46 chromosomes: 23 from each parent
advertisement

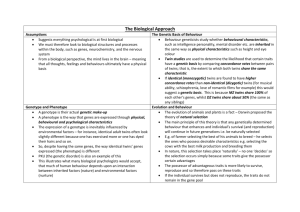
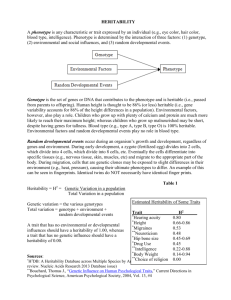
devt’l psych handouts, genetics & heritability 1 46 chromosomes: 23 from each parent Chromosomes: long strands of DNA Monozygotic twins (MZ): genetically identical Dizygotic twins (DZ): same as other siblings (50% similarity) -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3 Patterns of Genetic Expression single gene-pair inheritance (Mendelian) - allele: a single pair of genes that determines a characteristic - genotype: the genes we have - phenotype: the way genes are expressed - dominant allele: phenotypic expression - recessive allele: phenotypic expression only when both genes in the pair are recessive - incomplete dominance: dominant allele fails to completely mask the recessive one (e.g. sickle cell anemia) sex-linked inheritance – traits determined by genes on the sex chromosomes (23rd pair) - due to recessive genes on X-chromosome males more at risk - e.g. red-green colour blindness, hemophilia, muscular dystrophy polygenic inheritance – characteristics influenced by more than one gene pair - e.g. height, weight, intelligence, skin colour, temperament -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Chromosomal and Genetic Abnormalities - some congenital defects are due to abnormal genes and chromosomes e.g. too many or too few chromosomes 1 in 200 children devt’l psych handouts, genetics & heritability 2 abnormalities in sex chromosomes: - XXY, XXXY = Klinefelter’s syndrome (1 in 500 male births) - XYY = Supermale syndrome (1 in 1000 male births) - XO = Turner’s Syndrome (1 in 3000 female births) - XXX, XXXX, XXXXX = Superfemale syndrome (1 in 1000 female births) - Fragile-X syndrome (1 in 1000 children) Autosomal Abnormalities: - affecting chromosomes other than 23rd pair - most common: trisomy - Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) - less than 1 in 1000 when mother is < 29 - 1 in 220 when mother is > 35 - 1 in 25 when mother is > 45 Risks of any abnormality: - 1 in 450 for mothers under 29 - 1 in 150 for mothers over 35 - 1 in 12 for mothers over 45 Aging ova hypothesis ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Genetic Abnormalities due to Mutation Mutation: change in chemical structure of the gene(s) leading to a new phenotype. - genetic counseling amniocentesis chorionic villus sampling (CVS) ultrasound devt’l psych handouts, genetics & heritability 3 Research Methods: selective breeding research - Tryon (1940): maze-bright and maze-dull rats family study research - twin study: examine MZ twins raised together versus DZ twins raised together - adoption study: compare adoptees with adoptive family versus biological family -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Estimating Genetic vs. Environmental Contributions: concordance rate: the percentages of pairs of people in which, when one member shows the trait, the other does too. correlation coefficient: extent to which a trait in one member of a pair is related to presence of the trait in the other member. Heritability coefficient: H = (r for MZ twins – r for DZ twins) * 2 Non-shared Environmental Influence: NSE = 1 – r for MZ twins reared together Shared Environmental Influences: SE = 1 – (H + NSE) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- IQ is moderately heritable, H = .52 temperament is heritable, H = .40 Kagan (1989; 1988): identified children as socially inhibited or uninhibited at 21 months, 4 yrs, 5 ½, 7 ½. The first rating predicted subsequent ratings. Thomas & Chess (1977; 1970): infants can be categorized according to temperament: easy temperament difficult temperament slow-to-warm-up temperament devt’l psych handouts, genetics & heritability 4 Adult Personality and Heritability: introversion/extroversion heritable, H = .50 empathy generally personality traits are 40% hereditary, 60% environmental Canalization Principle (Waddington, 1966): genes can limit development to a small number of outcomes. infant babbling is mostly genetic for the first 10 months or so sometimes environmental influences over-ride genetic endowment (e.g. ducks preferring chicken calls) Range-of-Reaction Principle: genes establish a range of possible responses that a person will show to different life experiences -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Interaction of Environment and Heredity: passive genotype/environment correlations: the kind of home parents provide for their kids is partly influenced by their genotype evocative genotype/environment correlations: a child’s heritable attributes in turn affects how others treat them. active genotype/environment correlations: environments kids seek out are those that are compatible with genetic endowment.