis and Lyme disease d. Gram-positive bacteria – diverse group that include mycoplasmas and pathogens that cause anthrax, botulism, and TB e. Cyanobacteria – photosynthetic filamentous colonies; some solitary species use the pigment bacteriorhodopsin and inhabit saline waters 7. Mixotrophs are: a. Plasmodial slime molds b. Cellular slime molds c. Gametophyte and sporophyte generations that differ in morphology d. Organisms that can be heterotrophic and autotrophic e. Organisms that can be both parasitic and free-living 8. The Chlorophyta (green algae) are believed to share a common ancestor with plants because: a. The are the only multicellular algal protests b. The do not have flagellated gametes c. They are the only protists whose plastids evolved from cyanobacteria d. Their chloroplasts are similar in ultrastructure and pigment composition to those of plants e. They are the only algae that exhibit alternation of generations 9. Xylem and phloem are found in: a. All plants b. Bryophytes, ferns, conifers, and angiosperms c. Only the gametophytes of vascular plants d. The vascular plants, which include ferns, conifers, and angiosperms e. Only the vascular plants with seeds 10. What provides food for a developing sporophyte embryo in a gymnosperm seed? a. Endosperm b. Female gametophyte tissue c. Female sporophyte tissue d. Male gametophyte tissue e. Pine cone Answers 1. C 2. A 3. E 4. C 5. D 6. E 7. D 8. D 9. D 10. B (or A)