Transcription and Translation Exercise
Transcription and Translation Exercise
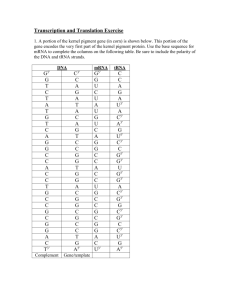
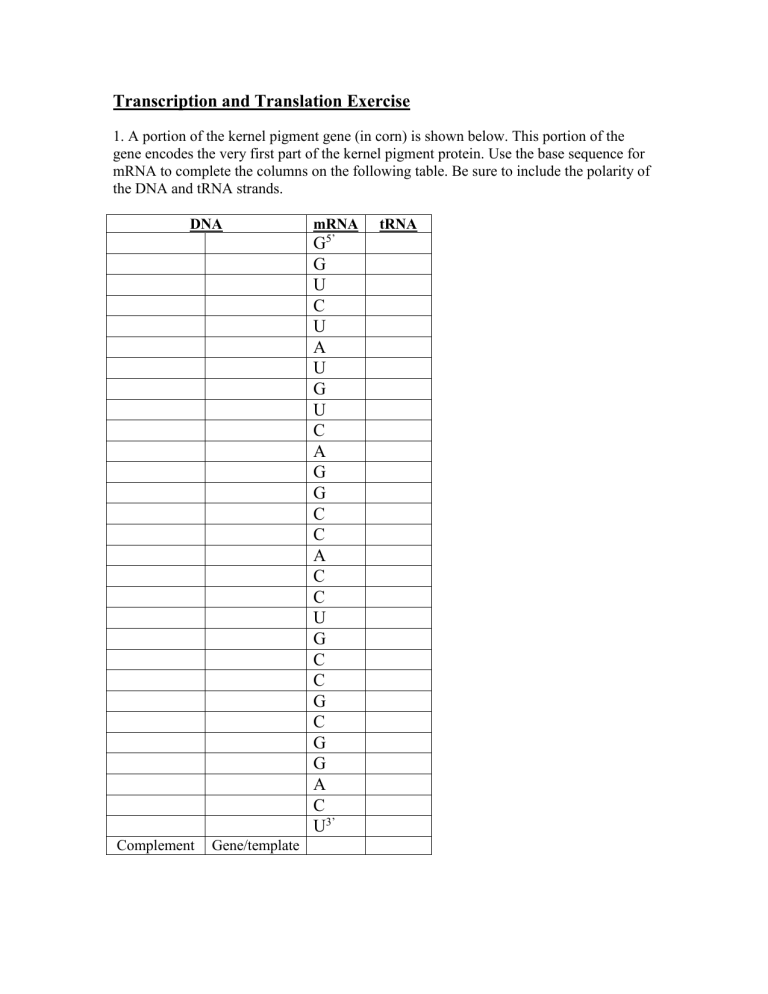
1. A portion of the kernel pigment gene (in corn) is shown below. This portion of the gene encodes the very first part of the kernel pigment protein. Use the base sequence for mRNA to complete the columns on the following table. Be sure to include the polarity of the DNA and tRNA strands.
DNA mRNA tRNA
G
5’
G
U
C
U
A
U
G
U
C
A
G
G
C
C
A
C
C
U
Complement Gene/template
C
G
G
A
G
C
C
G
C
U
3’
2. Describe the relationship between the gene sequence and the mRNA sequence.
3. Describe the relationship between the gene sequence and the tRNA sequence.
4. If the coding region of a protein coding gene contains 300 DNA nucleotides, how many amino acids will be used in protein synthesis?
5. If a protein has 150 amino acids, how many DNA nucleotides would make up the coding region of the gene?
6. What is the amino acid sequence for the very first part of the kernel pigment protein in the exercise above?
7. The allele of the gene above is dominant and codes for red kernel pigment (it is designated as R ). Another allele of this gene, the r allele (which is recessive), codes for white kernel pigment and is the result of a mutation in the R allele. In the r allele, the second nucleotide (base) in the second codon of the open reading frame (or coding region) is an adenine.
What does the second codon in the r allele code for?
8. A protein has the following amino acid sequence. Construct a DNA nucleotide sequence of this portion of the gene.
Phenylalanine-Glycine-Glycine-Alanine-Proline-Valine-Asparagine-Alanine
9. If you compared your sequence to one constructed by a classmate, would you expect to see any variations? What would be the reason for the difference?
10. Complete the following table:
Nucleotide Components and Function
Nucleic Acid Type DNA
Name of the sugar present in nucleotides mRNA tRNA
Name of bases present in nucleotides
Function of the type of nucleic acid
Describe the relative size and number of stands in each of the nucleic acids
Where can you find each of these in a eukaryotic cell?